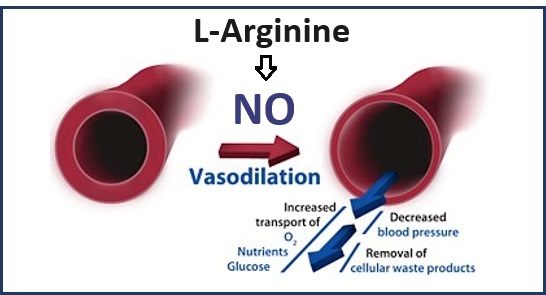
L-Arginine - Precursor to blood vessel dilator nitric oxide (NO)
What is L-arginine?
A semi-essential amino acid – your body struggles to supply enough, so you need to help out by obtaining it from diet
The many health benefits of L-arginine
Most of the health benefits of L-arginine are related to its being a precursor to NITRIC OXIDE (NO) in your body
NITRIC OXIDE – Blood vessel dilator
Cardiovascular benefits of L-arginine
Numerous studies show that L-arginine helps endothelial cells lining blood vessels to produce enough NO to promote blood vessel dilation and blood flow – and reduces plaque formation and risk of CVD. Here are links to just a few of these studies.
Involved in endothelial cell function to produce NO
Blood vessels synthesize NO via the enzyme endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), which converts L-arginine in the presence of oxygen to l-citrulline and NO. L-arginine is the only known nutritional substrate in your blood vessel lining available to endothelial cells (cells lining the inside of blood vessels) for NO production. NO signaling declines as a normal part of aging.
- Maintains optimal blood pressure
- Reduces coronary artery disease risk
- Treats heart failure
- Aids better recovery from MI
- Aids better recovery after coronary bypass surgery
- Reduces hypercholesterolemia
- Prevents atherosclerosis
- Beneficial in myocardial ischemia
- L-Arginine promotes angiogenesis in the chronically hypoxic lung
- Improves exercise capacity after heart transplant
- Appears to counteract hypertensive risk of oral contraceptives
Atherosclerosis treatment
Gerasimos Siasos, Dimitris Tousoulis, Charalambos Antoniades, Elli Stefanadi, Christodoulos Stefanadis. L-Arginine, the substrate for NO synthesis: an alternative treatment for premature atherosclerosis? Int J Cardiol. 2007 Apr 4;116(3):300-8. Epub 2006 Jul 24. PMID: 16860889
Sexual dysfunction / satisfaction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) / Good sexual function in men and women – increased microcirculation in genital tissues results in stronger erections and better sexual responsiveness.
- For men, an erection requires an unimpaired blood supply to the penis – leading medications for ED (E.g. Sildenafil (Viagra), vardenafil (Levitra) and tadalafil (Cialis)) reverse ED by increasing NO. However, supplemental arginine can increase NO, without the potentially dangerous side-effects (E.g. heart disease, stroke, sterility) of these medications.
L-arginine and pycnogenol significantly improved sexual function in men with ED;
6 g of L-arginine + 6 mg of yohimbine successfully treated men with ED.
.For women, estrogen is critical for maintaining vaginal and clitoral blood flow and vaginal transudate production (created by vasocongestion as vaginal area swells due to increased blood flow) attributed mostly to its regulation of NO signaling – both by increased mRNA transcription and protein synthesis, and also non-genomic mechanisms.
Affects genital blood flow to vagina and clitoris during sexual intercourse
- L. Arginine supplementation can improve sexual arousal in older women with declining estrogen by increasing NO production
Exercise tolerance
Helps body dispose of exercise-induced waste products: ammonia and lactate – seemingly by enhancing the L-arginine-nitric oxide (NO) pathway, also the ongoing repair/and replacement of damaged cells constantly releases nitrogen, which combines with hydrogen to form ammonia.
A Schaefer, F Piquard, B Geny, S Doutreleau, E Lampert, B Mettauer, J Lonsdorfer. L-arginine reduces exercise-induced increase in plasma lactate and ammonia. Int J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;23(6):403-7. PMID: 12215958
Building block of protein/ helps body’s production of amino acids:
- Creatine – important for muscle energy and nervous system function.
- L-proline – important for collagen synthesis and wound healing.
- L-glutamate – an excitatory neurotransmitter, essential for brain function, especially in left hemisphere (logic/reasoning, language, computational skills, learning and memory).
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) / Intermittent claudication
Hormonal health
Has endocrine effects – promotes release of human growth hormone (hGH) and prolactin.
Brain / neural health
L-Arginine increases brain function – subsequent to its effect in increasing L-glutamate, creatine and L-Proline, increased L-glutamate improves memory and learning capacity and increases in creatine and L-proline are important for CNS function.
L-Arginine has potent neuroprotective properties – and may be a therapeutic tool in ALS and neuropathy
Lee J, Ryu H, Kowall NW. Motor neuronal protection by L-arginine prolongs survival of mutant SOD1 (G93A) ALS mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Jul 10;384(4):524-9. PubMed
L-Arginine has a positive role in Alzheimer’s disease
Yi J, Horky LL, Friedlich AL, Shi Y, Rogers JT, Huang X. L-arginine and Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2009;2(3):211-38. Epub 2008 Oct 2. PubMed
Digestive health
L-Arginine accelerates healing of gastric ulcers – 32.5 – 300 mg/kg/day in a dose dependent manner
Brzozowski T et al, J. Healing of Chronic Gastric Ulcerations by L-Arginine (Role of Nitric Oxide, Prostaglandins, Gastrin and Polyamines) Digestion 1995;56:463-471 Link
NO improves trafficking of nutrients and may increase your ability to produce stomach acid
Other health issues aided by arginine
- Retard aging -combined with reduced calories
- Immune system support
- Reduce risk of INSULIN resistance (IR), Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity
- Asthma /Respiratory Health
- Liver / Kidney support
- Nerve regeneration
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
- Prevent Bone Loss
- Gastric Ulcers
- Cancer / Cachexia
- Decrease congestive heart failure symptoms
- Protect brain in heat stroke
L-arginine production in body
A healthy adult produces 2-4 g L-arginine / day – depending on:
- Age – production declines with age, beginning even in 30’s. Women tend to keep up production better than men;
- Not eating enough protein or adequately digesting it (requires protease enzymes)
- Lack of antioxidants compared to free radicals
- Your particular genetics require more L-arginine
Foods highest in L-arginine
- Seeds (sesame, pumpkin, sunflower)
- Seaweed (especially spirulina)
- Nuts (walnuts, almonds, peanuts)
- Coconut
- Eggs
- Whey
Taking an L-Arginine supplement
L-Arginine needs to be constantly replenished and should therefore be supplemented in a sustained-release form – since L-Arginine is the precursor to the desired, but short-lived gas nitric oxide (NO) and the body metabolizes arginine very quickly
- Typically recommended dose is 1000 mg of a sustained-release formula from natural sources
- Avoid artificial fillers or additives (E.g. magnesium stearate, stearic acid)
Vitamin C shown to enhance eNOS activity – NO is produced by endothelial cells (ECs) from the amino acid L-arginine, and activated by the enzyme eNOS (when “coupled” with cofactor BH4)
Huang A,Vita JA,Venema RC,Keaney JF Jr.Ascorbic acid enhances endothelial nitric-oxide synthase activity by increasing intracellular tetrahydrobiopterin. J Biol Chem.2000 Jun 9;275(23):17399-406.
Counterindications
Do not take L-Arginine if you have any kind of active herpes infection. E.g Herpes simplex, as in oral or genital herpes, or herpes zoster, as in shingles. If you have this type of infection, you should supplement with the amino acid lysine until the lesions are resolved and avoid L-arginine supplements during the infectious phase.