Fats / Oils - Healthy or not?

A fat lot of good!
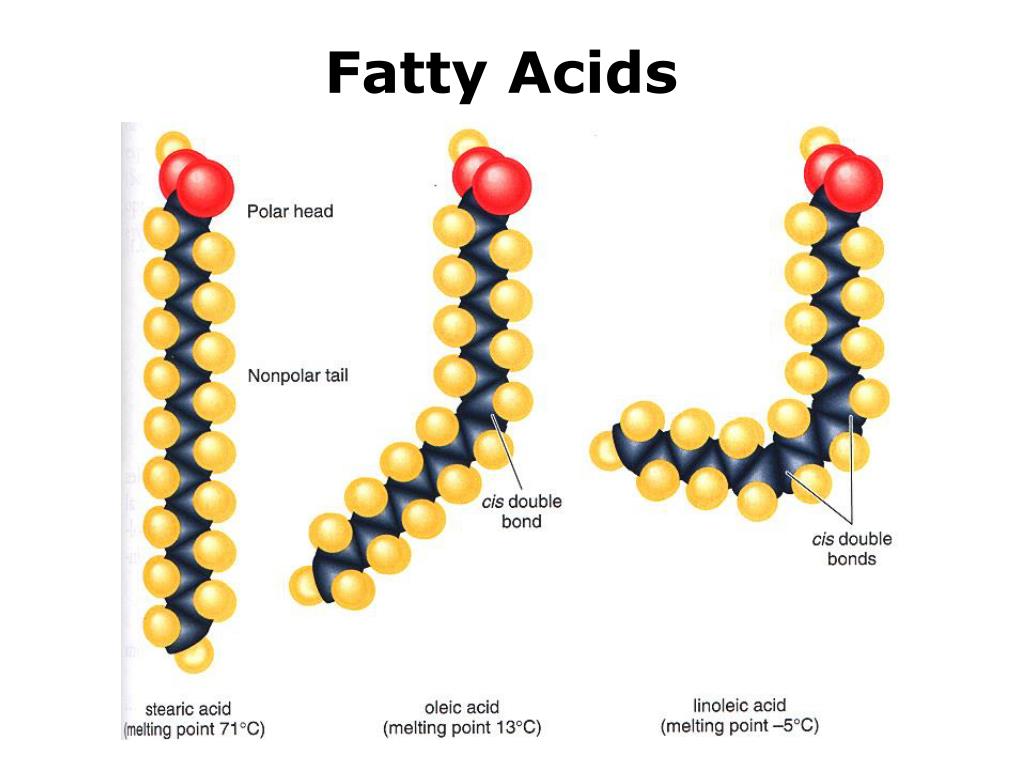
Solid fats and liquid oils contain fatty and / or waxy LIPID MOLECULES, each playing essential roles in our health.
Non-soluble in water, food lipid molecules predominate in fried foods, animal & fish fats, dairy products (such as cream, butter, and cheese), and vegetable, nut, & seed fats or oils.
Not counting water, 50% of our body is fat!
Lipids provide building blocks for the body’s cells, help regulate hormones, transmit nerve impulses, cushion organs, and store energy in the form of body fat.
Food fats and oils come in several forms:
Free fatty acids (FFAs)
- Saturated (SFAs)
- Monounsaturated (MUFAs)
- Polyunsaturated (PUFAs) – mainly the essential fatty acids (EFAs) (omega-6 and omega-3) –
Triglycerides (TGs) (95% of food fats)
Our bodies can make SFAs and MUFAs from consumed carbohydrates and proteins.
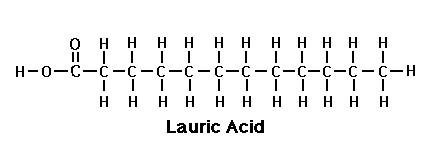
However, SFAs such as the medium-chain-length LAURIC ACID in coconut oil, and MUFAs such as OLEIC ACID in olive oil provide impressive health-protective benefits when consumed.
Our bodies CANNOT MAKE two sub-families of polyunsaturated fats called EFAs (Essential fatty acids) – i.e. They MUST be EATEN!
These are the Omega-3 and Omega-6 families of fatty acids, both crucial to our health, so of utmost importance that we include them in our diet.
TGs have a glycerol molecule joined to 3 fatty acids (usually at least one is a saturated fatty acid).
TGs, which have more than twice the energy of carbohydrates or protein, are the primary source of our cellular energy production. The digestive process splits the fatty acids from the TGs, but TGs can be reconstituted in the body to be stored in muscles and adipose tissue for later use.
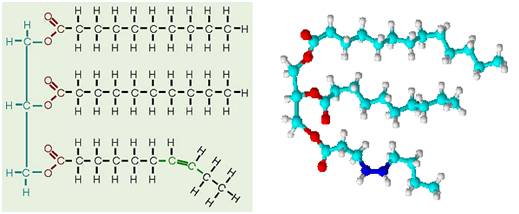
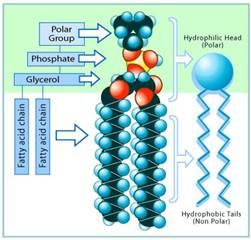
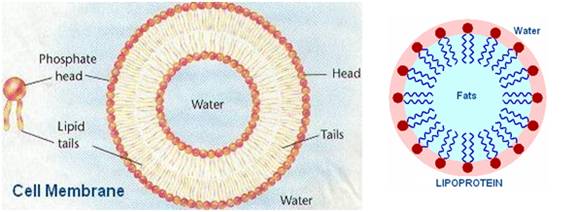
Phospholipids (PLs)
A glycerol molecule esterified to 2 fatty acids + a phosphate group.Used as structural components of cell and lipoprotein (fat transporter) membranes, utilizing their water-loving (hydrophilic) heads and water-hating (hydrophobic) tails. Can be synthesized by the body.
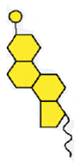
Esterified cholesterol (food form of cholesterol)
Much-maligned cholesterol is very much needed.
Yes – cholesterol can build up and cause a blockage in your arteries, but this is your body trying to save your life by providing a cholesterol-containing “patch” to prevent immediate death from bleeding out through a damaged / weakened arterial wall. It buys you some time to correct what is actually causing the damage.
Ischaemic CVD – Its real cause
Cholesterol is vital to your well-being.
Your most cholesterol-rich organ is your brain. Cholesterol provides permeability and integrity in cell membranes, and as a component of the myelin sheath around axons, it increases the rate of electrical nerve conduction. This insoluble, waxy sterol is the raw material for adrenal cortex production of the “mother hormone” DHEA, which is the precursor for the steroid hormones, including the sex hormones (estrogens, androgens (e.g. TESTOSTERONE) and progestagens), CORTISOL (Stress hormone), and ALDOSTERONE (controls water-levels and electrolytes). Cholesterol is also used to make vitamin D and fat-dissolving bile acids.
Your body makes 80% of its very necessary cholesterol.
Only 20% comes from food (only contained in animal sources). If you don’t eat enough, your liver and intestines will have to work harder to make up the deficit – cholesterol is that important!
Fat-soluble vitamins
Beware of harmful (altered, damaged) fats
Oxygen, encouraged by high heat and especially light, will damage fatty acids in seed, nut and bean oils making them toxic.
Unfortunately, the high heat used during the deodorization step not only removes the health-necessary essential fats, it also introduces toxic, unnatural trans fats (tFAs), hydrogenated fat, and lipid peroxides into the oils.
These toxic fats are now well-known to cause cellular dysfunction in the body, and are very much involved in today’s familiar health problems.
Health benefits of fats
- Cell membranes are comprised of fatty acids (in phospholipid form) and cholesterol
- Cholesterol is the raw material for all the body’s steroid hormones;
- Essential fats DGLA, AA, EPA, DHA convert to eicosanoids (hormone-like molecules) in a cell’s “neighborhood” (E.g. prostaglandins, leukotrienes), produced in the cell membrane for normal homeostasis and as the first response to trauma to mediate inflammation, fight infection, repair damage and control pain in the cell’s immediate vicinity.
- Unsaturated fatty acids keep cell walls fluid – controlling “traffic” in and out of cell;
- Lipids combine with protein to form lipoproteins – the transport vehicles for fats in the body.
- Lipids needed for nerve conduction and healthy brain function;
- Fat provides insulation and protective cushioning under skin and around organs – such as the heart;
- Eating fats as part of a meal slows down carbohydrate absorption – controlling blood sugar levels and staving off hunger for an extended time.
- All fats can carry the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. (These vitamins are themselves catalysts for the body’s processing of the water-soluble B and C vitamins).
- Fats are necessary for the conversion of carotene to vitamin A and for mineral absorption.
5 things to do for healthy fat consumption
Some dietary fats are harmful, some are absolutely essential. We need the right fats in the right quantities and proportions, in a natural, unaltered form.
(1) Consume polyunsaturated “Essential fats” omega-6 and omega-3 in balance
Most omega-6 fats promote an inflammatory / “call-to-action” effect. In contrast, ALL omega-3 fats counter the omega-6 effect with their anti-inflammatory / “back-to-normal” action.
Dietary essential fats (which your body cannot make), come from the small amounts found in legumes, grains, nuts, green vegetables, fish, olive oil and animal fat. The natural God-given diet found in native populations in temperate and tropical regions contains perfectly balanced amounts of omega-6 and omega-3 fats, and also includes the enzymes and minerals required to convert those EFAs into usable forms.
Today, we are suffering the health effects of a massive intake of omega-6 combined with a pitiful intake of omega-3.
Most farm animals and birds no longer go outside to eat grass or bugs to increase their omega-3 intake, and since early 1900’s, the Western world has been consuming omega-6-rich vegetable oils (abundant in grocery store bottles, margarines and processed foods). Even worse, these high-temp-processed oils are toxic!
(2) Consume healthy saturated and monounsaturated fats
Although these can be made by your body, certain foods contain health-enhancing, short/medium-chain saturated fatty acids (e.g. coconut oil, palm oil and butter). Also olive oil has health-beneficial properties.
(3) Moderate / balance saturated fat with "healing" essential fats
Too much saturated fat without sufficient “healing” omega-3 and omega-6 fats can be harmful. Traditional hard fats are used for “body fuel”, cell membranes, and fat deposits – but when we consume more than we use, they cause us to gain weight – both by altering INSULIN function and by storing the excess. They also make the blood “sticky” and overwhelm and interfere with the benefits of the healing essential fats.
Unless we are “working it off”, we need to balance our intake of saturated fat with the consumption of omega-3 and omega-6. This done, we may fully enjoy moderate amounts of organic, grass-fed whole milk, cream, butter and animal marbling fat (not the outer covering fat) – without any feelings of guilt or concern.

Ensure good daily source of anti-inflammatory / “back-to-normal” omega-3 fats – E.g. Wild salmon oil, krill oil, quality fish, flaxseeds or fresh flax oil.
(4) Eliminate unnatural, altered / toxic fats
Solvent-extracted / Refined vs. Expeller-pressed oils
Solvent-extracted / Refined, polyunsaturated grocery store oils and processed products containing these refined oils contain altered / toxic fats and should be considered inedible.
Typically found in transparent bottles on supermarket shelves, these high-temperature processed oils (solvent-extracted, refined, bleached and deodorizedto extend shelf-life) have lost much of their nutrient value, contain altered / toxic fatty acids (such as trans fats and lipid peroxides), and have been, and continue to be degraded by light. They are usually made from the cheapest, most inferior, intensely pesticide-sprayed plants. To detract from their poor nutritional, toxic condition, advertising labels focus on positive aspects, such as “Low in saturates” or “Cholesterol-free”, both naturally inherent in any seed oils containing predominatelypolyunsaturated fats.
Examples of solvent-extracted /refined oils to avoid (often used in processed products):
Corn, soybean, sesame, canola, sunflower and cottonseed oils. An added benefit of not eating processed foods containing these refined oils . . . You also remove many “empty” carbs (including sugar) from your diet.
In contrast, unrefined, low-heat, expeller-pressed oils, properly stored in dark bottles without air, are excellent for moderate dietary use.
This is also true of products that contain these oils, provided they have not been heated to higher than 320 °F.
Which oils to use for frying?
For frying and cooking, use avocado oil, expeller-pressed coconut oil, ghee, or palm oil and keep temp under 350ºF. These higher smoke-point oils/fats are less likely to produce toxic fats when exposed to high heat than lower smoke-point oils. Butter can also be used safely for low-heat sauteeing and baking (i.e. don’t let it burn).
Do NOT use olive oil for frying. From an unadulterated source, it is excellent for cold recipes, such as salad dressings. However, the MUFAs in the oil will be damaged by frying temps.
(5) Don't buy into the nonsense about cholesterol!
Eating moderate amounts of cholesterol will save your body the trouble of making this all-important lipid.
Cholesterol is being seriously maligned today (mainly for the purpose of selling cholesterol-lowering statin drugs).