HORMONES CHART - Types, sources and effects

INFORMATION ON STEROIDS
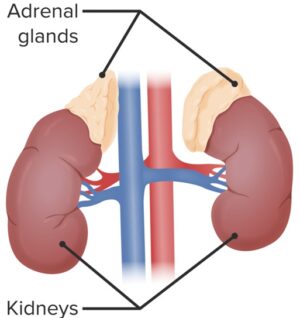
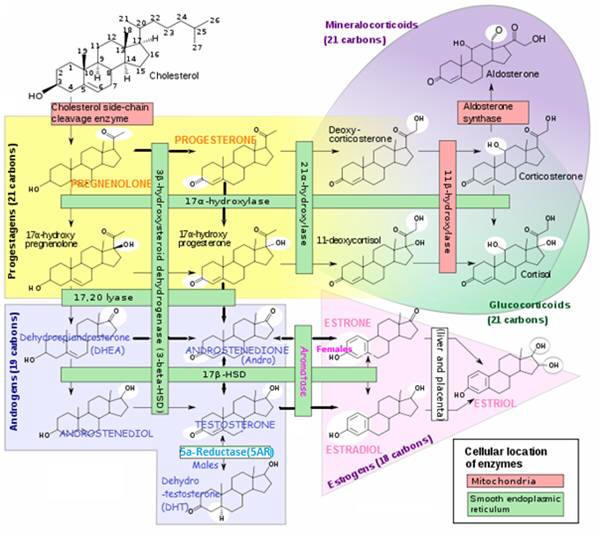
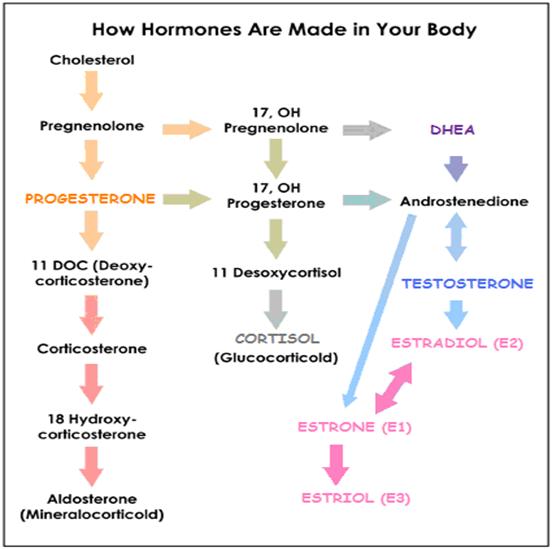
- You on Steroids – Control metabolism, inflammation, immunity, water-balance, sexual characteristics
- Sex steroids – “Your body is not your own”
- Synthetic steroids – “Frankenstein look-a-likes”
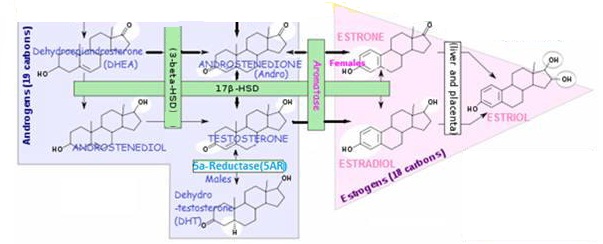
- Estrogens – “Predominantly female hormones” ESTRADIOL, ESTRONE, ESTRIOL
- Estrogen Dominance – Hormonal imbalance of our time
- Androgens – “Predominantly male hormones testosterone DHT
- Progestogens – “precursors to androgens, estrogens and corticoids”. PROGESTERONE, PREGNENOLONE

HORMONES CHART | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Catecholamine (CAT) – Adrenal “Fight or Flight”hormones released in response to stress; Part of the sympathetic nervous system. | ||||||||
Structure | Hormone | Abbr. | Source | Effect | ||||
A M I N E S
| Tryptophan | MELATONIN | Pineal gland | Antioxidant / causes drowsiness | ||||
| SEROTONIN | 5-HT | CNS, GI Tract | Controls mood, appetite, sleep | |||||
| Tyrosine | Thyroxine | T4 | Thyroid gland | Weak thyroid hormone (TH) form; ▲ BMR and sensitivity to catecholamines (CATs); affects protein synthesis | ||||
| Triiodothyronine | T3 | Thyroid gland | Potent TH form; ▲ BMR and sensitivity to CATs; affects protein synthesis | |||||
| Tyrosine CATs* | EPINEPHRINE (ADRENALINE) | Adrenal medulla | “Fight or flight”response; ▲ Oxygen /Glucose supply to brain/muscles (▲ heart rate, stroke volume, vasodilation, breakdown of liver’s glycogen & FAT cell lipids); Dilates pupils; suppresses non-emergency systems (E.g digestion, immune system) | |||||
| NOREPINEPHRINE (NORADRENALINE) | Adrenal medulla | “Fight or flight” response; ▲ oxygen /glucose supply to brain/muscles (▲ heart rate, stroke volume, vasoconstriction, blood pressure, breakdown of fat cell lipids); ▲ Skeletal muscle readiness | ||||||
| DOPAMINE | Kidney, hypothalamus | ▲ Heart rate, blood pressure Inhibit release of PROLACTIN & TRH | ||||||
| Histidine | HISTAMINE | Stomach | ▲ Stimulate gastric acid secretion | |||||
P O L Y P E P T I D E S | ||||||||
| Antimullerian hormone | Testes | Inhibit release of PROLACTIN & TRH | ||||||
| Adiponectin | Adipose | |||||||
| ADRENOCORTICOTROPIN HORMONE | ACTH | Anterior pituitary | Synthesis of glucocorticoids and weak androgens in adrenal cortex | |||||
| ANGIOTENSINOGEN / ANGIOTENSIN | AGT | Liver | Vasoconstriction /Release ALDOSTERONE from adrenal cortex | |||||
| Antidiuretic hormone (aka Vasopressin) | ADH | Posterior pituitary | Water retention in kidneys. /Moderate vasoconstriction /Release ACTH | |||||
| Atrial-Natriuretic peptide | ANP | Heart | ||||||
| Brain Natriuretic peptide | Heart | (Minor to ANP) Reduces blood pressure (by reducing ▼ systemic vascular resistance, blood water, sodium and fats) | ||||||
| CALCITONIN | Thyroid gland | Construct bone / Reduce blood Ca2+ | ||||||
| CHOLECYSTOKININ | CCK | Duodenum | Release pancreatic enzymes /Release bile from gallbladder / Hunger suppressant | |||||
| CORTICOTROPIN -RELEASING HORMONE | CRH | Hypothalamus | Release ACTH from anterior pituitary | |||||
| ENDOTHELIN | Endothelium, stomach | ▲ Increase blood pressure (by constricting blood vessels) ▲ Stimulates gastric acid secretion | ||||||
| ENKEPHALIN | Kidneys | Regulates pain | ||||||
| ERYTHROPOIETIN | Kidney | Stimulate erythrocyte production | ||||||
| FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE | FSH | Anterior pituitary | Female: stimulates maturation of ovarian Graafian follicles Male: spermatogenesis /Enhances sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) production by teste’s Sertoli cells | |||||
| GASTRIN | Stomach, duodenum | Gastric acid secretion by parietal cells | ||||||
| GHRELIN | Stomach | Stimulate appetite / GH secretion from anterior pituitary gland | ||||||
| GLUCAGON | Pancreas | Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver ▲ Blood glucose | ||||||
| GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE | GnRH | Hypothalamus | FSH and LH release from anterior pituitary | |||||
| GROWTH HORMONE-RELEASING HORMONE | GHRH | Hypothalamus | GH release from anterior pituiatary | |||||
| HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN | HcG | Placenta | Maintain corpus luteum in early pregnancy /Inhibit immune response to embryo | |||||
| HUMAN PLACENTAL LACTOGEN | HPL | Placenta | Decreases maternal INSULIN sensitivity to keep mother’s blood glucose available for baby ▲ INSULIN + IGF-1 production ▲ INSULIN Resistance (IR) & carbohydrate intolerance | |||||
P O L Y P E P T I D E S | GROWTH HORMONE | GH or hGH | Anterior pituitary | a.k.a. HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE (hGH); Stimulate growth & cell reproduction | ||||
| INHIBIN | Testes, ovaries, fetus | Inhibit FSH production | ||||||
| INSULIN | Pancreas | Inhibits GLUCAGON release /Promotes uptake of glucose in liver, muscle, & fat cells from blood, stored as glycogen in liver and muscle / Glycogenesis & glycolysis in liver /Lipid intake and TG synthesis in adipocytes | ||||||
| INSULIN-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR | IGF | Liver | INSULIN-like effects / Regulate cell growth & development | |||||
LEPTIN | Adipose tissue | ▼ Appetite ▲ Metabolism | ||||||
| LIPOTROPIN | Anterior pituitary | Lipolysis, steroidogenesis; Stimulates melanin production by melanocytes | ||||||
| LUTEINIZING HORMONE | LH | Anterior pituitary | Female: ovulation. Male: Stimulate Lehdig cell TESTOSTERONE production | |||||
| MELANOCYTE STIMULATING HORMONE | MSH | Anterior pituitary, pars intermedia | De novo melanin production by melanocytes in skin and hair | |||||
| NEUROPEPTIDE Y | NP Y | Stomach | Production: ▲ Increased by food intake ▼ Reduced by physical activity | |||||
| OREXIN | Hypothalamus | Wakefulness ▲ Energy expenditure ▲ Appetite | ||||||
| OXYTOCIN | Posterior pituitary | Release breast milk; Contraction of cervix/vagina Involved in: orgasm, trust between people, circadian homeostasis (body temp., activity level, wakefulness) | ||||||
| PANCREATIC POLYPEPTIDE | Pancreas | – Self regulates pancreatic exocrine and endocrine secretion; – Effects hepatic glycogen levels – Effects GI secretions | ||||||
| PARATHYROIID HORMONE | PTH | Parathyroid gland | Opposes CALCITONIN ▲ Blood Ca2+/indirectly stim. osteoclasts – Ca2+ reabsorption in kidney Activate vitamin D▼ (Slightly) blood phosphate: ▼ reuptake in kidney ▲ uptake from bones | |||||
| PROLACTIN | PRL | Anterior pituitary, Uterus | ▲ Milk production in mammary glands Sexual gratification after sexual acts | |||||
| PROLACTIN-RELEASING HORMONE | PRH | Hypothalamus | Releases PROLACTIN from anterior pituitary | |||||
| RELAXIN | Uterus | Unclear in humans | ||||||
| RENIN | Kidneys | Activates renin-angiotensin system (produces ANGIOTENSIN I from ANGIOTENSINOGEN) | ||||||
| SECRETIN | Duodenum | ▲ Secretion of bicarbonate: from liver, pancreas, duodenal Brunner’s glands ▲ Effects of CHOLECYSTOKININ ▼ (stops) Gastric juice production | ||||||
| SOMATOSTATIN | Hypothalamus, Islets of Langerhans, GI system | ▼ Inhibit release of pituitary GH and TRH ▼ Suppress release of: GASTRIN, CCK, SECRETIN, MOTILIN, VIP, GIP, ENTEROGLUCAGON in GI system ▼ Lowers gastric emptying rate ▼ Reduces smooth muscle contractions and blood flow within the intestine ▼ Inhibit pancreatic release of INSULIN and GLUCAGON ▼ Suppress pancreatic exocrine secretion. | ||||||
| THROMBOPOIETIN | Liver, kidneys, striated muscle | Produce platelets | ||||||
| THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (aka THYROTROPIN) | TSH | Anterior pituitary | ▲ Thyroid gland secretion of T4 and T3 | |||||
| THYROTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE | TRH | Hypothalamus | ▲ Releases TSH ▲ Stimulates PRL release | |||||
S T E R O I D S | INFORMATION ON STEROIDS
| |||||||
| Gluco-corticoid | CORTISOL | Adrenal cortex | Anti-inflammatory / Immunosuppressive ▲ Stimulate gluconeogenesis | |||||
| Mineralo-corticoid | ALDOSTERONE | Adrenal cortex | Increase blood volume (reabsorbs sodium in kidneys) Potassium and H+ secretion in kidney | |||||
S E X S T E R O I D S | A n d r o g e n s
| TESTOSTERONE | Testes | Libido/ Anabolic (Energy building):▲ muscle mass/strength , bone density, growth | ||||
| DEHYDRO-EPIANDROSTERONE | DHEA | Testes, ovaries, kidneys | Virilization, anabolic | |||||
| ANDROSTENEDIONE | ANDRO | Adrenal glands, gonads | Substrate for Estrogen | |||||
| DIHYDRO-TESTOSTERONE | DHT | Multiple | ||||||
S T E R O I D S | S E X S T E R O I D S | E s t r o g e n s
| ESTRADIOL | E2 | Ovaries, testes | Females: Structural:Maintain blood vessels/skin Protein synthesis:Production of hepatic binding proteins Coagulation:▲ Circulating levels Fats:▲ HDL, TGs ▲ LDL, fat deposition Fluid balance:▲ Salt (Na) Hormones:▲ GH, CORTISOL, SHBG GI tract:▲ Bowel motility Melanin:▲ Pheomelanin Cancer:Promotes hormone-sensitive cancers LUNG FUNCTION:▲ Supports alveoli. Males: | ||
| ESTRONE | E1 | Ovaries | ||||||
S E X S T E R O I D S | ESTRIOL | E3 | Placenta | |||||
P r o g e s t a g e n s | PROGESTERONE | Ovaries, pregnant placenta, Adrenal glands | Support pregnancy:Convert Other:▲ Epidermal growth | |||||
| PREGNENOLONE | ||||||||
| Sterols | CALCITRIOL (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3) | Skin, proximal tubule of kidneys | Active form of vitamin D ▲ Calcium and phosphate absorption from GI tract and kidneys | |||||
| CALCIDIOL(25-hydroxyvitamin D3) | Skin, proximal tubule of kidneys | Inactive form of vitamin D | ||||||