Atherosclerosis is a life-saving INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE to prevent you from bleeding to death!
What is atherosclerosis? (Greek: athero=paste, sclerosis=hardening)
Atherosclerosis occurs as a result of the immune system’s INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE to an arterial blood vessel wall DAMAGE. Intended as a temporary fix, plaque (a paste mainly consisting of cholesterol and fat) is laid down to prevent bleeding out through a damaged arterial wall.
19th Century Inflamed Arteries
Based on his detailed autopsy studies and pathology investigations of those who had died of heart disease, late 19th century, German physiologist Rudolph Virchow proposed that the origin of heart disease was inflammation of the heart and the arteries. He found that their arteries looked as though they had been wounded inside, similar to an infected skin abrasion
Why be concerned about atherosclerosis?
Most cardiovascular disease (CVD) and peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a consequence of atherosclerosis. If the actual cause of arterial wall damage is not addressed, arterial plaques can grow in size, causing a narrowing (stenosis) of the arterial lumen. Not only does this increase blood pressure, but eventually it can block the smaller arteries – such as the coronary arteries providing blood to the heart (causing a heart attack), or a piece can break away from plaque, travel in the bloodstream and end up blocking / bursting the small arteries in the brain (causing strokes), or blocking peripheral arteries to the legs, feet or arms (causing pain and / or nerve / tissue damage), or setting the stage for several other undesirable possibilities:
- Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) – atherosclerosis narrows the coronary arteries
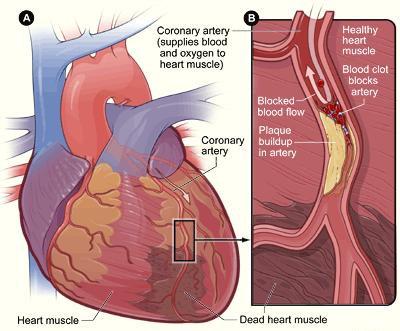
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction) – a blood clot develops from plaque, typically in one of the coronary arteries, causing a blockage, called a thrombosis), which blocks the oxygen supply to the heart
- Arrhythmia – irregular heartbeat
- Stroke – blockage of carotid artery supplying oxygenated blood to the brain
- Angina – chest pain
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Thrombosis – clot formation attached to blood vessel wall in an artery or vein obstructing blood flow;
- Hemorrhagic burst (blood vessel rupture).
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Atherosclerosis is sometimes accompanied by hardening of the artery lumen (arteriosclerosis), which eventually:
- Decreases circulation
- And reduces arterial elasticity
- Compromises the dilation of blood vessels when needed – such as during strenuous exercise.
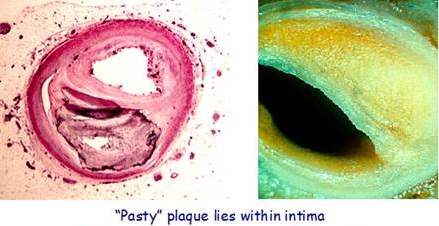
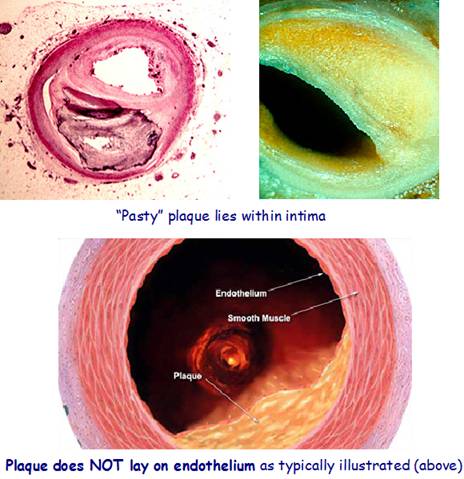
Plaque accumulation (swelling) in an artery is always in the intima (between the endothelial lining and the smooth muscle wall)
Atherosclerotic plaques characteristically occur in high pressure / turbulent areas in arterial blood vessels
In regions of branching and marked curvature at areas of geometric irregularity. i.e. where blood undergoes sudden changes in velocity and direction of flow.
It does not occur in veins carrying deoxygenated blood. i.e. under pressure 8 times lower than the arteries
Occurs In any medium / large artery supplying oxygenated blood under high pressure, but most frequently affects the following arteries:
- Aorta – Largest artery – supplies blood to all body parts. The aorta extends about 1 foot from the heart to the pelvis, however, plaque most commonly occurs in the abdominal aorta and if present there, it is probably in other arteries)
- Coronary arteries leading to coronary heart / artery disease (i.e. CHD or CAD). There are 2 main coronary arteries that branch off the aorta and supply blood to the heart muscle. Atherosclerosis/arteriosclerosis reduces their supply, leading to blood insufficiency (ischemia) to the heart;
There’s that incorrect depiction of plaque placement again! 🙂
- Iliac / Femoral Arteries –atherosclerosis / arteriosclerosis causes a decrease in blood flow to the legs and feet that can injure nerves and other tissues.
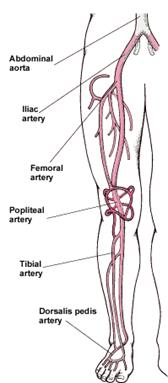
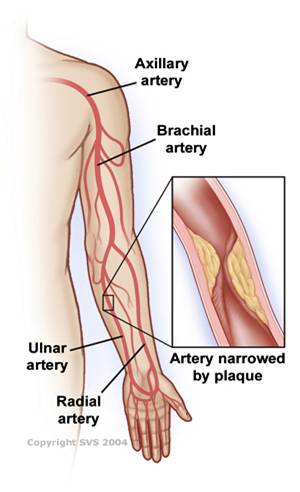
- Axillary / Brachial Arteries. Arm artery disease is a rare form of PAD, but the most common cause is atherosclerosis in the arm arteries, which can cut off circulation to the hand; symptoms include pain, weakness, fingers turning blue, and gangrene.
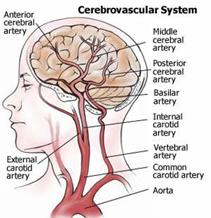
- Carotid and Vertebral Arteries. Atherosclerosis reduces the oxygen-rich blood supply to the brain. Carotid artery disease accounts for well over 95% of symptoms causing cerebrovascular disease. When the carotid arteries are obstructed, you are at an increased risk for a stroke.
Why does atherosclerosis occur?
Contrary to popular opinion, atherosclerosis / ischaemic CVD is NOT caused by high blood cholesterol or triglycerides
CVD involving restricted blood flow due to atherosclerosis is a consequence of damage to an arterial wall weakened by a long-term, low-level deficiency of vitamin C
The body deals with a weakened arterial wall by initiating an inflammatory response to save your life – by placing a cholesterol-containing patch over the damage to prevent you bleeding out. This is meant to be a temporary measure, to buy you time to fix what is actually causing the damage and restrengthen the wall.
by adding dietary vitamin C for your body to be able to produce tissue-connective collagen.
Scurvy occurred in the 1700 and 1800’s on sailing ships due to lack of vitamin C. Thousands of lives were lost until limes were added to the ship’s food inventory on long overseas journies.
.
Several culprits can damage the arterial wall
(a) Mechanical / Hemodynamic stress
(b) Oxidant / Antioxidant Imbalance allowing damaging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and/or reactive nitrogen species (RNS) to go unchecked.
(c) Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). A result of excessive intake of sugar / fructose / carbohydrate;
(d) Elevated homocysteine levels. A consequence of too much meat and/or dairy products;
(e) Overly acid-forming diet
Vitamin C deficiency is the primary cause of a weakened arterial wall
Vitamin C (together with the amino acids lysine and proline), maintain arterial structural integrity by their role in forming connective tissue components collagen and elastin. Arteries (and every other body tissue) constantly undergo decay, repair, and replacement. Tissue repair and replacement requires a binding protein called collagen, which the body produces using vitamin C (ascorbate). An insufficiency of ascorbate will cause artery walls to form lesions (wounds) as they fall into disrepair.
A chronic deficiency of vitamin C leads to chronic scurvy. Eventually the lesions would rupture and you would bleed to death through the arterial wall.
Atherosclerosis / CVD caused by weak walls due to chronic scurvy
Fix the wall / Prevent the injuries
Chronic inflammation of the endothelial cells (ECs) lining the arterial wall is caused by nutrient deficiencies and lifestyle choices. NOT by elevated cholesterol and calcium, whose deposits in the arteries are secondary to the primary causes.
“Cardiovascular DIY Fix” -♪”How can you mend a broken heart?”♪♫
The atherosclerosis process
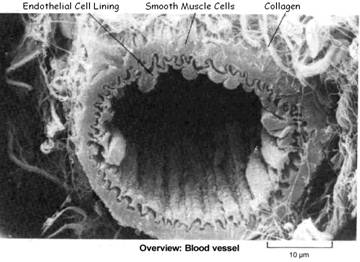
Endothelial cells (ECs) lining the inside of the artery function as a barrier. ECs prevent toxic substances in the blood from entering the elastic smooth muscle in the middle of the vessel wall.
Chronic injury irritates /inflames the endothelium causing the ECs to initiate an inflammatory immune response for the purpose of healing or controlling the damage. This involves a complicated series of steps, including T-cell activation, foam-cell formation, smooth muscle migration, and blood platelet adherence and aggregation, for the purpose of depositing an artery-thickening plaque over the damaged area to prevent a person from bleeding to death through a weakened arterial wall (usually under high pressure). This process is called atherosclerosis.
For more details on the development of atherosclerosis: