Thyroid Hormone Production (In detail)
Production of thyroid hormones Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) takes place in the thyroid follicles
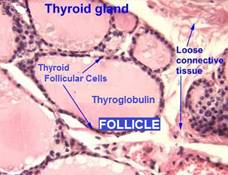
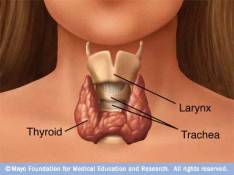
The functional units of the thyroid gland are spherical follicles – balls of follicular cells with hollow centers, each follicle consists of:
- Thyroid follicular cells (simple cuboidal type, aka. thyroid epithelial cells, follicular epithelial cells, thyrocytes); form the outside boundary . . .
- Filled with a viscous material called colloid – which contains mostly glycoprotein thyroglobulin (Tg) molecules, that provide:
- The glycoprotein backbone for synthesis and storage of thyroid hormones
- A convenient depot for iodine storage and retrieval – when external iodine availability is scarce or erratic.
Iodine + Amino acid tyrosine → T3 and T4
These are the 7 MAIN steps that take place in thyroid’s hormone production:
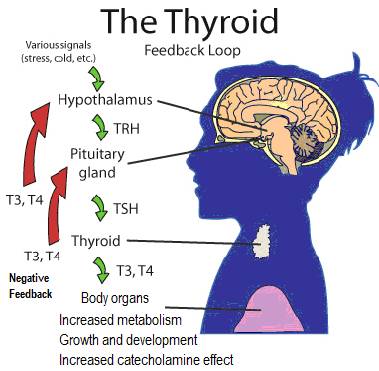
(1) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulation
- TSH receptors on the surface of thyroid follicular cells respond to TSH (aka. thyrotropin) to initiate the production of T4 and T3 thyroid hormones.
(2) Iodide transport from circulation to the follicular lumen
- Iodide intake and concentration –Iodide (I–) (obtained through food or supplements) is taken up from circulation and concentrated into the thyroid follicular cells (thyrocytes) via the thyroid epithelial sodium-iodide “pumps” (Na/I symporters (NIS), expression stimulated by TSH) at the basolateral membrane (see diagram), which co-transport iodide with sodium; these pumps enable iodide to be concentrated in the thyroid follicular cell to about 30 times its concentration in the blood.
- Passive transport across the apical plasma membrane – iodide is shuttled across the membrane into into the follicullar lumen via pendrin (another transporter).
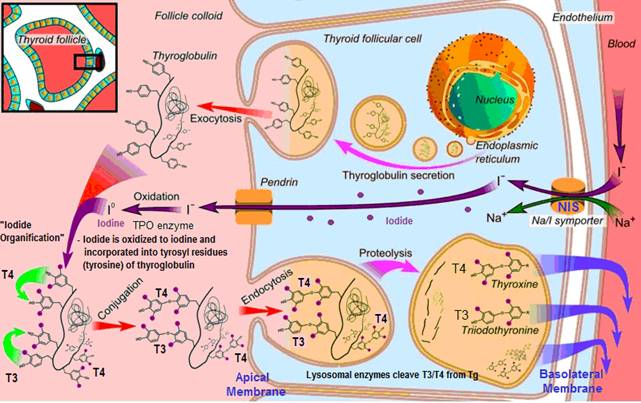
(3) Thyroglobulin (Tg) synthesis
- Tg is a protein containing large numbers of tyrosine amino acids required for thyroid hormone molecules
- TSH stimulates thyroid follicular cells to take up amino acids from circulation for the synthesis of thyroglobulin (and also for TPO enzymes) – Tg is produced by thyrocyte ribosomes and secreted by the endoplasmic reticulum into the follicular cell.
- Tg translocates to the follicular lumen (via exocytosis) – where it will be ready to be incorporated into thyroid hormone molecules
(4) Iodide is oxidized to iodine
Iodide (I–) is oxidized to atomic iodine (I0) via the TPO enzyme mediated by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) – taking place at the apical membrane (iodide is an electron donor in the presence of H2O2 and peroxidase, thus decreasing radical damage):
- Thyroperoxidase (TPO) is stimulated by TSH (which up-regulates its gene expression) – and by definition, a peroxidase requires H2O2 for its oxidative function . . .
- H2O2 is produced at the apical plasma membrane stimulated by TSH – via the enzyme Thyroid NADPH oxidase (that requires both calcium and NADPH). In vitro, H2O2 seems to be regulated by iodide (which increases H2O2 at low iodide concentrations, inhibits at high concentrations).
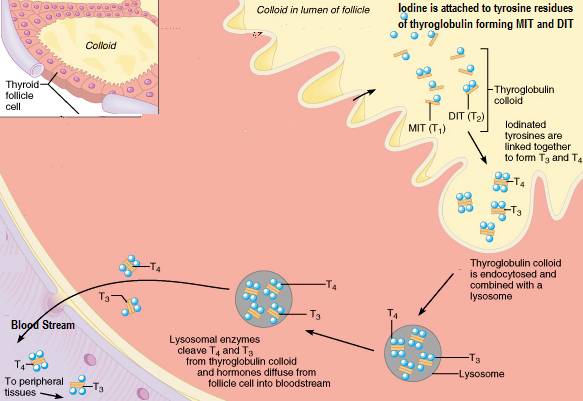
(5) Iodine organification / Thyroglobulin (Tg) iodination
Iodine is incorporated into tyrosyl (amino acid tyrosine) residues of Tg molecules and to free tyrosine, forming iodotyrosines MIT and DIT
- 1 iodine added to tyrosine forms monoiodotyrosine (MIT)
- 2 iodines added to tyrosine forms diiodotyrosine (DIT) (contains 2 iodides);
(6) Formation and storage of thyroid hormones in follicle colloid
Products of Tg iodination (MIT and DIT) are combined (by a covalent bond) to make the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 – where as part of thyroglobulin, they can be stored for up to 3 months in follicle colloid. These couplings are also catalysed by the TPO enzyme..
- MIT + DIT → T3 (3 iodides) Via TPO
- DIT + DIT→ T4 (4 iodides) Via TPO (more efficently than DIT + MIT, explaining why the thyroid produces more T4 than T3)
Side note: In addition to the thyroid gland, organification of iodide and NIS expression also occurs in lactating and cancerous mammary glands. Cann et al, Iodide Accumulation in Extrathyroidal Tissues, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 1999.
(7) TSH stimulates the release of T3 and T4
- The follicular cells reabsorb iodinated, colloid Tg from folicular lumen – by endocytosis at the apical membrane;
- Thyroid hormones are cleaved from the Tg – Tg is combined with a lysosome, and T3 and T4 are cleaved from their peptide linkage to the iodinated tyrosines in Tg with the help of proteases in lysosomes; Each Tg molecule forms approximately 10 thyroid hormone molecules
- T3 and T4 are then released into circulation to perform their duties – lipophilic T3 and T4 hormones are bound to protein carriers thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) and albumin to be carried to target tissues.
- With good health, ~80% of the thyroid’s hormone production is T4 and ~20% T3 (active form) – Also, some T4 is converted by the thyroid to its biologically active form T3.