Suffering with insomnia? - Simple solutions to sleep like a baby again

You have insomnia if you experience:
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Waking frequently during the night
- Waking too early in the morning and not being able to get back to sleep
- Waking feeling un-refreshed
Studies indicate that almost 2/3 of Americans have difficulty falling and staying asleep. If you feel the need for a nap in the daytime, you are probably one of them, since fatigue is one of the top 10 reasons Americans visit a physician.
Sleeping problems are even common in young adults (17-30yrs). A German study found that 12% of 4-5 year old children had difficulties falling asleep.
Consequences of insomnia:
Affects your hormone levels setting the stage for some serious health problems. Insomnia has been associated with accelerated aging, cancer, diabetes, depression and obesity.
Increased risk of accidents. As reported in Business Week, “Studies show that someone who has been awake for 24 hours has the same mental acuity as a person with a blood alcohol level of 0.1, which is above the legal limit for driving in most states.”
Insomnia has many possible underlying causes
Desynchronization of the biological clock
E.g. if unable to fall asleep, called delayed sleep-phase syndrome (DSPS), your biological clock has lost its timing mechanism, making you more alert in the evening.
- Staying awake too many hours or too much light in the evening (maybe from a brightly lit computer screen) can alter your proverbial “timing belt”. Actually, it is only blue light which suppresses MELATONIN production, and there are some ways to filter out the blue light.
- Lack of exposure to light. Japanese researchers studied 10 nursing home residents with insomnia and found thatincreasing their exposure to light increased their MELATONIN production (proportional to brightness) and improved their sleeping patterns/quality. Exposing elderly patients to 4 hours of bright, artificial light at midday for 4 weeks (roughly equal to the amount received by a young control group), caused their MELATONIN production to be similar to the young control groups. (J. of Endocrinology, 2001)
- Too much light in your bedroom can keep you awake. Once in bed, darkness allows your biological clock to produce MELATONIN -a signal for sleep. Even a small amount of light (E.g. from moonlight through a crack in the curtains) disrupts your circadian rhythm and affects your pineal gland’s production of MELATONIN and SEROTONIN. MELATONIN levels are reduced by 50% when exposed to a low-level incandescent bulb for only 39 minutes at night.
Hormonal imbalance
Decreased MELATONIN / Hormone Imbalance/Depression. The major cause of insomnia is decreased levels of MELATONIN. Depression is often related to a SEROTONIN deficiency; thus it follows that since MELATONIN is produced from SEROTONIN, that insomnia is likely to be present with depression.
Stress. Over-stimulates the brain and is associated with high CORTISOL levels, affected by:
- Negative emotions. Including worry, fear, anxiety.
- Positive emotions. Such as excitement, anticipation, or watching thrillers on TV.
- Overactive adrenals. Chronic insomniacs found to have significantly higher levels of adrenal stress hormones, suggesting that these individuals suffer from sustained, round-the-clock activation of the body’s system for responding to stress. This hyperarousal is also a risk factor for both psychiatric illness (E.g. depression) and medical illness (E.g. high BP, obesity, osteoporosis). (J. of Endocrinology, 2001)
Nutrient-related causes
Caffeine-containing drinks/foods before bedtime
- Promotes the exact reverse of what you want to happen as you go to sleep. Caffeine speeds nervous system and other major body systems. E.g. 15 minutes after downing a cup of coffee, blood adrenaline level rises, triggering an increase in heart rate, breathing rate, urinary output, and production of stomach acids.
- Caffeine also prompts adrenal hormones to release sugar stored in the liver, which stimulates sugar cravings to replenish the stores. A blood sugar roller coaster effect ensues as the quick high is followed by a sugar slump.
Nutrient deficiencies
- Potassium deficiency. Causes inability to fall /stay asleep.
- Zinc deficiency. Causes one to wake up hours earlier than wanted.
Optic nerve damage
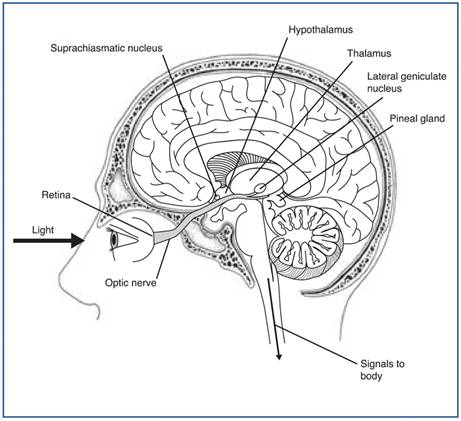
Optic nerve damage causes problems sleeping, falling and staying asleep, and daytime sleepiness. A non-visual part of the retina uses daylight to synchronize your body’s sleep patterns, telling the body when to sleep and when to get up. It resets the internal body clock and regulates the release of hormones such as MELATONIN (the “Body’s natural sleeping pill”hormone). Studies on blind people found that those with damage to the optic nerve (connects eye to brain) were far more likely to need daytime naps and suffer from daytime sleepiness than blind people without damage to nerve.
EMF Disturbances
- Cell phone use before bed. Can have electromagnetic affects on your brain and the rest of your body that cause insomnia, headaches and confusion;
- Unshielded wiring in walls / electric clock too close to head / electric blankets in your bedroom. Such unnatural EMF frequencies have a deleterious effect on cellular communication in the body.
Sharing a bed
If either you or your partner suffer from insomnia and share a bedroom, neither of you is getting the high quality sleep you need for good health.
Parasites
Ammonia (produced by parasites). Ammonia is a strong brain irritant (E.g. a person can sometimes be awakened from a coma by smelling ammonia “smelling salts”). The liver and kidneys can convert ammonia to urea for excretion. However, the brain, lacks the required enzyme, ornithine curbamyl-transferase, to make the conversion.
Solutions for insomnia
The National Sleep Foundation recommends 7-9 hours sleep for 10 year olds and up as guideline for personalization
Boost body's MELATONIN levels
You do not have to take a MELATONIN supplement to increase your MELATONIN level. These supplements force a specific body on your body. It is better to let your body determine its production by giving it necessary precursors and other promoters.
How to Boost MELATONIN **HIGH PRIORITY!**

A couple of unusual, but successful therapies
Meridian Tapping Technique (MTT). A gentle tapping technique learned in several minutes. MTT can resolve some of the emotional stresses at the root of your insomnia. Typically, results are quick and long lasting.
Use Beck’s “Brain tuner” for insomnia. Utilizes Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) to balance body’s hormones
Avoid caffeine and other stimulants before bedtime
Includes tea, coffee, cola drinks, tobacco, alcohol. The half-life of a single dose of caffeine ranges from 3-12 hours. This means that that one quarter of the caffeine in that morning cup of coffee could even still be present at bedtime. Caffeine prevents deep sleep because it creates a stress scenario in the body. Cherniske (author of “Caffeine Blues”) found that supposed depression disappeared 2 months after giving up coffee.
Do’s and don’ts on eating before bed
- Avoid grains and sugars in the evening, which inhibit sleep by raising blood sugar. Also, when blood sugar drops down low later in the night, it could cause you to wake up and not be able to fall back asleep.
- Eat high protein snack several hours before bed. Provides L-tryptophan for MELATONIN and SEROTONIN production. Tryptophan also detoxifies ammonia (parasites produce this brain stimulant)
Make sleeping environment comfortable and conducive to sleep
Sleep in complete darkness. When the blue component of light hits the eyes, it disrupts the circadian rhythm of the pineal gland and production of MELATONIN and SEROTONIN.
- Use room darkening drapes/shades, wear an eye mask.
- Turn off TV’s and computers in the room
- If light seeps under your door, seal it off with a rolled up towel
- Don’t put the light on in the bathroom (or use a blue-filtering light)if you get up in the middle of the night;
Keep bedroom temperature cool (< 70 °F) and have a window open for fresh air;
Wear bed socks when it’s cold. Cold feet can wake you up.
Reserve the bedroom for only sleep and sex. Creates a mental association that the room is for those activities. i.e. NOT reading, telephone conversations or watching TV.
Reduce stimulating activities before bedtime:
- Do something relaxing before bed. E.g. listen to music, read.
- Don’t do mind-disturbing activities before bed. Watching TV, especially a violent movie, computer time, reading email – its stimulating effect on the brain extends the time taken to fall asleep.
- Don’t exercise or take a hot bath just before bed. Raising your body temperature makes it more difficult to fall asleep. Exercise also raises CORTISOL levels.
If you suspect you have parasites . . .
Take ornithine. Detoxifies ammonia, which is present in your brain when you have parasites;
- Dose: 2- 500mg capsules on 1st night, 4 caps. 2nd night, 6 caps. 3rd night, then keep the dose that worked best for you. Can take up to 5 days to take effect.
Do a parasite cleanse to get rid of these uninvited guests
Other important considerations
Exercise moderately for at least 30 minutes every day. Helps you fall asleep, but don’t exercise too close to bedtime or it has a stimulating effect;
Sleep separately to your “disturbing” spouse. If your partner snores, hogs the covers, moves around or gets up frequently during the night;
Keep regular bedtime hours. To reinforce your biological clock.
- “Early to bed, early to rise”. Our body systems do most of their recharging from 11 p.m. -1 a.m., especially adrenals and gall bladder, which unloads its toxins during these hours. If awake, the toxins back up into your liver and then the rest of your body.
- If you have insomnia. And you don’t go to sleep within 15-20 minutes, get up and leave the bedroom; also, don’t nap in the day
Magnet therapy. Apply the North pole of a small round magnet on the forehead between the eyebrows for 10 minutes before retiring. Can take a month or two to have a complete effect.
Adaptogen. Non-toxic substance that increases resistance to stress, fatigue, anxiety. Trauma, E.g. Tulsi tea (Indian equivalent of coffee)
Sedatives. Most sedatives bind to GABA receptors in the brain to inhibit the wakefulness network. However, they also disturb circuits for mood and memory and often have side effects, such as tremors, or daytime sleepiness.
- Ambien. There for those who haven’t been able to sleep for several nights which can affect the safety of you and others. Ambien is a short-acting hypnotic and generally not addictive. Since it is metabolized overnight, there is no residual drowsiness in the morning.
A “Sheep counting” mechanism to get to sleep. Imagine a field full of 100 sheep on the right-hand side of your mind. Look at each sheep and you will see the word ‘SLEEP’ shorn into their sides in BIG letters. Then sheep #100 walks slowly to the middle of your field of view. Again, see the word SLEEP on his side. She jumps over a low jump. Again, see the word SLEEP on her side. Then she walks over to the left side of your mind – see the word SLEEP – and curls up and goes to sleep. Then repeat for sheep #99 and so on. If you do this fully and slowly, chances are you won’t even get to #80.
If possible, avoid working the night shift.
References
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (January 2001) 86:129-134