EFA Functions
Cell membrane integrity depends on EFAs
You are basically a bunch of fat-encased cells!
The proper functioning of each CELL, which makes up YOU, determines your overall health
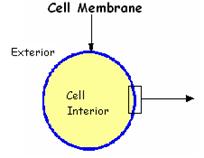
Each of your cells is surrounded by a FATTY MEMBRANE separating the cell’s internal workings from its environment . The proper consistency of this membrane is critical to the life of the cell determining what goes in and out of the cell.

EFAs determine the membrane integrity of the cell organelles. E.g. the mitochondria for energy production, the nucleus containing your DNA chromosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum for protein synthesis.
EFAs in phospholipids form the single-layer envelope surrounding lipoproteins, which transport fats in the blood:
- Chylomicrons. Transport food fats from the intestines;
- VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL and Lp(a) cholesterol. Transporting triglycerides, cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K.
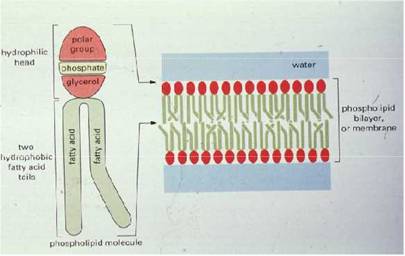
Phospholipid bilayer cell membrane.
The cellular membrane consists of a double layer of phospholipids (each containing 2 fatty acids, usually one SFA plus one unsaturated fatty acid, joined to a water-loving head), with their water-hating tails intertwining with the tails of phospholipids from the other layer.
EFAs improve the ability of the blood to transport oxygen and nutrients to the cells
EFAs make red blood cells (erythroycytes) more flexible. Such that they fit more easily through capillaries, and thus more effectively supply nutrients and oxygen to tissues and cells.
Membrane flexibility, fluidity and permeability is especially dependent on the presence of Omega-3 DHA

EFAs provide “oiliness”. Carrying slight negative charges, EFAs repel one another, keeping them apart. All PUFAs tend to disperse over surfaces, and move apart helping to provide fluidity, flexibility and permeability characteristics of the membrane. In contrast, long-chain SFAs provide RIGIDITY to the cell membrane. SFAs also serve to keep PUFAs separated, so that they are unable to react with each other.
Omega-3 DHA is a major structural component of brain cell membranes. With its 6 double-carbon bonds it is the most reactive, and the most “curled-up”(space-filling) omega-3 fatty acid
Cholesterol is used to control membrane fluidity. The body compensates for the fatty acids you eat, by adding or removing “stiffening” CHOLESTEROL to or from the membrane. Eating too many PUFAs would cause the membrane to become too PERMEABLE, so cholesterol is brought in from the blood. Conversely, too many dietary SFAs will cause cholesterol to be put back into the blood, causing your blood cholesterol to rise. The rise and fall of cholesterol in these cases are compensatory actions, not necessarily bad or good.
- Cholesterol is used by the body to “stiffen” the membranes after consumption of PUFAs , and removed after SFA consumption, explaining why blood cholesterol drops and rises in response to our diet.
EFAs help anchor the membrane protein channels and pumps
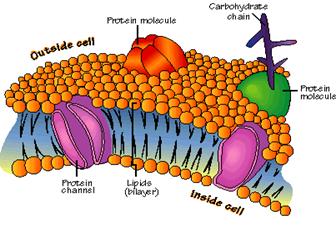
Proteins in the cell membranes significantly affect what enters and exits the cell. EFA electrostatic forces provided by the electron clouds at their double carbon bonds combine with these protein molecules.
Cellular Nutrition / Waste Transport. A deficiency of the “curly” EFAs will cause nutrition and waste to be unable to go in and out of the cell as required, leading to gradual deterioration of cells and tissues, ultimately resulting in death.
– Caffeine, alcohol, and smoking use up stores of DHA