Cholesterol - "Our Hero!" - Much maligned cholesterol is not responsible for heart disease

Misguided hypotheses continue, but it has been well established that:
- Dietary saturated fat has LITTLE EFFECT on blood cholesterol levels
- High blood cholesterol levels have NOT BEEN PROVEN to CAUSE heart disease.
Cholesterol and saturated fat – NOT the “Darth Vader” of ischaemic heart disease

Present in ALL our cells, cholesterol has important responsibilites
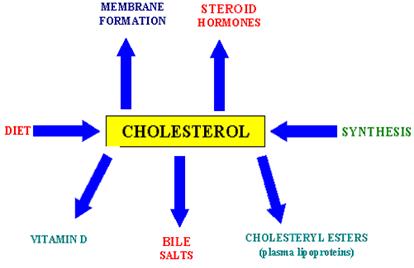
Regulates cell membrane integrity
Makes membranes less permeable to most biological molecules


Cholesterol can fit into spaces between phospholipids and inhibit the diffusion of water-soluble molecules across the membrane. Cholesterol is moved between cell membranes and the blood depending on which dietary fats you are eating. Consumed polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) replace saturated fat in the membrane, causing the membranes to become less dense. In order to maintain their watertight protection and structural integrity, cholesterol is either synthesized by the cell or moved from the blood into the membranes, temporarily lowering serum cholesterol levels. Conversely, cholesterol is removed from the cell membrane into the blood (raising serum cholesterol levels) when dietary saturated fat provides the required integrity.
Membrane cholesterol content varies with particular tissue membrane function
- Membranes with high cholesterol-to-phospholipid ratios function as a protective barrier – have high stability and low permeability.
Nerve Function Protection – The highest concentration of cholesterol in the body is found in the critical brain and nervous system. Every second molecule in the myelin sheath surrounding and insulating nerves is cholesterol, where it affects proper nerve conduction and normal brain function, by providing structural balance to their high polyunsaturated content.
- Organelle membranes inside cells have low cholesterol ratios – making them fluid and permeable; e.g. mitochondria.
- Intestinal wall Integrity – Cholesterol’s role maintaining the intestinal wall integrity prevents leaky gut syndrome and other intestinal problems.
Precursor to sex hormones

DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone), the “mother” steroid hormone. Synthesized from cholesterol by the adrenal cortex. DHEA is the precursor for estrogen, TESTOSTERONE and PROGESTERONE (to prevent miscarriage in pregnancy, the placenta produces cholesterol, from which it makes PROGESTERONE); cholesterol stored in the ovaries and testes is converted to steroid hormones.
DHEA is also called the “anti-aging” hormone. Good evidence supports that increasing DHEA blood levels decreases risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, senility, Alzheimer’s disease, and premature death. People with a positive outlook actually create a self-sustaining cycle of DHEA production!
Raw material for vitamin D
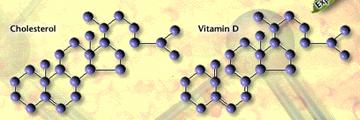
Cholesterol provides the raw material to make vitamin D.
- D regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism to support bone health.
- Vitamin D is also required for nerve function, growth, mineral metabolism, muscles, INSULIN production, reproduction, and the immune system.
Raw material for adrenal stress hormones
The more stress we are under, the more cholesterol our body makes.
This because the CORTICOSTEROID stress hormones are synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal cortex:
- CORTISOL – Provides suitable response to stress, also controls carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism and is a potent anti-inflammatory agent that protects against heart disease;
- CORTISONE – Promotes glucose synthesis for fight or flight response to stress. Suppresses inflammation.
- ALDOSTERONE – Controls electrolyte and water levels, mainly by promoting sodium retention in the kidney.
Raw material for bile salts
Required for fat digestion and the metabolism of the fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K
Cholesterol is oxidized by the liver into bile acids, which along with cholesterol are excreted from the liver into bile and stored in the gallbladder. Fat consumption causes bile to be “squirted†from the gallbladder into the upper small intestine (duodenum) to digest fat. Approximately 95% of bile acids are reabsorbed from the intestines, and the remainder lost in the feces.

Brain's SEROTONIN receptors need cholesterol to function properly
Dozens of studies link cholesterol deficiency to:
- Aggressive emotions and actions [Annals, 1998, J. AMA, 1997]


- Depression / Suicide – Canadian researchers found that those in the lowest quarter of total cholesterol concentration had > 6 times the risk of committing suicide as those in the highest quarter. Epidemiology 2001 Mar;12:168-72
Cholesterol is transferred to tissues in lipoprotein carriers to repair damage caused by chronic inflammation
it is the repair “superglue” used to keep cell membranes from falling apart. E.g. when your arteries are damaged or lacking structural integrity due to insufficient dietary vitamin C.

Important for naturally breast-fed babies

Breast milk has 6 times more cholesterol than cow’s milk. Soy milk has none. Infants on low-cholesterol formulas have low cholesterol levels, even though their livers are working hard to produce the missing cholesterol;
Cholesterol and other lipids travel in water-soluble "suitcases" called lipoproteins
~ 1 Tbsp. of cholesterol is carried and circulated in our blood in water-soluble “suitcases”, called lipoproteins.
Tiny protein-covered packages that allow fatty cholesterol to travel in watery blood. A typical 150# body has a total cholesterol content of a little over an ounce (35g)
There are five main different types of lipoproteins that change from one form to another:
- Chylomicrons. Packaged in the digestive system, they are very large particles that mainly carry triglycerides (TGs) from food.
- Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). Made by the liver; also carry TGs to tissues; Body’s cells extract fatty acids from VLDLs, changing them into intermediate density lipoproteins, and with further extraction, into LDL particles.
- Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). Begin as VLDLs, but as their fatty acids are extracted, some are removed rapidly by the liver, and some are changed into LDLs.
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Carry mainly cholesterol, since most of their previously-carried triglycerides have been extracted. LDL delivers cholesterol TO tissues. Called “bad cholesterol” for no valid reason. BTW, the standard blood cholesterol test does not measure LDL – it only estimates it.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL). So-called “good cholesterol”, removes cholesterol FROM circulation and artery walls and returns it to the liver for excretion.
References
Annals of Internal Medicine 1998;128(6):478-487;
The Journal of the American Medical Association 1997;278:313-321;

















