Parasites -"Uninvited Guests"

Parasites - inside me!?
What are parasites?
Parasites are organisms living on or in a host who depend on the host to provide them food. Parasites have the potential for causing health issues in the host, sometimes undiagnosed. However, since they depend on the host for their survival, they rarely kill the host.. There are more than 130 different kinds of parasites that can inhabit the human body, ranging from a microscopic size to single and multi-celled worms. However, there are 3 main types:
Ectoparasites. Lives on the outside of its host. They are called vectors, meaning they can carry diseases between animals and humans, usually by infecting blood.
- Head lice, pubic lice (crabs)
- Fleas
- Mites (small arachnid spider relatives <1mm in size; some may cause scabies).
- Ticks. Usually encountered in wooded / grassy areas. After painless, itchless bites they burrow into your skin
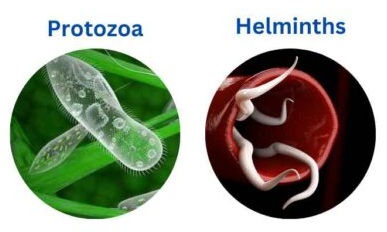
Helminths. Visible parasitic worms usually resident in your GI tract. Main types are:
- Flukes (trematodes). Flatworm picked up from contaminated water or aquatic critters such as fish, crabs and snails. Can infect blood, bladder, liver, lungs, intestines, other organs.
- Tapeworms (cestodes). Adult tapeworms can live up to 30 years and grow up to 10 feet from pork or over 30 feet from cows! flatworms feed on food in your intestines and lay eggs that exit in poop. Eggs can transfer to another host via poor hygiene, or eggs or larvae consumed by animals (e.g. pigs, cows) migrate to their muscle tissue, which is then consumed as undercooked meat such as pork or beef. Properly cooked meat will kill the eggs or larvae. Eggs can also be transferred in Infected water
- Roundworms (nematodes). Many different types of these small parsites live in your intestines and spread by infected poop or via soil.
Protozoans. You need a microscope to see these many types of one-celled organisms, which can live in your intestines, blood or tissues. Transferred via contaminated food / water, from person-to-person contact, or bite of a vector. Main ones infecting humans are:
- Amoeba. Entamoeba histolytica causes dysentery. Move using pseudopods (temporary “false” feet)
- Ciliates. Only Balantidium coli a problem in humans, causing dysentery. Use cilia (short-hairlike protusions) to move
- Flagellates. Giarda intestinalis causes giardiasis; Trypanosoma brucei causes sleeping sickness. Use flagella (whip-like appendages, longer than cilia) in a wave-like motion to propel themselves
- Sporozoans. Adults cannot move. Plasmodium causes malaria. Form reproductive cells called spores.
Usual characteristics of people with intestinal parasite infections
- Present in any disease, in any person, at any ageUnder-nourished and weak
- Undernourished and weak
- Infected with viruses, fungi, or bacteria
- Have various types of chemical and metal poisoning
How do parasites gain entrance into the body?
- Produce, dairy, undercooked meat
- Infected water
- Via a transmitting agent. E.g. a mosquito
- From pets. Pets host numerous parasites
- From the air. Carries microscopic parasites and fungi
- From one another. Via blood, saliva, semen, through sexual contact, the nose, skin and breast milk; meaning by kissing on the mouth, sex, nursing and child bearing.
Where do parasites reside in the body?
- Most parasites live in the digestive tract
- Many are in the blood and lymphatic systems
- Parasites can also settle in the joints and muscles. Where they form cysts which create inflammations with the resulting pain often attributed to arthritis.
- CNS. Their toxic by-products (mainly ammonia) can attack the central nervous system often resulting in restlessness, depression, anxiety, hypertension and fatigue.
- Parasites tend to hang out in areas where heavy metals are lodged – heavy metals E.g. mercury, cadmium, kill good bacteria which would normally kill parasite larvae.
Symptoms of human INTESTINAL parasites
The symptoms of a fungal or parasitic infection are often identical to those of a bacterial or viral infection, resulting in false diagnoses.
- Eating more than normal but still feeling hungry
- Gastrointestinal / Digestive Problems – constipation, diarrhea, stomach bloating, gas; bulky stools with excess fat in feces; food insensitivities / environmental tolerance, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS);
- Anemia
- Allergies – parasites can irritate, inflame, and perforate the intestinal lining. This increases the permeability of the intestinal walls allowing large undigested molecules to pass into the blood stream leading to food allergies.
- Asthma
- Weakened immune system – Chronic fatigue, chronic bacterial or viral infections
- Nervousness – restlessness, anxiety
- Joint and muscle pains and inflammation often assumed to be arthritis
- Hives, rashes, weeping eczema, cutaneous ulcers, swelling, sores, papular lesions, itching dermatitis (can occur if parasites penetrate the skin );
- Experience multiple awakenings during the night particularly between 2 and 3 am
- Drooling while sleeping – damp lips at night and dry lips during the day
- Grinding teeth while asleep
- Depressed, apathetic, lethargic
- Difficulty gaining or losing weight – no matter what you do
- Chronic candida – did a candida program which either didn’t help at all or helped somewhat but you still can’t stay away from bread, alcohol, fruit, or fruit juices;
- Yeast infections
- Itchy ears, nose, anus (especially at night)
- Chronic ear or sinus infections
- Forgetfulness, slow reflexes, unclear thinking
- Loss of appetite
- Yellowish face
- Fast heartbeat, heart pain, pain in the navel
- Pain in the back, thighs, shoulders, navel arthritic pains
- Heart pain
- Numb hands
- Bed wetting
- Burning sensation in the stomach
- Problems with menstrual cycle /Prostate problems or sexual dysfunction in men
- UTIs
- Hemorrhoids
- Cysts/Fibroids
- All skin problems
- Water retention (mostly from tapeworms)
- Crawling feeling under skin
- Floaters
- Liver/gallbladder trouble
Parasite actions are a menace to the immune system and an underlying cause for many health problems
- Secrete toxins. Parasites release toxic wastes – actually their feces and urine. Parasite urine is practically pure ammonia, very harmful to the brain.
- Steal vital nutrients from our bodies
- Can irritate or exaggerate other health problems you may be experiencing