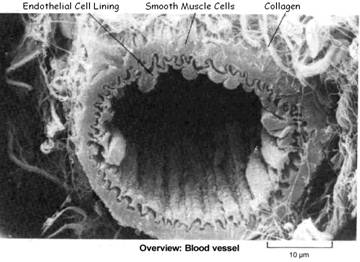
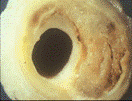
What injures arterial lining leading to atherosclerosis / CVD?

Damage to the arterial lining can be inflicted by several mechanisms, irritating /inflaming the arterial lining (endothelium) and causing an inflammatory response leading to atherosclerosis / CVD. The offending culprits include:
(a) Mechanical/Hemodynamic Stress
Usually in a location under high pressure or turbulence. Blood flowing under high pressure generates fluid shear-stresses at each heartbeat, which can damage areas leaving the heart, usually where the blood vessels are stretched and bent
Damage does not occur in random locations
- Veins (which are under 8 times less pressure than arteries) do not have atherosclerosis.
- Pulmonary arteries generally don’t develop atherosclerosis. Having 1/5 of body’s systemic pressures
- Damage occurs in regions of high pressure, branching and marked curvature, at areas of geometric irregularity. Where blood undergoes turbulent changes in velocity and direction of flow;
Increased blood pressure can be due to emotional stress, or progressing atherosclerosis.
(b) Oxidant/ Antioxidant imbalance
A lack of antioxidants to control oxidative stress (especially in the presence of heavy metals). Basically the oxidant molecules in your body are outnumbering the antioxidants; highly reactive oxidant molecules can be present in food and water, produced by the body in response to several factors, including elevated blood sugar levels, toxins (Excess exposure to chlorine, in particular, has been implicated as a predominant source of oxidants), cigarette smoking, emotional stress, microbial infection, and in a variety of conditions E.g. hypertension, immune injury, and diabetes.
Oxidants can be introduced into or created in the body. By eating fried, cured or aged foods, or trans fats in polyunsaturated oils (created during typical oil processing methods). White blood cells create ROS and RNS in the body when reacting to an adverse factor, such as emotional stress, trauma, infection or toxins. ROS are also produced with high blood sugar levels
Oxidative metabolism requires a balance of oxidants and antioxidants. Oxidative metabolism is designed to extract energy by controlled oxidation of substrates and, at the same time, to prevent uncontrolled oxidative damage via antioxidants. A good analogy is “to use fire for warmth, but to not get burnt”.
A major reason your arteries are incurring damage, is because too many highly reactive, oxidant ions/molecules being produced in the body, have overwhelmed the body’s antioxidant presence. Uncontrolled free radicals ROS (Reactive Nitrogen Species) and other reactive species are likely to take part in chemical reactions with your body’s proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and DNA.
Life’s Oxygen Paradox – Meet Dr. ROS Jeckyll and Mr. ROS Hyde
(c) Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) increases damaging AGEs
Glycation of sugar molecules lead to Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGEs), some of which are implicated in age-related chronic diseases including CVD. Glycation is the haphazard process (without the controlling action of an enzyme) of adding sugar molecules to lipid molecules or proteins, to form a glycolipid or glycoprotein, and harmful by-products, aptly called AGEs (Advanced Glycation Endproducts).
AGEs can be formed outside or inside of the body:
- Exogenously. AGEs are typically formed when sugars are cooked with proteins or fats. Food manufacturers add AGEs to foods as flavor enhancers and colorants to improve appearance.
- Endogenously. Glycations occur mainly in the bloodstream to some of the absorbed simple sugars, i.e. glucose, fructose and galactose.
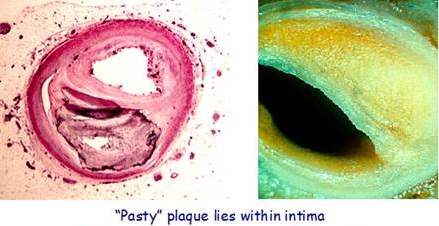
AGEs can directly damage the endothelium and other biomolecules, including connective tissue collagen, elastin and fibrinogen in the blood vessel walls, and so weaken the arterial wall
Fructose and galactose have about 10 TIMES the glycation activity of glucose (Bunn and Higgins, 1981) High fructose corn syrup is commonly used in many processed foods, fructose has become an excessive component in today’s Western diet;
Cholesterol and Fat is Damaged by Glycation – Increased amount and duration of glucose in the blood allows more glycation to occur, inflicting damage on tissues via lipid oxidation (Bucal etal, 1993)
Hyperglycemia increases glyco-oxidation, which increases the formation of oxidized LDL, and its accumulation in the artery wall – and is positively correlated with arterial disease in many diverse populations.
Glucose and fructose glycate and inactivate the enzyme glutathione reductase, responsible for maintaining the body’s major cell-protecting antioxidant enzyme Glutathione (GSH) – Glucose, glucose 6-phosphate and fructose all displayed a time-dependent inhibition of glutathione reductase activity, suggesting that these sugars glycate this enzyme. (Blakytny and Harding, 1992)
Circulating AGEs bind LDL cholesterol and increase its accumulation in arterial wall -glycation of LDL cholesterol increases the proportion of lipoproteins that are taken up via inflammatory cellsand decreases the proportion taken up by liver cells (hepatocytes) via classical LDL receptors, thus contributing to atherosclerosis by increasing accumulation of LDL cholesterol in the artery wall.
- Glycated sugar creates inflammation, which activates defensive immune system macrophages – scavenger cells with special receptors for AGEs, called RAGEs (again how aptly named) that bind to the AGEs to remove them.
(d) Elevated levels of Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a by-product of normal metabolism of the amino acid methionine – abundant in red meat, milk and its products.
- Its levels increase with certain nutrient deficiencies – especially a deficiency of the B-vitamins.
- High levels of homocysteine correlate to greater arterial tissue damage leading to atherosclerotic plaque growth – It is theorized that homocysteine produces oxysterols (oxygenated derivatives of cholesterol), which cause cholesterol oxidation.
(e) Overly acid-forming diet
An overly-acid diet is generally the result of:
▲ Dehydration
▲ Eating more meat and dairy, less fruit and vegetables
▲ Eating more cooked food than raw;
When blood is less alkaline than is ideal, it can act as an irritant to the arteries;
References
Blakytny R, Harding JJ (1992) Biochem J, Glycation (non-enzymic glycosylation) inactivates glutathione reductase
Bucal R et al (1993) Lipid advanced glycosylation: pathway for lipid oxidation in vivo
Bunn HF, Higgins PJ (1981) Reaction of monosaccharides with proteins: possible evolutionary significance. Science 213:222-4