Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 101
Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood-brain-barrier, leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries
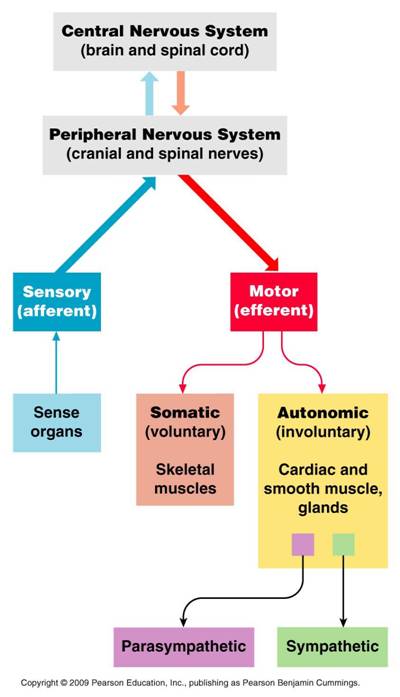
The PNS is comprised of nerves (neurons) that are either MOTOR or SENSORY
Which one is determined by direction of nerve impulses:
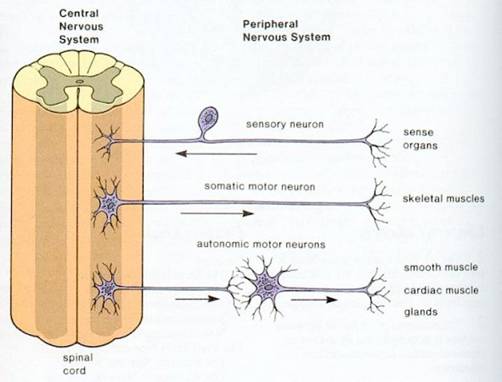
(i) Sensory/afferent neurons. Relay nerve impulses toward the central nervous system (CNS). E.g. A touch or painful stimulus creates a sensation in the brain after information about the stimulus travels through the spinal cord to the brain via afferent nerve pathways.
(ii) Motor /efferent neurons. Relay nerve impulses away from the CNS
PNS nerves are used for control of SOMATIC (Conscious/voluntary) or AUTONOMIC (Subconscious/involuntary) functions
(i) SOMATIC nervous system (SNS) (Conscious/voluntary control)
Includes all of the nerves that serve the skeletal muscles and the exterior sense organs and also includes reflexes. Connects skeletal muscles with cells specialized to respond to sensations, such as touch and pain.
(ii) AUTONOMIC nervous system (ANS) (Generally subconscious control)
Motor and sensory neurons connecting the CNS with internal organs (E.g. heart), smooth muscle, glands.
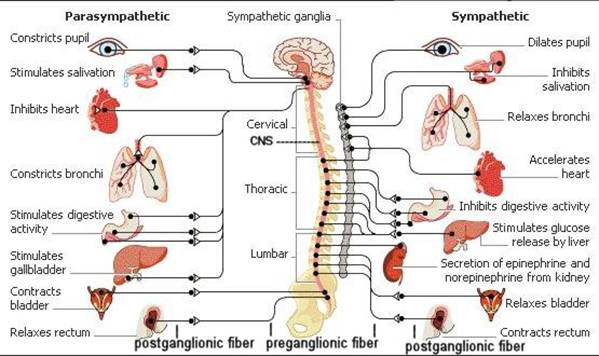
SYMPATHETIC nervous system. Mobilizes energy and resources during times of stress and arousal
PARASYMPATHETIC nervous system. Conserves energy and resources during relaxed states.
ENTERIC nervous system. Neurons directly control the digestive tract, pancreas, and gallbladder.
Damage to peripheral nerves of SNS or ANS is called peripheral neuropathy, which can affect communication signals between body parts and the brain. This affects both sensory nerves (e.g. pain sensations), motor movemant (muscles) or involuntary controls for breathing, digestion, heart rate, blood pressure, bladder function etc
The PNS in humans comprises:
12 pairs of cranial nerves. Emerge directly from the brain, sensory nerves, motor nerves, or mixed nerves. All of them control the head, face, neck, and shoulders, except the vagus nerve, which controls the internal organs.
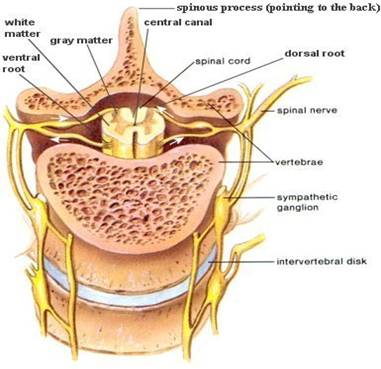
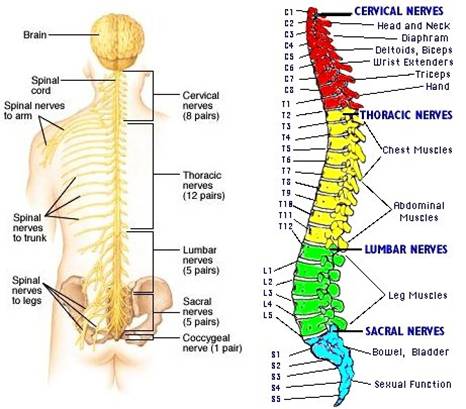
31 pairs of spinal nerves. Emerge from segments of the spinal cord; mixed nerves that take impulses to and from the spinal cord.