DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) - The Mother Hormone

"Fountain of Youth?"
- The most abundant hormone in the body and the second most protective (after PROGESTERONE)
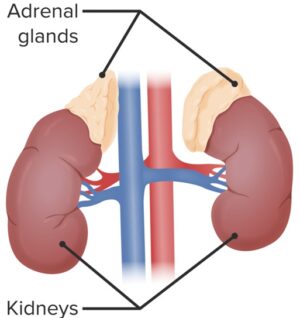
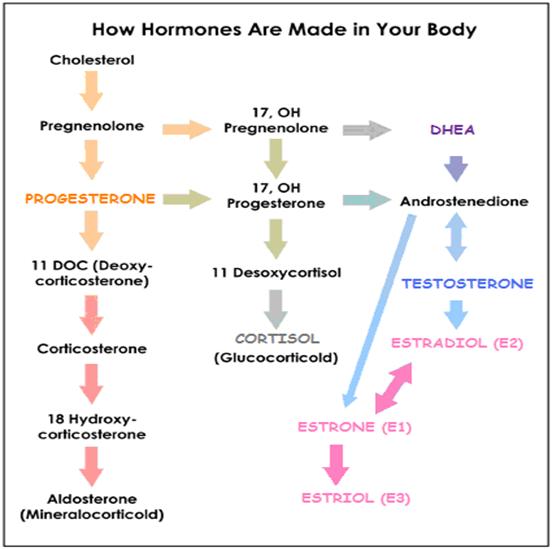
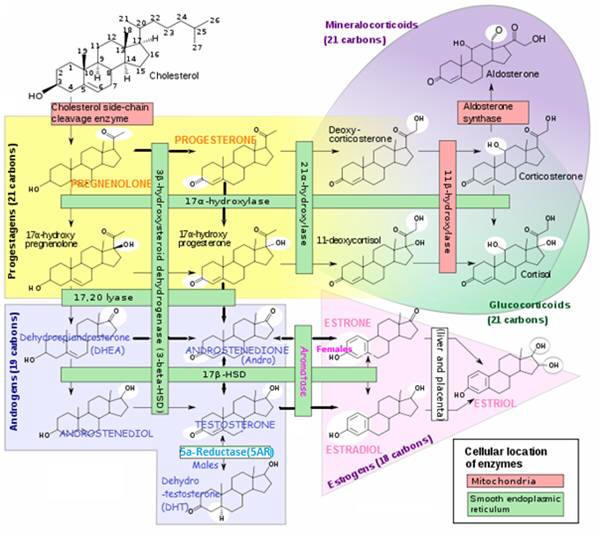
- Derived from cholesterol and secreted by the adrenal glands (atop the kidneys)
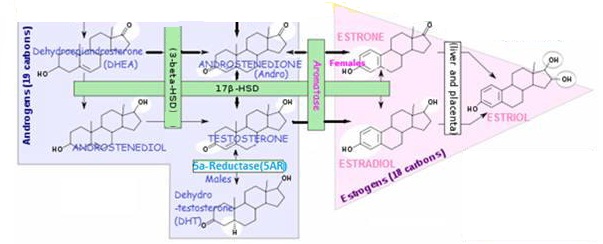
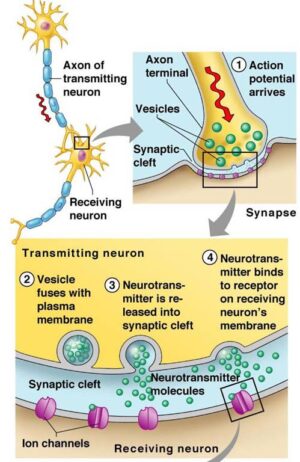
- Taken up by the brain, liver, kidneys and other tissues and converted to other biologically active steroid hormones, depending on the tissue.
- Precursor to estrogens (such as ESTRADIOL, ESTRIOL) and androgens (such as TESTOSTERONE)
- When supplemented – provides well-being, stamina, balanced mood, and fights depression and anxiety.
- Lowers INSULIN resistance / improves INSULIN sensitivity – Linked to decreases in visceral and subcutaneous fat areas
- Boosts immune function
- Helps in anti-aging – improves cognitive function in the elderly
- Fights chronic inflammation – strongly inhibits cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), which has a crucial mediatory role in the immune response
- DHEA levels fall drastically between the ages of 20 and 40
- Used by athletes to increase muscle density
- Involved in bone formation – stimulates activity of osteoblasts, bone-forming cells that secrete an extracellular matrix
- Can affect nitric oxide (NO) production / blood flow
- It’s sulfate form is DHEA-S, metabolized from DHEA, and with greater stability than DHEA and so more indicative of adrenal function, since DHEA levels can fluctuate throughout the day
- Obesity
- Type II diabetes
- Osteoporosis
- Immune dysfunction / autoimmune disease
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular disease / High blood pressure
- Depression, cognitive dysfunction
- Low libido / erectile dysfunction
- Loss of well-being