Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
Overview
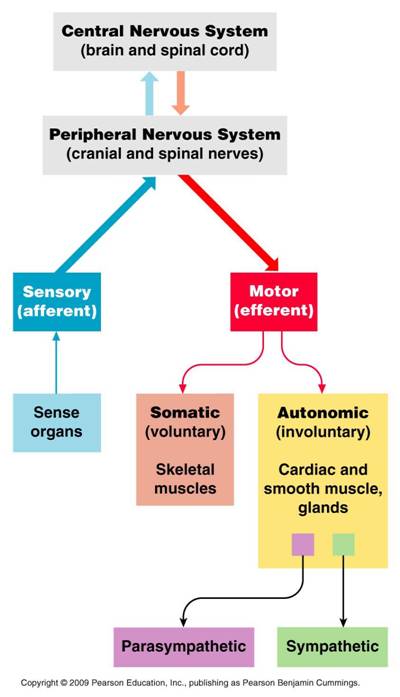
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when muscles and tendons in the hand put pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Causing pain, tingling, numbness and/or weakness in the hand.
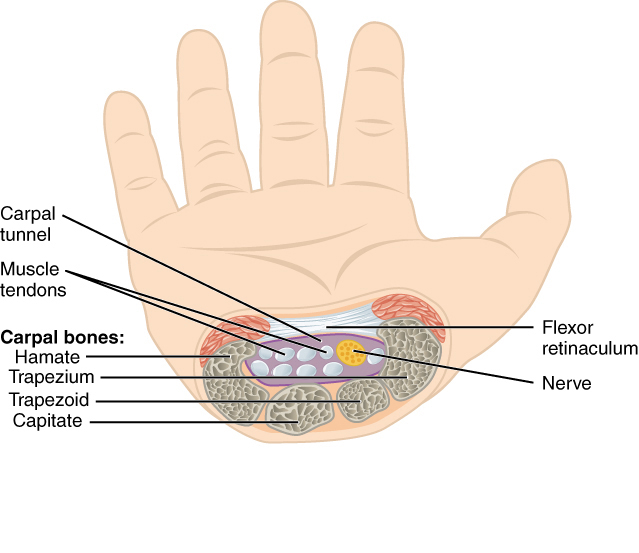
The median nerve. Runs from the forearm to the hand through a small space in your wrist called the carpal tunnel. It controls movement of the thumb and adjacent 3 fingers, but not the little finger. The carpal tunnel. A passageway located on the palm side of the wrist connecting the forearm to the hand. The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous ligament covering the carpal bones and forming the carpal tunnel together with the arched carpal bones of the wrist. Nine tendons connected to the flexor muscles of the forearm pass through the carpal tunnel and if any of these tendons swell or degenerate, they can “pinch” the median nerve causing pain. |
Symptoms
- Pain, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness in the hand – with pain sometimes radiating into forearm and shoulder
- Symptoms in thumb, pointy finger, middle finger and thumb side of ring finger, but NOT the little finger
- Pain often more pronounced at night
- Temporary relief by shaking the hand
Causes
Anything causing swelling that makes the carpal tunnel smaller – including:
- Making repetitive movements with the hand or wrist – especially if the hand is bent downwards (i.e. lower than the wrist). Such activities include excessive /prolonged keyboarding, clicking a mouse button, excessive use of pruning shears, repetitively lifting heavy weights, scrubbing, using vibrating hand tools, twisting a screwdriver
- Inflammatory conditions / illnesses – such as pregnancy, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, hypothyroidism, gout
A Harvard study suggests that there may be a genetic disposition to CTS
Treatments for CTS
- Treat swollen / inflamed tendons trapping the median nerve
- Heal / repair the tendons – which are fibrous connective tissue
- Address source of inflammation
Treatments
Wild oregano oil (Massage diluted oil (1 part WOO to 3 parts carrier oil) into palm side of wrist every 4 hours or as needed)
Arnica gel/cream
Comfrey (Symphytum Uplandicum, Symphytum Officinale) cream or oil – Comfrey is the time-proven remedy for rebuilding connective tissue. /Massage into palm side of wrist every 4 hours or as needed. Alternatively, use an overnight comfrey leaf “mash” poultice — chop up” the leaves (a small food processor works well for this), optionally add some vitamin E and/or wheat-germ oil and apply to palm side of wrist. Cover with some comfrey leaves and tape to hold mash next to wrist and then place hand in a plastic bag held on with a not-too-tight elastic band on the forearm and leave overnight. Sleep on old sheets in case it leaks – stains will not come out!
St John’s Wort cream – used topically on palm side of wrist every 4 hours or as as needed. Popular European remedy for pain.
Ginger root (Zingiber Officinale) overnight poultice – place fresh, ginger root slices ( sliced thin lengthwise) on the inner wrist, cover with a little plastic and use a bandage to hold it in place.
PEMF therapy using such as SOTA® MAGNETIC Pulser
Avoid more trauma to the hand and try to relieve pressure on the median nerves
- Try and rest your hand longer than usual between activities
- Use the non-affected hand if possible
- Keep wrist in neutral position as much as possible
- Keep wrists straight when typing – hands a little higher than wrists
- Relax shoulders when arms at your sides
- Wear a wrist splint at night or hang your affected hand over the side of the bed – prevents the wrist from flexing and putting extra pressure on median nerve.
Address illnesses / conditions causing inflammation
Utilize short-term anti-inflammatory therapies
Vitamin B6 – 100mg twice/day – Andrew Weil, M.D. suggests B6 is a therapeutic agent to treat nerve compression injuries. Not a lot of study support for this though.