Our body is overwhelmed with "invaders"

Some problems are caused by foreign “invaders” entering the body
Free radicals are produced when the immune system deals with microbes, toxins and unnatural electromagnetic radiation in the body.
Free radicals first deplete our body’s inventory of antioxidants and then start causing damage to our body “parts” (cells/tissue). Our body uses its precious oxygen to get rid of invading microorganisms and toxins(e.g. artificial ingredients, pesticides and heavy metals). This can overwhelm our immune system if it is not working up to par, disrupts the Cell” battery” level and cellular energy production (by reducing oxygen availability and by structural damage to mitochondrial membranes) , and makes conditions more microbe-friendly.
Detrimental to cells.
E.g. in heart muscle cells and neurons the accumulation of cellular garbage may be a very significant factor in cellular aging and death.
Microorganisms – Bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa
“If I could live my life over again, I would devote it to proving that germs seek their natural habitat-diseased tissue – >rather than being the cause of the diseased tissue; i.e. mosquitoes seek the stagnant water, but do not cause the water to become stagnant”
– Rudolph Virchow (founder of pathology)
Present in our food and environment
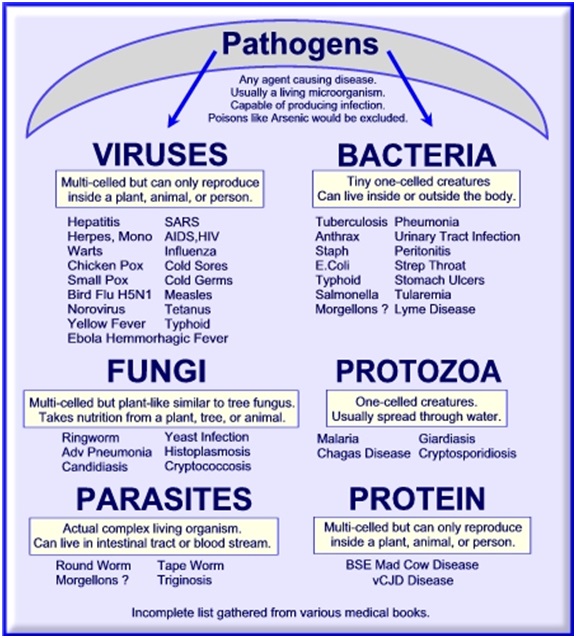
Microorganisms lie dormant inside our body’s cells, developing into more and more harmful forms under more acidic, low-level oxygen, toxic conditions (from primitive microbes (endobionts) to bacteria to fungus, within their family species).
- This is according to several eminent scientists. Including Antoine Béchamp (a contemporary of Pasteur) and Gunter Enderlein, who found that Louis Pasteur’s theory was wrong – viz. that all micro-organisms can only hold one form (monomorphic) and can only come from outside the body.
- Micro-organisms thrive according to the medium and especially the pH level in which they live (most prefer a pH of ~6.5-7.5, but some can thrive in battery acid!). Some experiments showed that when the body becomes extremely toxic, bacteria can mutate into a virus. It is reported, that on his deathbed and in his notes, Pasteur admitted that Béchamp was right, and yet the textbooks still teach Pasteur’s “germ theory”.
- In summation. Microbes can exist in us in a dormant form without causing any detriment to our health, unless our condition deteriorates due to nutritional deficiencies and toxin presence (including the toxic effect of negative emotions), or because we are dead! Only then, when the microbes are stimulated into action, do we notice their presence (well actually, we don’t notice them if we’re dead)
Exposure to unnatural electromagnetic field (EMF) frequencies
Unnatural, man-made EMFs lower the cell’s ability to produce energy – by depolarizing the cell membrane (i.e. running down the Cell “battery”).
Examples include:
- Radiation treatment
- High tension wires
- Cell phone transmissions
- Old-style TV monitors
- Computers
Toxins – Where do they come from?
By-products of cellular metabolism in the body
AGEs (Advanced Glycation End-products).
AGEs are the end products of haphazard glycation reactions implicated in many chronic aging diseases. In glycation, a sugar molecule bonds to either a protein or lipid molecule without an enzyme to control the reaction, where they interfere with molecular and cellular functioning throughout the body. The skyrocketing sugar consumption in recent decades has significantly increased AGE formation and fructose and galactose apparently have 10-fold the glycation activity of glucose, the body’s primary fuel. McPherson et al, 1988
Lipid peroxidation debris.
From reactive species (E.g. free radicals) oxidizing fats in the body
Stress
Stress has poisoning effect similar to that of toxins and is a major contributor to free radical production in the body.
Think about this when you are allowing a domineering boss, financial worries, looming deadlines, marital problems, testy children and past or present emotional issues to “get to you”.
Toxins enter the body from various sources (accumulating in cells with age)
From eating toxin-containing foods.
Eating foods containing dyes, preservatives, herbicides, pesticides, excessive toxic heavy metals; drinking “chemical cocktail” soft drinks; drinking / cooking / bathing in “treated” (chlorinated / fluoridated) water. Examples of harmful ingredients include:
- Fats processed at high temperatures or solvent extracted. Deep-fried foods: Typical “grocery store” oils (i.e. not cold-pressed) contain trans fats.
- Aspartame (NutraSweet, Equal, Sugar Twin); Sucralose (Splenda);
- Water chlorination, fluoridation
- Genetically modified foods / GMOs
- MSG (free monosodium glutamate)
- Xenoestrogens – “Gender benders”
From direct contact. Chemicals can enter through the skin or seep through the sensitive membranes in the mouth, including:
- Cleaners. E.g laundry soap residue in clothes, sheets
- Personal care items. E.g. bars of soap, shaving cream, hand lotion, toothpaste, deodorant, cosmetics, facial creams, hair spray, cologne, perfume, shampoo and hair conditioner (your pores are nicely opened by hot shower water).
Bathing / showering in chlorinated /chemically treated water. By breathing contaminated air. From, such as:
- Chemical air fresheners / deodorizers.
- Combustion engine fumes – e.g. car exhaust fumes”
- Industrial smokestacks.
- Petrochemical paints and solvents.
- Tobacco smoke.
- Poisonous mercury vapors.
Recreational Drugs
- Nicotine.
- Cocaine.
Excessive use of pharmaceuticals.
E.g. Antibiotics kill beneficial intestinal bacteria. We have the illogical approach of trying to deal with problems caused by a toxic overload by ingesting more toxic chemicals in the form of pharmaceuticals E.g. aspirin, antihistamines, countless drugs. Cox-1 inhibiting NSAIDs are a major cause of peptic ulcers.
Consumed AGEs.
In addition to endogenous production, pro-inflammatory AGEs (see above) are also in foods we eat. AGEs are formed when sugars are cooked with proteins or fats without water. E.g. donuts, barbecued meats, cake, and dark colored sodas, caramelized / browned foods.
Eating microwaved food.
References
McPherson JD, Shilton BH, Walton DJ (March 1988). “Role of fructose in glycation and cross-linking of proteins”. Biochemistry 27 (6): 1901-7.doi 10.1021/bi00406a016 PMID