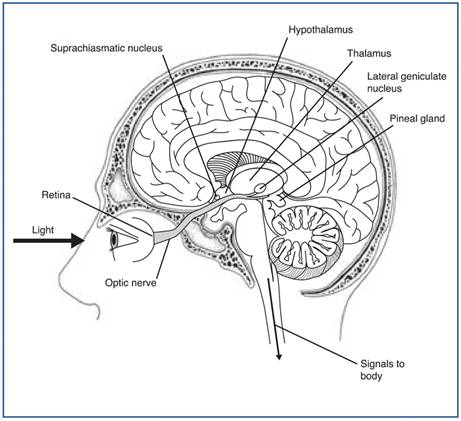
Vertebral Column
Vertebrae (bones)
- Cervical (7 vertebrae): Located in the neck.
- Thoracic (12 vertebrae): Located in the upper and mid-back.
- Lumbar (5 vertebrae): Located in the lower back.
- Sacral (5 fused vertebrae): Located in the pelvic region.
- Coccygeal (4 fused vertebrae): Forming the coccyx or tailbone.
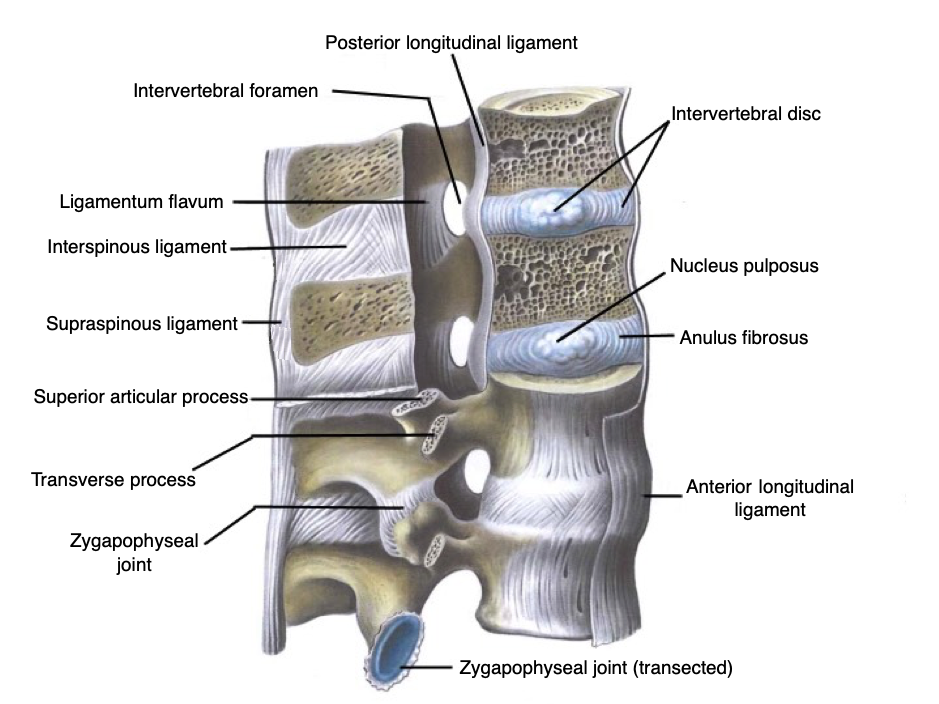
Posterior longitudinal ligament. Separates invertebral discs from tubal spinal cavity / canal, which houses and protects the nerve-carrying spinal cord, from base of skull to lower back..
Meninges. 3 protective membranes surround spinal cord
Invertebral discs. Providing cushioning and flexibility, a connective, spinal disc, composed of strong elastic tissues, separates each vertebra. When the spine bends or rotates, these spinal discs allow smooth, low-friction movement between adjacent vertebrae. Each disc contains a soft inner substance with a surrounding outer layer, which maintains the structure of the disc.
When the tough outer portion of the disc weakens, it is possible for the gel-like center of the spinal discs to bulge outwards into the spinal canal.
In more severe cases, it can lead to a herniated disc. A herniated disc occurs when a tear in the outer layer of the disc allows the inner substance to leak into the spinal canal.