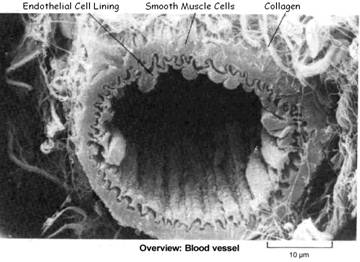
Common ischaemic cardiovascular diseases - HBP, Coronary heart disease, Heart attack, Stroke, Arrythmia, Angina, Thrombosis / Embolism.
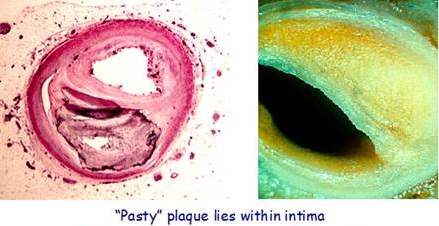

Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) aka. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) / Ischaemic Heart Disease (ICD)
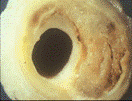
CHD can result in a reduced blood supply to the heart (ischaemia). This occurs primarily as a consequence of atherosclerotic blockage in the walls of the aorta and 2 main coronary arteries that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. American Heart Association, 2008
In the U.S., Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) kills one person every minute. CHD is the most common cardiovascular disease in the Western world and responsible for about half of heart disease related deaths. CHD claimed 371,506 American lives in 2022, with more women than men dying each year since 1984.
CHD can cause arrhythmia (abnormal heartbeat).

Chronic high blood pressure (HBP) / hypertension
HBP occurs due to narrowing of the body’s smaller arteries (arterioles) increasing resistance to blood flow. This can be caused by the presence of arterial plaque (atherosclerosis) or the body’s constriction of blood vessels in response to many triggers.
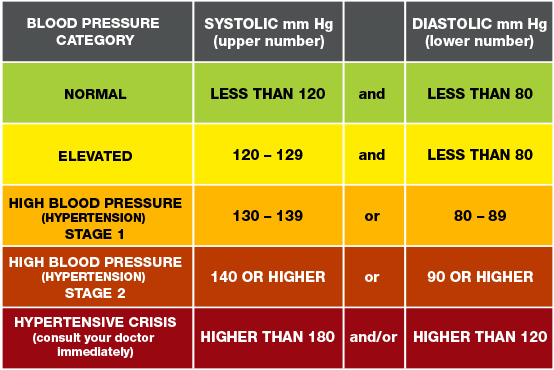
Normal blood pressure is typically less than 120 / 80 (systolic pressure / diastolic pressure) mm Hg. A chronic HBP higher than 130 / 80 is considered to be hypertension – almost half of U.S. adults in 2017 American college of Cardiology
Hypertension is either primary (due to such as age, genetics, lifestyle /diet and occurs over time) or secondary (5-10% of people with HBP have a specific attributable cause, such as hyperthyroidism)
Hypertension is categorized depending on the level of your blood pressure
Both globally and in N. America high blood pressure presents the highest risk factor for death (measured across all age groups and both sexes). After HBP, comes smoking, high blood sugar, obesity and outdoor air pollution. World in data, 2017

Heart Attack - a.k.a. Myocardial Infarction (MI)
The peak time for a heart attack is between 6:00 A.M. and 12:00 noon.
A heart attack occurs when coronary arteries supplying the heart with oxygenated blood become narrowed by atherosclerotic plaque reducing or blocking the blood flow. Without oxygen the heart muscle suffers injury and begins to die. If not quickly treated this can be fatal.
Atherosclerotic plaque rupture forming a blood clot (called arterial thrombosis) is present in coronary arteries of 80-90% of fatal heart attacks. Davies MJ et al, Thrombosis and acute coronary artery lesions in sudden cardiac ischemic death, NEJM, 1984. A blood clot (thrombus) forms where atherosclerotic plaque ruptures inside the wall of a coronary artery, which can obstruct oxygen-carrying blood flowing to the heart, thus reducing or cutting off its oxygen supply.
Calcified plaques (composed mostly of calcium) are less likely to cause a heart attack than soft, non-calcified plaques. Soft plaque tends to rupture more easily and form a clot.
Each year, more than a million people in the U.S. have a heart attack, and about half of them die. Of those who die, about half of them do so within 1 hour of the start of symptoms, and before reaching the hospital. The life quality and longevity of an MI survivor is mainly determined by the amount of damage done to the heart muscle. If treatment is not started quickly, the affected area of heart muscle begins to die. If a person survives a heart attack, the injured area of the heart muscle is replaced by scar tissue, which weakens the pumping action of the heart and can lead to heart failure and other complications.
Thrombosis / Embolism
Thrombosis. The formation of a blood clot inside an artery (arterial thrombosis) or vein (veinous thrombosis) or heart chamber can cause a blockage to blood flow. Arterial thrombosis can reduce oxygen supply pumped from the heart and is the most common cause of heart attacks and strokes. Veinous thrombosis can block blood flow back the heart for oxygenation by the lungs, and is the most common cause of a pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung).
Embolism. Occurs when a clot / thrombus breaks off from where it was formed (now called an embolus) and travels in the blood to get stuck in a smaller vessel, where it can cause a blockage resulting in such as a stroke or pulmonary embolism..

Stroke
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced. Causing brain cells to die as oxygen and glucose delivery is disrupted. Sensation, movement or function controlled by the damaged part of the brain is impaired. Stroke kills one third of its victims. There are 3 types of strokes:
Hemorrhagic Stroke. Leakage or rupture of a blood vessel in or around the brain, as a consequence of a weakened vessel wall (brain aneurism) and/or increased blood pressure; the leaking blood damages brain cells by putting pressure on them;
Ischaemic Stroke. A clot in the large-sized internal carotid or vertebral arteries supplying the blood to the brain, usually as a consequence of;
Thrombosis (clot) in the large-sized internal carotid or vertebral arteries. These arteries supply the blood to the brain;
Embolism. When a small clot, originating either from a large artery (E.g. carotid artery) or from the heart, travels (embolizes) to the brain’s supply arteries causing (a) Blockage of an arteriole in the brain affecting just a small part of the brain, or even (b) Blockage of the larger arteries supplying the brain.
Mini-stroke /Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA)

Angina
Angina is felt as a heavy, tight squeezing pain in the chest. Caused by low blood flow yielding a poor oxygen supply to the heart; generally occurs when the heart is working hard and thus requiring more oxygen soon after a meal.

Arrythmia - Possible consequence of CVD
Arrythmia is a condition in which the heart beats too fast (bradycardia), too slow (tachycardia), too early (premature contraction) or with an irregular rhythm (flutter or fibrillation). This occurs when electrical signals to the heart that coordinate heart beats stop functioning properly. Symptoms can sometimes be felt as palpitations (a feeling that your heart has added or skipped a beat, or rapid pulsations), possibly including dizziness and/or difficulty breathing.

The SA node (a.k.a. sinus node) is the heart’s primary natural pacemaker. Normal heart rhythm of 60-100 beats per minute is controlled by the SA node, a cluster of cells located in the right atrium. The specialized cells of the SA node generate regular spontaneous “slow response” (i.e. slow depolarization) action potentials through the muscle tissue of the atrial and ventricle chambers at a rate of 100-110 action potentials (“beats”) per minute. These are tempered by the autonomic vagal nerve bringing the resting heart rate down to 60-80 “beats” per minute. Normal range is 60-100 “beats” per minute. A rate below 60 is termed sinus bradycardia, and a rate above 100 is termed sinus tachycardia. “Slow response” action potentials are carried into the cell primarily by relatively slow Ca++ currents, whereas most non-pacemaker action potentials are produced by cells that elicit action potentials that carry the depolarizing current via fast Na+ currents (ie. fast depolarization), in such as nerve and muscle cells.
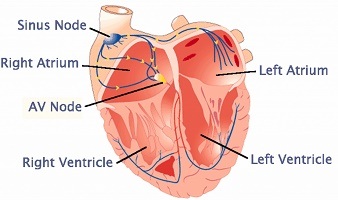
“The heartbeat”. Action potentials generated by the SA node spread through and depolarize the atrial tissue causing atrial contraction, then the impulse travels via the Atrioventricular (AV) node to the ventricles to elicit ventricular contraction.
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) / Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can cause arrythmia. CHD/CAD reduces the blood supply to the heart, which reduces the oxygen supply to cardiac cells – lacking oxygen, heart muscle cells can depolarize (Technically, this means that a cell membrane potential becomes more positive as positive ions move from the outside to the inside of the cell, which initiates an action potential interfering with the normal rhythm of the heart), leading to:
Altered impulse formation. Involves changes in rhythm that are caused by:
- Changes in the spontaneous activity of heart’s SA node pacemaker cells
- Abnormal generation of action potentials at sites other than the SA node. Other pacemaker sites within the atria and ventricles (called ectopic foci) can cause additional beats or take over from the SA node, which normally suppresses these other pacemaker cells with its higher rate.
Altered conduction of impulses
- AV block. Impulses are not conducted from the atria to ventricles through the AV node. Can be caused by excessive vagal action or drugs that reduce conduction Eg. beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers
- Abnormal conduction pathways between atria and ventricles. Eg. accessory pathways.
With arrhythmia, it is important to ensure a sufficiency of magnesium
- Magnesium is an effective calcium channel blocker. These drugs are often prescribed for atrial fibrillation and work by interrupting the movement of calcium into heart and blood vessel tissue to help slow the heart rate by blocking the number of electrical impulses that pass through the AV node into the lower heart chambers.
- Study found that magnesium deficiency decreased the activity of the cell membrane sodium / potassium pumps in the heart of rats. This may lead to an increase in intracellular Na+, resulting in a change in the membrane potential, and may contribute to the arrhythmias associated with magnesium deficiency. Effects of dietary magnesium on sodium-potassium pump action in the heart of rats.
- The quickest method to increase your magnesium levels is transdermally.