Sunscreen lotions do what?

What is SPF (Sun Protection Factor)?
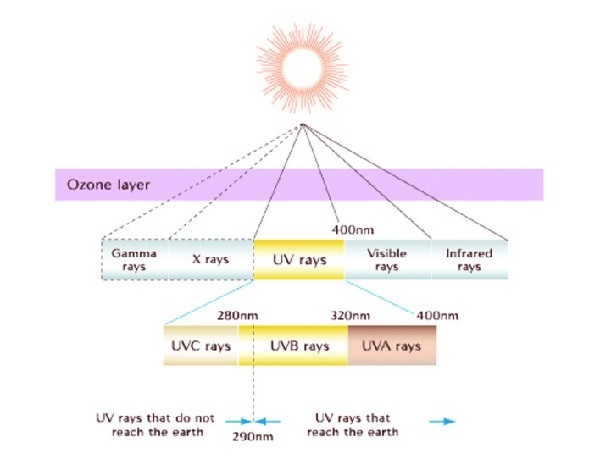
The SPF number is determined experimentally indoors. Human subjects are exposed to a light spectrum to mimic noontime sun and some subjects wear sunscreen and others do not. The amount of light that induces redness in sunscreen- protected skin, divided by the amount of light that induces redness in unprotected skin is the SPF. It is mainly a measure of UV- B protection and ranges from 1 to 100. Remember it is UV- B radiation that reddens/burns skin, not UV- A. UV- A causes oxidative damage and destroys vitamin D in skin, which if present, protects against melanoma.
For example. A sunscreen with an SPF of 15 filters 93% of the UV- B, and will supposedly delay the onset of sunburn in a person who would otherwise burn in 10 minutes to burn in 150 minutes, allowing a person to stay out in the sun 15 times longer. However, this is not accurate since exposure depends not only on length of time in sun, but also time of day, geographic location, weather conditions, skin type, amount applied and more.
An SPF of 30 is not twice as protective as an SPF of 15 – properly used, an SPF of 15 protects the skin from 93% of UV-B radiation, and an SPF 30 provides 97% protection. SPF 50 provides 98% protection.
The “protectiveness” of clothing can also have an SPF rating. The following are SPF’s of various types of clothing:
- Nylon Stockings – SPF 2
- Hats – SPF 3- 6
- Summer- weight clothing. SPF 6.5
- Sun- protective clothing. Up to SPF 30
Many sun lotions do not screen for UV- A, unless the label specifically says so
They are thus screening out the beneficial UV-B (and so limiting vitamin D production, while allowing the dangerous UV-A to filter through).
- SPF rating is only for protection against UV- B rays (responsible for sunburn) – and not UV-A rays that penetrate more deeply into the skin (and may also be responsible for causing cancer and wrinkles). Sunscreen molecules protect against direct DNA damage by absorbing the UV-B instead of it being absorbed by DNA.
- UV-A Protection. Only a sunscreen that protects against both UV-A and UV-B rays can be labeled “Broad Spectrum“, according to the FDA. Some sunscreen lotions now include compounds, such as UV-A blockers titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, and UV-A absorber avobenzone, to help protect against UV-A rays. There are also naturally occurring compounds found in rainforest plants that have been known to protect the skin from UV radiation damage, such as the fern Phlebodium aureum. For a sunscreen to be labeled broad-spectrum, the FDA requires that it protect against both UV-A and UV-B rays.
Use sunscreen lotion ONLY under unavoidable situations. E.g. You’re forced to be in the direct rays of the sun for a longer time than is safe, and blocking the sun with strategic clothing or sunshades is impractical. You must go into intense sunlight without having the opportunity to gradually build up to it
- Use a NATURAL Ingredient Sunscreen Lotion – Not a Toxic Commercial Sunscreen. Chemicals used in sunscreens are absorbed through your skin and end up circulating in your blood stream
The 3 main chemical sunscreen filters actually react with UV to create ROS (the very problem you’re trying to prevent!). Octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC), Oxybenzoneand octocrylene soak deeply into the skin, where a U. of California research team found that absorbed UV rays can react with these chemical filters to generate reactive oxygen species, considered responsible for skin cancer and premature aging
Best to toss your sunscreen in the trash if it contains any of these harmful chemicals:
- Octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC). Main chemical used in sunscreens to filter out UV- B light; present in 90% of sunscreen brands. A Norwegian study found that OMC killed mouse cells even at low doses, and particularly when exposed to sunshine!
- Oxybenzone and Dioxybenzone. Two of the most powerful free radical generators known to man! Oxybenzone (aka. benzophenone 3)screens UV- A, and is known to cause contact eczema;
- Octocrylene
- Butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane. Common UV- A filter demonstrating toxic properties
- Para amino benzoic acid (PABA)
- PABA synthesized from petrochemicals. The type that causes skin allergies/irritations and the type used in most commercial sunscreens
- Natural PABA. A B-vitamin produced in the intestines, which actually helps prevent sunburn and sun damage to skin; it is available as a food- grade supplement (fair-skinned people could benefit from its sun-protection with 1 – 2 500 mg PABA capsules/day when exposed to sun in summer months)

- Octyl salicyclate
- Avobenzone
- Cinoxate
- Padimate OPadimate O
- Phenylbenzimidazole
- HomosalateHomosalate
- Sulisobenzone
- Menthyl anthranilate
- Trolamine salicyclate
Some non-toxic / Natural ingredient sunscreen brands:
- “Natural Sunscreen with Green Tea ” (SPF 15) by Dr. Mercola. Active ingredients: Titanium Dioxide (3.5%), Zinc Oxide (3.5%); Other ingredients: Deionized water, sunflower Oil, Lecithin, Coconut Oil, Glycerine, Xanthan Gum, Green Tea Extract, Jojoba Oil, Tocopheral Acetate (Vitamin E), Shea Butter, Eucalyptus Oil. This lotion does leave a not particularly attractive white film on the skin.
- Badger SPF30. Active Ingredient: Micronized Zinc Oxide 18.75%;
- Mexitan Tropocal Sands SPF 30. Active ingredients: Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide; Other ingredients: Sunflower Oil, Green Tea Extract, Coconut Oil, Almond Oil,Lanolin,Tocopherol Acetate (Vitamin- E), Eucalyptus Oil, Ascorbyl Palmitate (Vitamin C)
Carotenoids, other antioxidants, and undamaged essential fats are "Edible SunBlock"
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are members of a family of nutrients that protect plants and animals from excess sunshine
Carotenoids absorb/reflect UV rays. When we ingest them, carotenoids are deposited in skin, and similar to melanin, their molecules prevent sunburn by reflecting and absorbing UV rays. In addition, they have an antioxidant role to protect against oxidative stress, which can lead to cancer. Carotenoids are converted to vitamin A in the body.
Best food sources of carotenoids. Eggs, spirulina, chlorella, dark- green leafy vegetables (kale, spinach, collards), and yellow- orange fruits and vegetables (apricots, cantaloupe, carrots, sweet potatoes, yams, and squash). The recommended daily intake of carotenoids is 4- 8oz / day of these foods.
Astaxanthin is the most potent carotenoid. Red pigment found in algae, salmon, trout, shrimp (incl. krill), and lobsters. The algae are normally green. But when subjected to sunshine, they produce the red pigment naturally. Once ingested, astaxanthin is 1,000 times more effective at protecting skin from UV damage than other carotenoids.
- Current research supports the need for 2 mg of astaxanthin for a month to prevent sunburn. It takes weeks to build up in tissues.
- Astaxanthin also appears to protect against age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Astaxanthin must be taken with fat, since it is fat-soluble. Krill oil is an excellent source.
Essential fats
Essential Fats in skin absorb UV rays – electron-rich omega- 3 and undamaged Omega- 6 fatty acids deposited in the skin from foods, such as omega- 3 from oily fish, krill oil, and flax seed, and omega- 6 from cold- pressed seed oils (i.e. not typical grocery store /restaurant /processed food oils that have been damaged by high- temp processing) have electron clouds at their many double carbon bonds (“kinks”) that resonate at the same frequency of sunlight. They thus absorb the sun’s energy and protect the skin from burning.
You should control dietary Omega- 6: Omega- 3 fat ratio. Omega- 6 fats (typically consumed as heat- processed seed oils lacking sun- resonating electrons) were shown to increase the risk of skin cancer, while omega- 3 fats decreased it. Omega- 3 fatty acids have an anti- inflammatory role, whereas most omega- 6 fatty acids promote inflammation.
“Epidemiological, experimental, and mechanistic data implicate omega- 6 fat as stimulators and long- chain omega- 3 fats as inhibitors of development and progression of a range of human cancers, including melanoma.”
Cancer Res 2000 Aug 1;60(15):4139- 45;
Guangming Liu, et al,Omega 3 but not omega 6 fatty acids inhibit AP- 1 activity and cell transformation in JB6 cells, National Academy of Sciences, 2001
Today’s typical fat consumption is heavy on the damaged (poor electron content) omega- 6 fatty acids (E.g. in heat- processed corn, soy, canola, safflower, and sunflower oils) and light to non- existent for the omega- 3 fats (E.g. in walnuts, flaxseed and seafood). Ideally you should aim for a 1:1 ratio, which was the more typical ratio consumed prior to the invention of the seed press and the world of processed foods. This is accomplished by supplementing your diet with omega- 3 fat and eliminating typical grocery store oils, products containing them, and food at restaurants using them (E.g. in deep fryers, salad dressings, and nearly all processed foods).
Virgin coconut oil
Add 1- 3 Tbsp to diet. May be as effective as sunscreen at blocking sun’s harmful rays;
Korać, Radava R., and Kapil M. Khambholja. “Potential of herbs in skin protection from ultraviolet radiation.”Pharmacognosy reviews 5.10 (2011): 164.
Add to other sunscreen use Usually not totally effective on its own