Himalayan or sea salt - GOOD salt is NOT your enemy

Do not consume regular table salt
Processed table salt is an unnatural chemical form of salt. Excessive drying heat (>1200ºF) alters natural chemical structure of the salt. “Chemically cleaned” table salt is 97.5% sodium chloride (devoid of trace minerals) and the other 2.5% is iodine and chemicals. E.g moisture absorbents, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, and aluminum hydroxide. (Aluminum deposits into your brain – a potential cause of Alzheimer’s disease).
Low sodium diet MAY increase heart attack risk
“Researchers studied the relationship between a low-sodium diet and cardiovascular mortality. Nearly 3,000 hypertensive subjects were studied. The result of this study was that there was a 430% increase in myocardial infarction (heart attack) in the group with the lowest salt intake versus the group with the highest salt intake”. (Alderman, 1995) – David Brownstein, M.D. “Salt your way to Health”
Review study of healthy people on low-sodium diets found LDL increased 4.6% and triglycerides 5.9%; (Jurgens, 2003)
Another review reported cholesterol increased 2.5% and triglycerides 7% (Graudel et al, 2011)
Both studies found that salt restriction produced only minor reductions in blood pressure (on average), with a somewhat stronger effect in those with high blood pressure.
Too much salt IS AS BAD AS too little
Average person consumes an excessive daily 4-6 grams, some as much as 10 grams. Processed table salt is found in almost all processed foods and also added at the table.
Excess Salt depletes body’s cellular water. Water molecules must surround the sodium chloride to break them up into sodium and chloride ions in order to help neutralize them. This takes water from your cells. Your body uses 23 times the amount of cell water to neutralize every gram of sodium chloride that your body cannot get rid of. This causes excess fluid in your body tissue, which can contribute to cellulite, rheumatism, arthritis, gout, and kidney / gall bladder stones.
Unrefined Himalayan or Celtic sea salt
Supplies precious TRACE MINERALS in natural form

When consumed in moderation, good sea or Himalayan salt provides trace minerals – which are missing in many chronic disorders, including cardiovascular disease.
Ingest a daily minimum of 1/2 tsp. unrefined, Himalayan or Celtic sea salt (Both good choices, with Celtic containing a few more trace minerals than Himalayan salt).
Properties of unrefined, Himalayan and Celtic Sea Salts
- Contaminant-free
- Has perfect crystalline structure (as seen under an electron microscope) – the interconnectedness of each molecule provides a harmonious vibrational energy component of the 84 elements present. The picture on the left (below) shows refined sea-salt. The natural Himalayan salt shown on the right clearly has a more structured crystalline form.
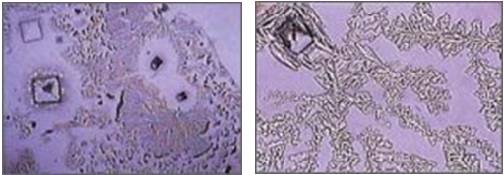
- Contains almost all of the estimated 85 elements needed by the body – all in colloidal form (small enough for your cells to readily absorb them).
Spectral analysis of Himalayan salt
Health benefits of natural, unrefined salt
- Regulates water content throughout the body.
- Promotes healthy pH balance in body’s cells – particularly brain cells.
- Promotes blood sugar balance and help reduce the signs of aging.
- Assists in the generation of hydroelectric energy in body’s cells.
- Absorbs food particles through your intestinal tract.
- Supports respiratory health.
- Promotes sinus health.
- Prevents muscle cramps.
- Promotes bone strength.
- Regulates sleep – it naturally promotes sleep.
- Supports your libido.
- Promotes vascular health.
- Essential for the regulation of blood pressure – in conjunction with water.
Unrefined salt also has health benefits when applied to the body – use a 1% solution (the same concentration as found in tears and amniotic fluid). For comparison, the sea is a 3½% concentration.
- Salt Bath – Use 2¼ pounds in a normal sized tub. Body absorbs minerals through the skin. Also rejuvenates your skin.
- Apply a 1% solution to rashes, insect bites – amazing, simple, effective and cheap remedy; also rejuvenates the skin.
Spectral analysis of Himalayan pink salt
This list shows the amounts of all the trace minerals, electrolytes, and elements contained in Himalayan salt
You gotta love their names! – How about Technetium, Gadolinium and tantalum!?
- Hydrogen H 1 0.30 g/kg DIN
- Lithium Li 3 0.40 g/kg AAS
- Beryllium Be 4 <0.01 ppm AAS
- Boron B 5 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Carbon C 6 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Nitrogen N 7 0.024 ppm ICG
- Oxygen O 8 1.20 g/kg DIN
- Fluoride F- 9 <0.1 g/kg Potentiometer
- Sodium Na+ 11 382.61 g/kg FSM
- Magnesium Mg 12 0. 16 g/kg AAS
- Aluminum Al 13 0.661 ppm AAS
- Silicon Si 14 <0.1 g/kgAAS
- Phosphorus P 15 <0.10 ppm ICG
- Sulfur S 16 12.4 g/kg TXRF
- Chloride Cl- 17 590.93 g/kg Gravimetrie
- Potassium K+ 19 3.5 g/kgFSM
- Calcium Ca 20 4.05 g/kgTitration
- Scandium Sc 21<0.0001 ppm FSK
- Titanium Ti 22<0.001 ppm FSK
- Vanadium V 23 0.06 ppm AAS
- Chromium Cr 24 0.05 ppm AAS
- Manganese Mn 25 0.27 ppm> AAS
- Iron Fe 26 38.9 ppm> AAS
- Cobalt Co 27 0.60 ppmAAS
- Nickel Ni 28 0.13 ppm AAS
- Copper Cu 29 0.56 ppm AAS
- Zinc Zn 30 2.38 ppm AAS
- Gallium Ga 31 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Germanium Ge 32 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Arsenic As 33 <0.01 ppm AAS
- Selenium Se 34 0.05 ppm AAS
- Bromine Br 35 2.1 ppm TXRF
- Rubidium Rb 37 0.04 ppm AAS
- Strontium Sr 38 0.014 g/kg AAS
- Ytterbium Y 39 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Zirconium Zr 40 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Niobium Nb 41 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Molybdenum Mo 42 0.01 ppm AAS
- Technetium Tc 43 unstable artificial isotope – not included
- Ruthenium Ru 44<0.001
- Rhodium Rh 45 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Palladium Pd 46 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Silver Ag 47 0.031 ppmAAS
- Cadmium Cd 48 <0.01 ppm AAS
- Indium In 49 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Tin Sn 50 <0.01 ppm AAS
- Antimony Sb 51<0.01 ppm AAS
- Tellurium Te 52<0.001 ppm FSK
- Iodine I 53 <0.1 g/kg potent iometrie
- Cesium Cs 55<0.001ppm FSK
- Barium Ba 56 1.96 ppm AAS/TXR
- Lanthan La 57 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Cerium Ce 58 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Praseodynium Pr 59<0.001 ppmFSK
- Neodymium Nd 60 <0.001 ppmFSK
- Promethium Pm 61 unstable artificial isotope – not included
- Samarium Sm 62 <0.001 ppmFSK
- Europium Eu 63 <3.0 ppm TXRF
- Gadolinium Gd 64 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Terbium Tb 65<0.001 ppm FSK
- Dysprosium Dy 66 <4.0 ppm TXRF
- Holmium Ho 67 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Erbium Er 68 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Thulium Tm 69 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Ytterbium Yb 70 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Lutetium Lu 71 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Hafnium Hf 72 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Tantalum Ta 73 1.1 ppm TXRF
- Wolfram W 74<0.001 ppm FSK
- Rhenium Re 75 <2.5 ppm TXRF
- Osmium Os 76<0.001 ppm FSK
- Iridium Ir 77<2.0 ppmTXRF
- Platinum Pt 78 0.47 ppm TXRF
- Gold Au 79 <1.0 ppm TXRF
- Mercury Hg 80<0.03 ppm AAS
- Thallium Ti 81 0.06 ppm AAS
- Lead Pb 82 0.10 ppm AAS
- Bismuth Bi 83<0.10 ppm AAS
- Polonium Po 84<0.001 ppm FSK
- Astat At 85 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Francium Fr 87 <1.0 ppmTXRF
- Radium Ra 88 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Actinium Ac 89<0.001 ppm FSK
- Thorium Th 90 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Protactinium Pa 91 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Uranium U 92 <0.001 ppmFSK
- Neptunium Np 93 <0.001 ppm FSK
- Plutonium Pu 94<0.001 ppm FSK
Additional Combined Elements
- Water H2O 1.5 g/kg DIN
- Ammonium NH4+ 0.010 ppm Photometrie
- Nitrate NO3- 0.09 ppm Photometrie
- Phosphate PO4 3-<0.10 ppm ICG
- Hydrogencarbonate HCO3- <1.0 g/kg Titration
The sodium chloride content is 97.41% and meets the worldwide necessary standards for table salt.
Legend:
g/kg -Grams per kilogram
DIN -German Standards Institute
ICG -Ionchromatography
AAS -Atom absorbtion spectrometry
TXRF -Total reflection – X-Ray – Floresence-Spectometry
ppm -Parts per million
FSM -Flamespectrometry
FSK -Frequency Spectroscope
References
Alderman M (1995) Low urinary sodium is associated with greater risk of myocardial infarction among treated hypertensive men. Hypertension; 25:1144-1152
Graudal NA, Hubeck-Graudal T, Jurgens G. (2011 Nov 9) Effects of low sodium diet versus high sodium diet on blood pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterol, and triglyceride. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (11):CD004022. PubMed
Jurgens G1,Graudal NA. (2003) Effects of low sodium diet versus high sodium diet on blood pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterols, and triglyceride. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.(1):CD004022. PubMed