The Sleep Debt
Getting too little sleep creates a “sleep debt”. Much like being overdrawn at a bank. Eventually, our body will demand that the debt be repaid, until which time our judgment, reaction time, and other functions are impaired.
Can we learn to sleep less? The majority of people who are lacking sleep don’t think as well and make mistakes.The few people who really can do with only a few hours of sleep without detracting from their performance did not learn how to do that, they were born that way.
Accumulated lost sleep must be paid back. Most people need 7-9 hours of sleep a night, NOT COUNTING the time it takes to fall asleep.The brain keeps a tally of the amount of sleep you have had over at least the past couple weeks (longer times have not been studied). If you have not had enough sleep, your tendency to fall asleep is increased. But will be decreased when you start paying back the sleep debt to your body. If someone who needs 8 hours of sleep gets only 6 hours of sleep a night, after five days they owe their body 10 hours sleep, which is not made up by sleeping in on the weekend.
The time it takes you to go to sleep is in direct proportion to your sleep debt. If you fall asleep without caffeine faster than 15-20 minutes, you are sleep deprived.If you fall asleep within 5 minutes you are severely sleep deprived.10 minutes is borderline.
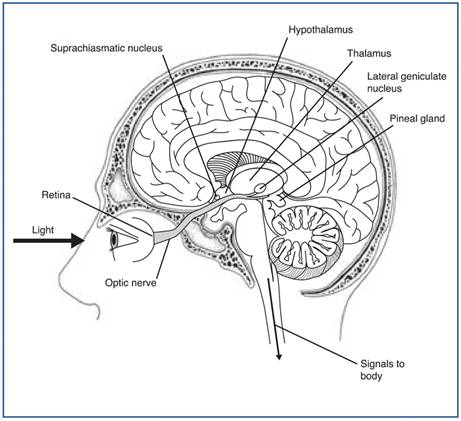
Short naps don’t make much difference to sleep debt. The body wants full sleep cycles of at least ~ 1 ½hours.
“Early to Bed” takes a change in lifestyle. Turn off the TV and go to bed earlier every night to get more sleep on a regular, ongoing basis.
Real life disasters resulted from a sleep debt
The Exxon Valdez disaster (America’s 2nd worst accidental oil spill, BP oil spill was the largest). The final report identified severe sleep-deprivation of a 3rd mate as the main cause of the disaster. The captain had handed over command to the 3rd mate and left the bridge.The 3rd mate had slept only 6 hours in the previous 48.Recognizing the danger of a collision with a reef, he ordered the ship to starboard but did not notice that the autopilot was still on and that the ship had not turned. Twice lookouts warned the 3rd mate about the position of lights marking the reef, but unable to interpret the danger in what they said, he didn’t check or register why the ship had not turned.Finally, when he realized that the copilot was turned on, it was too late.
Space shuttle Challenger explosion. The final report found to have been due to mistakes made by the NASA manager experiencing severe sleep deprivation;
American Airlines flight in South America flew into a mountain and killed 149 people. The pilot was so sleepy that he pressed the wrong button for navigation;
Many serious accidents in hospitals related to sleep deprivation;
Traffic accidents many times involve sleep-deprived teenagers or adults at the wheel. A sleep debt greatly increases the effects of alcohol.
Effects of a sleep debt
Sleep debt makes us feel lousy and act obnoxiously. In contrast, good sleep improves mood and feelings.However, we often don’t realize that it is lack of sleep causing the bad feelings because “Clock-dependent alerting” masks this effect at certain times of the day.
Lack of Sleep / Sleep debt can dangerously impair brain functions. After 40 years of study, Dement concluded that sleep debt is the most important factor in the quality or excellence of psychological and cognitive function. When we are sleep deprived, cognition functions are one of the first to go.In addition, once you repay your sleep debt, you may find that people or things that you previously found dull and uninteresting are now in fact interesting.
Impaired Performance. Australian researchers found that after 17 hours awake, at 1.00 am, a sleep-deprived group had the same test scores as drinking volunteers who had blood-alcohol levels of 0.05 %. After 24 hours awake, the sleep-deprived group had the same coordination deficits as those with blood-alcohol levels of 0.1%:
- Less alert
- Ability to think/concentrate diminished
- Slow reflexes
- Memory disorders
- Muscle fatigue
- Mood swings
- Aggressive behavior
- Difficulty situating oneself in time and space
- Hallucinations similar to when falling asleep (midway between reality and dreaming). Can be fatal at work or driving
Impaired Creativity. After decades of study, Rothenberg found that motivation is a common trait in highly creative people, and he demonstrated that almost all creative acts come after long sustained perseverance. Dement found that motivation is one of the first things to go when sleep is short-changed.
Chronic health problems. Lack of sleep disturbs regulatory mechanisms that are normally at work during the night. Typical problems include obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure
If we have sleep debt, why aren't we sleepy all day long?
"Clock-dependent alerting" alters are wakefulness at different times of the day:
Wakefulness is at its lowest around mid-day. This is the time when many societies traditionally took (or still take) a siesta.
There are two main times when your biological clock will make you extra alert:
• In the morning. When you wake up.
• Very late afternoon, around 6 pm, with the peak at possibly 9 pm. Possibly this energy is meant for healing, and we are meant to be in bed. If you have a serious health pain or problem – get to bed by 7pm, and if you wake up at 4 am – get up and start your day (This does not apply to teenagers, who are meant to go to bed late and sleep in).