Nebulizing Medicine - For lungs, bronchial tract, sinuses, throat / IV alternative
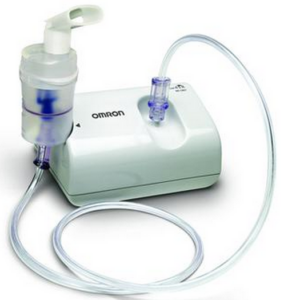
What does it mean to nebulize medicine ?
A nebulizer facilitates a fast and effective absorption of medicine – by breaking down the liquid medicine into fine particles, which are then inhaled into the lungs by the patient through a mouthpiece or face mask.
What are the benefits of using a nebulizer?
Medicine applied through a nebulizer is ideal for direct contact treatment to the lungs, bronchial tract, sinuses and throat – the medicine and moisture is nebulized directly onto these tissues, where it is locally absorbed by tissue cells.
This method of delivery to the tracheobronchial tree, also very effectively delivers medicine into the blood stream – and thus systemically into the rest of the body. Almost as effective as an IV, it reaches the blood stream via the rich network of blood vessels in the lungs.
Nebulization by-passes the stomach and liver – enabling a large percentage of the active ingredient to reach target tissues.
Particularly used to treat asthma, lung cancer, emphysema, respiratory infections(E.g. pneumonia, tuberculosis, influenza), chemical poisoning – and actually can systemically treat any problem requiring the administration of a medicinal.
Thins and moistens secretions:
- Thins secretions and mucus making it easier to expel pulmonary secretions
- Makes coughing easier while lessening the need to cough
- Keeps your windpipe & trachea lining and stoma moist & healthy
- Moistens the air that goes into your lungs
- Hydrates & moisturizes your nasal passages, mouth and throat
Which type of nebulizer to use?
Several devices are available to create the drug aerosol particles – including jet nebulizers, ultrasonic nebulizers, metered-dose inhalers, and dry powder inhalers, through which particles can reach the upper and lower respiratory tracts and be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. Studies show that the device used really doesn’t matter, as long as it’s used properly. Nebulisers: their effectiveness, indications and limitations
Aerosolized drugs have several advantages – including:
- Frequently a more convenient method of drug delivery
- Especially helpful to treat infants, children and intensive care patients – who are generally unable to swallow pills;
- Quick onset of action
- Low incidence of systemic adverse effects – Side effects wear off quickly but can include racing pulse, tremors, nausea and insomnia. Nebulizer asthma treatments can also raise blood pressure and aggravate glaucoma.
- Typically, does not cause pain to the patient
Procedure for using a liquid nebulizer
(1) Add the liquid medicine to the cup attached to the device –medicine should be added at the time of usage and not before that. If taking more than one liquid medicine by nebulization, check if they can be mixed together or whether they should be taken separately.
(2) Close the cup and connect its tube to the air compressor
(3) Turn the compressor on –and when the compressed air reaches the nebulizer cup, it will vaporize the medicine, creating a mist.
(4) The mist is inhaled by the patient, through the mouthpiece or face mask
- Place the mouthpiece in your mouth and breathe in slowly, taking deep breaths to inhale the vapor completely.
- At full inhalation, hold your breath for a 2-4 count to allow absorption in the lungs. If you are treating colds or sinus problems, you can also alternate breathing through your nose.
- Tap the cup regularly to ensure the right dispensation of medicine and don’t remove the mask, until the medicine is used up completely.
- It will take about 10 to 20 minutes to finish nebulization depending on what type of medicinal is used.
- Nebulizing is generally carried out five times a day for best results.
Alternative medicines administered via a nebulizer
Using a nebulizer, alternative medicines can be administered directly into the lungs for many difficult-to-treat conditions – pharmacists, respiratory therapists, and pulmonologists positively exploring this form of therapy at the Ohio State University Medical Center, are calling this “Off-label nebulization”.
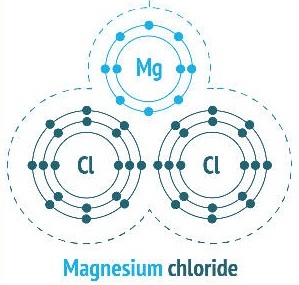
- Nebulizing Magnesium Chloride
- Nebulizing Sodium Bicarbonate
- Nebulizing Iodine
- Nebulizing Ionic Colloidal Silver
- Nebulizing Hydrogen Peroxide
- Nebulizing Grapefruit Seed Extract
- Nebulizing Glutathione.
- Nebulizing DMSO
- Nebulizing Eucalyptus oil – time-tested, known bronchial-dilator.