Glutathione (GSH) - "King of the antioxidants"

GSH is the PRIMARY antioxidant and detoxifier in the cell's cytoplasm
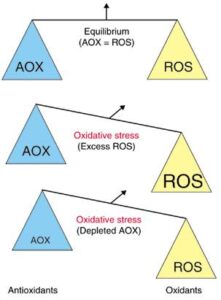
Glutathione (GSH) provides a “Bullseye” for oxidation by radicals. Glutathione is a reducing agent (i.e. it donates electrons). The cysteine in this tripeptide (glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine) provides the biological activity of GSH as a highly reactive free sulfhydryl group (SH or thiol group) which neutralizes radicals in a 1-electron oxidation-reduction transfer. The reduced form (GS-SG) is regenerated in a redox cycle involving gluthathione reductase, using NADPH as an electron donor.
GSH + ROS → Neutralized ROS + GS-SG (oxidized GSH)
(Glutathione disulfide)
E.g. 2GSH + H2O2 → GS-SG + 2H2O
GS-SG + NADPH + H+ → 2 GSH+ NADP+
Glutathione Reductase
In addition, glutathione “wears many other hats”:
- Recycles other antioxidants in the body. Reduces oxidized Vitamin C and Vitamin E to their unoxidized states.
Dehydroascorbate + 2GSH → GSSG + Ascorbate
- Helps red blood cells carry oxygen. Helps keep their shape, enhancing their delivery to vital organs; also prevents formation of methemoglobin, an altered form of hemaglobin produced by heme iron-oxidation, which is unable to carry oxygen,;
- Needed for protein synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis / DNA repair and cellular function. By aiding amino acid transport across cellular membranes.
- Immune system enhancer. Needed for creation / maintenance of T-Cell lymphocytes -the body’s frontline defense against infection.
- Detoxifies toxins in the body. Including heavy metals, cigarette smoke, fuel exhaust, etc.. (Phase I and II detoxification reactions).
- Potent anti-cancer /anti-viral agent
- Involved in maintaining brain function
Why would we have a glutathione deficiency?
Glutathione is produced in the body, CANNOT be directly ingested, and requires cysteine
Glutathion is produced inside EVERY cell requiring the amino acid cysteine that is difficult to obtain. Although glutathione is non-essential (meaning it does not have to be in diet), this crucially important antioxidant is synthesized “in-house” from its precursor amino acids, glycine, glutamate and cysteine with the dietary trace mineral selenium as a cofactor.
Glycine and glutamate are readily available (both in foods and produced in body), but cysteine is more difficult to obtain and is the rate-limiting factor in glutathione production.
Gene deficiency may be at the root of low glutathione levels
Certain genes produce enzymes that allow the body to create and recycle glutathione in the body. E.g. GSTM1, GSTP1
These genes are in short supply in about 1/3 of the population, who are more apt to suffer chronic disease. Since these genes were not needed in the pre-industrial era, they probably evolved out of production in our body, but today, we are bombarded with chemical and electromagnetic pollution, which rapidly depletes our mediocre glutathione supplies.
Families with genetic tendencies for lower amounts of glutathione production tend to have certain problems. E.g. schizophrenia, alcoholism, bipolar disease, depression, attention deficit disorder, constipation, and autism.
The best way to increase glutathione levels is to obtain cysteine
Why not just supplement glutathione?
Most oral glutathione supplements have been shown to be poorly absorbed. Ironically, they may interfere with your body’s own ability to produce glutathione in the long-termCysteine is a difficult amino acid for the body to obtain
In foods, it may not survive digestive journey – and even if it does, it has difficulty entering cells.- Harsh stomach acids can destroy bonds in cysteine consumed in plant or meat sources
- Free cysteine that survives the trip into the bloodstream cannot enter the cells – it needs to be part of a larger molecule;
– Dr. Jimmy Gutman “Glutathione. Your Key To Health
Best supplement is RAW cow’s milk whey powder
Provides cystine (two bonded cysteine molecules), glycine and glutamate for glutathione production.- Raw milk whey contains 3 highly bioactive proteins containing large amounts of cystine:
- Lactoferrin and Lactalbumin -immunoglobulins, critical to creating the right metabolic environment for high glutathione activity.
- Serum albumin – rarely in other foods, whey contains a unique cysteine residue (glutamylcysteine) that naturally occurs in bovine serum albumin. This fragile immune component of whey is highly bioactive in its affinity for converting to glutathione.
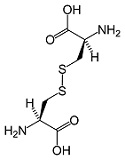
- The cysteine in whey is in the form of cystine, which can enter cells. Each cysteine molecule is bonded with another cysteine molecule by a disulfide bond or bridge -to make a paired unit, called cystine (pronounced /sis-‘ta-yn/). Cystine can easily enter cells where it breaks down back into two cysteine molecules and participates in the formation of glutathione.
- Dietary cysteine induces greater levels of glutathione in mice fed whey protein than dietary (free) cysteine, which showed no positive immunological response Drs. Bounous and Batist, “Immunoenhancing property of dietary whey protein in mice: role of glutathione”, Clinical and Investigative Medicine Europe PMC
CYSTINE MOLECULE
These disulfide bonds are very fragile and easily denatured by heat and mechanical stress – bonds are damaged by pasteurization of milk and mechanical stress during centrifuging.
For beneficial cysteine, whey protein should be:
- Cold-pressed from non-pasteurized milk, containing non-denatured proteins
- Derived from grass-fed cows
- Free of hormones, chemicals and artificial sugar;
Quality whey protein sold on amazon.
“Breast is Best”
Human breast milk contains large amounts of lactoferrin, serum albumin and alpha lactalbumin, as well as other immunoglobulins. So it is loaded with bonded cysteine. This is one of the reasons why mother’s milk is such a strong immune system builder for a baby, and why it is very important for a mother to breastfeed her child. Baby formula will NOT supply bonded cysteine for building glutathione.
Consuming foods containing cysteine and/or methionine increases body’s glutathione levels
Cysteine can be made from the essential amino acid methionine (not produced by the body, so must be obtained from diet) by the methylation pathway. E.g. methionine is in meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, quinoa, buckwheat, sesame seeds, Brazil nuts, and to a lesser degree dry spirulina.
Sulfur-rich foods supply cysteine
Cysteine is a SULFUR-containing amino acid. It contributes to the sulfhydryl group (SH) in the glutathione (GSH) molecule; Sulfur – Healing Mineral
- Highest levels of cysteine in RAW milk products, eggs, and meat. More in RAW or undercooked sources. Less in PASTEURIZED dairy products.
- Also found in smaller quantities in UNCOOKED, fresh fruits and vegetables. Highest sources of precursor amino acids are spinach, potatoes, asparagus, avocado, squash, okra, cruciferous vegetables (cauliflower, broccoli, kale, collards, cabbage, watercress), walnuts, garlic, onions and tomatoes;
- Cooking destroys some bioactivity of cysteine – In food, cysteine is bound into protein molecules by amide (peptide) bonds. High temperatures during cooking can break down these bonds and destroy bioactivity of cysteine, but, to a large extent, cysteine does survive cooking.
Giovanelli J (1987); Clemente et al (1998); Chau et al (1997)
Ensure sufficiency of selenium in diet
~200 mcg/day. Body’s “in-house” production / recycling of glutathione requires this trace mineral. Excellent sources (best from food, but supplement if you have to):
- 2-3 organic brazil nuts (100mcg)
- 4 oz cod or halibut (53 mcg) / 4oz tuna (53 mcg) / 3.2 oz sardines (48 mcg) / 4 oz salmon (43 mcg)
- 4 oz turkey (36 mcg), 4 oz beef, chicken or lamb (31-37 mcg)
- 1 cup barley (36 mcg);
- 5 oz Crimini mushrooms (23 mcg)
Ensure B6, B12 and folate
These B-vitamins are crucial methylation and transulfuration pathways in production of glutathione. These B-vitamins support SAMe, and other methyl donors, which donate a methyl group (CH3) to another molecule to make it bio-active; SAMe is also the precursor for synthesis of cysteine and glutathione in the transulfuration pathway. Take supplements in their active forms: Folate (5-MTHF), B6 (P5P), B12 (methylcobalamin).
SAMe – Precursor to 3 main metabolism pathways
Other glutathione boosters
Exercise boosts body’s glutathione levels. 30 minutes/day of aerobic exercise, as in a brisk walk
Magnesium is required for glutathione synthesis. Magnesium deficiency often results in low serum glutathione levels.
Magnesium – Antioxidant glutathione synthesis
Other antioxidants work together to recycle glutathione. Including vitamin E (take 400IU mixed tocopherol supplement) and vitamin C.
MELATONIN increases glutathione production. This hormone is produced when you get a good night’s sleep in total darkness
Herb milk thistle. An excellent source of the antioxidant compound silymarin, which may help prevent glutathione depletion in your liver. Glutathione is crucial in the liver for detoxification and can become depleted by alcohol consumption and general toxic overload.
- Ellagic acid (highest in raw blackberries and black raspberries, raw chestnuts, pomegranate juice and walnuts) and quercetin (apple and mango peels) recycle glutathione
- Curcumin. Increases liver cell’s (hepatocytes) production of glutathione.
Alpha Lipoic Acid. Operates as an antioxidant in both its oxidized and reduced states and has been shown to enhance glutathione levels.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) has mixed reviews
This oral supplement NAC is sometimes taken as a precursor for cysteine and glutathione; however, clinical studies are controversial. In particular, study doses tend to be very high for effectiveness, sometimes up to 8000 mg /day PubMed.
- Some studies demonstrate that NAC supplementation by itself is NOT effective in increasing cysteine levels within the cell.
- NAC-induced increases in glutathione levels did occur when NAC administered in dangerously high dosages.
LEONORE A. HERZENBERG e3t al, Glutathione deficiency is associated with impaired survival in HIV disease (,March 1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 1967-1972 Link
- High NAC supplementation can deplete zinc, copper and some trace minerals
- NAC use has been associated with some serious side effects
Glutathione can be nebulized
Glutathione can be introduced into the lungs and bronchial area via a nebulizer. According to a study in Alternative Medicine Review in 2000, nebulized glutathione has had remarkable success in emphysema and other lung disorders such as asthma and bronchitis; it can also be used for colds and sinus problems.
References
Giovanelli J (1987) “Sulfur amino acids of plants: an overview.” In: “Sulfur and Sulfur Amino Acids,” Methods in Enzymology, vol. 143; eds. Jakoby W, Griffith O; Academic Press, Orlando, Florida; pp. 419-426.
Clemente A, Sanchez-Vioque R, Vioque J, Bautista J, Millan F (1998) “Effect of cooking on protein quality of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) seeds.” Food Chemistry, vol. 62, pp. 1-6.
Chau C-F, Cheung P C-K, Wong Y-S (1997) “Effects of cooking on content of amino acids and antinutrients in three Chinese indigenous legume seeds.” Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, vol. 75, pp. 447-452.