The Thyroid - "The Body's Thermostat"
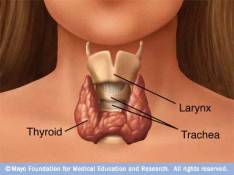
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland. It sits at the front of the neck, behind and below the Adam’s apple and wraps around the windpipe (trachea). It is the largest endocrine gland in the body.
- The main function of the thyroid is to produce the master metabolism thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These control the metabolism rate of the body’s cells, and therefore the pace of body processes
- Additionally, the thyroid “C” cells (parafollicular cells) produce the hormone CALCITONIN. This hormone controls calcium concentration in the blood.
Thyroid production of thyroid hormones depends on 3 key components:
- Adequate raw materials. Especially iodine
- An efficiently working thyroid – presence of certain factors can damage it
- Appropriate controls – to keep production in normal range
Thyroid hormones are produced in the thyroid gland’s numerous follicles. The ouside of these small globular sacs are lined with cuboidal, FOLLICULAR CELLS (aka. thyrocytes) and are filled with a fluid called COLLOID, which contains the T3 and T4 prohormone, called THYROGLOBULIN (Tg).
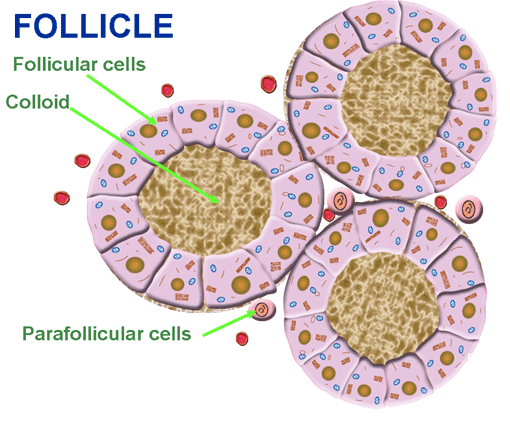
mage Credit: http://people.upei.ca/bate/html/notesonthyroidfunction.html
The thyroid hormones influence every organ, tissue and function in the body:
Details on these master metabolism hormones, their production and functions:
Thyroid Hormones T3 / T4 – “Master Metabolism Hormones”