Vitamin C / Ascorbic acid (AA)💡 - "God's Medicine"

Vitamin C is also called ascorbic acid (AA) or ascorbate
“There are more than ten thousand published scientific papers that make it quite clear that there is not one body process (such as what goes on inside cells) and not one disease or syndrome (from the common cold to leprosy) that is not influenced directly or indirectly by vitamin C”
Drs. Cheraskin, Ringsdorf, and Sisley – “THE VITAMIN C CONNECTION”

Emphasized vitamin C attributes

- Needed daily. Can not be stored in the body long-term.
- Water soluble. E.g. vitamin C will remain in soup water.
- Required for collagen production in connective tissue throughout the body.
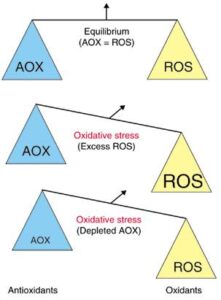
- Antioxidant. Biomolecules do not function properly when their electrons, have been “stolen” by oxidants in the body (these can be a consequence of toxins, microbial infection or just consequential to normal metabolic processes). If, present, antioxidants sacrifice their electrons to the electron-stealing oxidants to protect the biomolecules and so avert potential disease. As an antioxidant, AA has the ability to regenerate (chemical term is REDUCE) all significant oxidized antioxidants, being able to donate 2 electrons per molecule, rather than 1.
- Has the ability to penetrate all cells and tissues and can cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) to enter the brain.
- The adrenal glands have the highest concentration of vitamin C, which peaks under any type of stress, when vitamin C is mobilized from other body tissues.
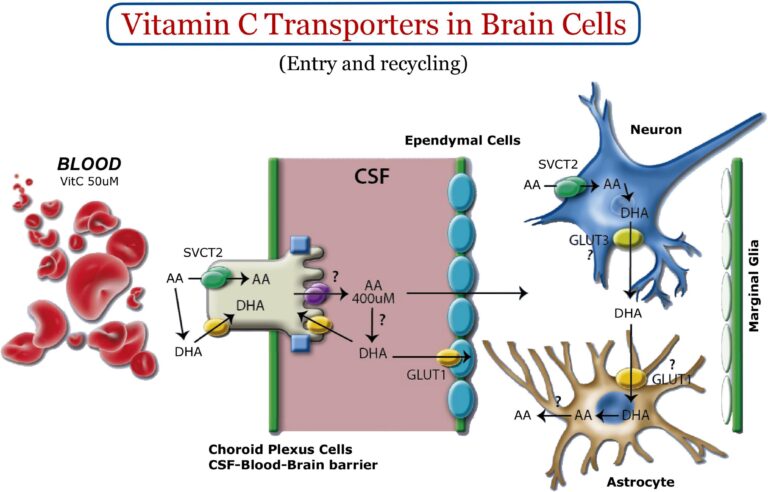
- The brain has a high priority for the body’s vitamin C, which is concentrated in the extracellular fluid around neurons 4-8 times higher than blood plasma. Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) has 400 μM, extracellular fluid around neurons 200-400μM and blood 50μM. The small molecular size of vitamin C’s oxidized form (DHAA) allows easy passage through the BBB. It is possibly converted to ascorbic acid (AA) in the CSF, which is oxidized to DHAA protecting neurons and converted back to AA by neural-supporting astrocytes.
- Excess, unabsorbed vitamin C is excreted from the body.In sweat and feces, but mainly in the urine. Having diarrhea is a good indicator that you have over-supplemented and can help determine your individual requirement.
- In plants, humans, all animals and fish. From the largest whale to the smallest amoeba; unlike most other animals, birds, fish, and plants, the human body cannot make vitamin C
Most creatures and plants synthesize their own Vitamin C – Man does Not
Functions of vitamin C (AA)
Major WATER-Soluble antioxidant
- In the body. Antioxidants sacrifice themselves on our body’s behalf. Antioxidants donate their electrons to oxidants (e.g. free radicals), which would otherwise steal them from and so damage parts of your body. Likewise in food, antioxidants protect it from decay. AA is an oxidant scavenger – oxidizing harmful reactive-oxygen-derived species (ROS). such as hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide and singlet oxygen; AA being a water-soluble antioxidant is significant because ~70% of the body is water. The brain is an easy target for oxidative damage and since antioxidant levels tend to diminish with age, it is not unexpected to find more brain related problems in the elderly, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- In Foods. AA, predominant in fresh foods, is easily oxidized to DHAA, which like AA also has antiascorbutic activity (i.e.fights scurvy) during processing, storage, preparation and cooking. DHAA is then either converted back to AA (by an enzymatic process involving the enzyme dehydro-ascorbate reductase), or oxidized into irreversible, non-ascorbutic products.
- AA is a strong antioxidant in an AQUEOUS solution
- AA is much more easily oxidized in an ALKALINE and AEROBIC environment
- UV RADIATION (e.g. sunlight) will oxidize AA, regardless of oxygen presence.
Manufacturing collagen in connective tissue
Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals (25-25% of protein content) and the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of connective tissue holding most of the body together. Gives structure to bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, muscle, blood vessels, heart valves, invertebral discs, cornea, retina, skin, teeth, capillary walls, joint linings and the ground substance between cells.
- AA works as a coenzyme to convert (hydroxylate) amino acids proline and lysine to hydroxyproline (needed for a stable extracellular matrix) and hydroxylysine (needed for formation of cross-links in the fibers), both important to the collagen structure
Examples of collagen needs. Anti-aging (reduces aging-lines, wrinkles in skin), maintaining arterial integrity, wound repair, healing burns, healthy gums, prevention of easy bruising, and bone fracture.
Boosts immunity
Seems to enhance combative white blood cell (WBC) immune function and activity – partially protective against colds and flu, and other infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal-related diseases
- Increases interferon levels (an immune system “weapon”)
- Increases secretion of thymic hormones, which stimulate WBC production
- Inhibits oxidative destruction of WBC’s – increases their mobility
- Increases serum immunoglobulins (antibodies)
- Leukocytes have highest C concentration of any blood cells
- Some studies show WBC increase at doses of 3-10g of vitamin C
- High blood sugar reduces immune system benefits of vitamin C
- Vitamin C needed by Immune System WBCs, but Glucose and Vitamin C compete for cell entry – In the 1970’s, Dr. Linus Pauling found out that vitamin C was needed by WBCs to be able to phagocytize viruses and bacteria. White blood cells require 50 times higher concentration inside the cell as outside, so they have to accumulate vitamin C.
- Glucose and C compete, but the playing field is not equal – Glucose and Vitamin C have similar chemical structures, and compete for INSULIN pumps to enable INSULIN-mediated cell entry. However, the evolutionary “fight-or-flight” response favors glucose entry into cells at the expense of vitamin C. If there is more glucose around, there is going to be less vitamin C allowed into the cell. Blood sugar of a mere 120 reduces the phagocytic index by 75%, slowing the immune system down to a crawl.
Cholesterol-related functions
- Helps reduce cholesterol levels and high blood pressure
- Aids in cholesterol metabolism and elimination
- Required in the synthesis of bile acids from cholesterol
Major anti-inflammatory / antiviral / antibacterial / antifungal activities
A result of Vitamin C‘s multiple roles in immune system enhancement, antioxidant ability, adrenal support and collagen production
- Anti-inflammatory activity. In its antioxidant and immunity roles, vitamin C combats inflammation-causing microorganisms, irritants, and free radicals, improving conditions such as cystitis, bronchitis, prostatitis, bursitis, osteo/rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic skin problems, e.g. dermatitis; vitamin C‘s enhancement of collagen production may also improve joint membrane integrity in arthritis; In gouty arthritis, vitamin C improves the elimination of the irritant, uric acid, through the kidneys.
- Anti-bacterial activity. “It is likely that the bactericidal effect of AA takes place by way of free radicals formed during oxidation of AA in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is formed during the reaction of ascorbic acid and oxygen, and macrophages lack peroxidase. It has been shown that ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide together have a pronounced bactericidal effect, which is increased by a small concentration of copper ions. The presence of free radicals has been demonstrated by electron-spin resonance spectroscopy, and the bactericidal activity is completely inhibited by free-radical inhibitors.” Linus Pauling, 1974
- Anti-viral activity
- Several bacterial viruses (aka bacteriophage, infects / replicates inside bacteria) are 99% inactivated by 20 min. exposure to AA concentrations. This can be attained in the blood by a large C intake. Murata et al, 1971.
- Viral inactivation does not occur in the absence of oxygen. Study concluded that deactivation results from single-strand scissions of phage DNA by free radicals formed during the autoxidation of AA. Murata, 1973
- Some protection against viral diseases: poliomyelitis, hepatitis, fever blisters, shingles, virus pneumonia, measles, chicken pox, virus encephalitis, mumps, infectious mononucleosis Stone I, 1972
- Anti-fungal activity
Enhances vitamins
- Works synergistically with Vitamin E and Beta-carotene. Vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-caroteneboth reinforce and extend each other’s antioxidant properties and activities.
- Indirectly protects vitamins A, E, and some B vitamins from oxidation (including riboflavin, thiamine, folic acid, and pantothenic acid);
- Enhances B-vitamins -By vitamin C‘s influence on intestinal flora. Helps metabolize folic acid (Vitamin B9) by helping to regulate conversion of folic acid to folinic acid;
Other important functions
- Controls allergic response. In the presence of copper ions, vitamin C prevents histamine accumulation, which assists in its degradation/elimination. Evidence exists that vitamin C also modulates prostaglandin synthesis to modulate histamine response and cause relaxation
- Needed for body’s enzyme systems. 300 known enzyme systems require vitamin C
- Detoxification. Heavy metals, pesticides, and other pollutants. Vitamin C is a powerful chelating agent for heavy metals.
- Helps increase thyroid hormone production. Vitamin C stimulates production of thyroxine (T4)
- Maintains normal tissue growth and repair
- Prevents blood clotting
- Aids in the absorption of inorganic iron; needed for iron mobilization from spleen
- Promotes proper calcium absorption
- Participates in metabolism of certain amino acids to neurotransmitters and steroid hormones
- Maintains your adrenal cortex and ovaries
- Vitamin C administration increases mitochondrial Vitamin C concentrations. Where Vitamin C is readily oxidized by oxidants produced by our energy-making mitochondria inside cells

The many health benefits of Vitamin C
Most people suffer from chronic subacute scurvy. Dr. Linus Pauling and his research partner Dr. Mattias Rath determined that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a symptom of a chronic vitamin C deficiency. This author surmises that many other symptoms, including bleeding gums, random nosebleeds, slow healing wounds (E.g. in diabetics), hemorrhages in disease such as Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis , are also consequences of a low-grade C deficiency, enough to cause weakened connective tissue, but not full-blown scurvy.
Studies using health beneficial vitamin C have been negatively slanted. After first promoting the health benefits of consuming Vitamin C in the 1940’s, the medical / pharmaceutical industry probably realized that its use would seriously cut into their profits and so campaigned against it. Studies discounting the benefits of Vitamin C used insufficient amounts or procedures were not followed.
Health problems associated with Vitamin C deficiency | ||
| • Adrenal Insufficiency | • Fatigue | • Osteoarthritis |
| • Alcoholism | • Gallbladder disease | • Parkinson’s disease |
| • Allergies | • Gingivitis | • Periodontal disease |
| • Any tissue-related malady | • Glaucoma | • Peptic ulcers |
| • Asthma | • Hepatitis | • Peripheral vascular disease |
| • Atherosclerosis | • Herpes simplex | • Preeclampsia |
| • Auto-immune disorders | • Herpes zoster | • Menopause |
| • Cancer | • High blood pressure | • Mitral valve prolapse |
| • Candidiasis | • Hives | • Multiple sclerosis |
| • Capillary fragility | • Infections | • Osteoarthritis |
| • Cataracts | • Infertility | • Parkinson’s disease |
| • Cervical dysplasia | • Inflammatory disorders | • Radiation exposure |
| • Crohn’s disease | • Eczema | • Rheumatoid arthritis |
| • Common Cold | • Macular degeneration | • Risk of death (all causes) |
| • Coronary Heart Disease | • Menopause | • Skin ulcers |
| • Depression | • Mental Illness | • Skin sun damage |
| • Diabetes | • Mitral valve prolapse | • Sports injuries |
| • Disk Herniation | • Multiple sclerosis | • Wound healing |
| • Eczema | ||
Vitamin C reduces heart disease
- Strengthens the collagen structure of arteries
- Protects against oxidation damage of arterial walls
- Lowers total cholesterol
- Lowers blood pressure
- Inhibits platelet aggregation
Atherosclerosis is a vitamin C deficiency disease. Although eventually harmful, oxidized cholesterol deposition in artery walls provides a temporary, life-saving repair until access to vitamin C allows arterial damage to be repaired
Cardiovascular Disease – Chronic inflammation response to damaged arterial walls
Vitamin C increases lifespan / reduces risk of death
In one of the largest and most detailed studies of vitamin C, UCLA doctors showed that taking vitamin C could produce an increase in longevity. 5 to 7 years for men, and 1 to 3 years for women. The study, based on 11,384 individuals , found that as little as 300 mg. of C extended lifespan by 6 years. Engstrom JE et al, 1992
Researchers have demonstrated that vitamin C slows down telomere shortening by 52-62 % in a controlled experiment. Telomeres are the end caps of DNA that shorten with many generations and limit the number of replications of DNA. Furumoto K, et al, 1998
20,000 men and women aged 45 -79 followed 4 years. Just a 50 mg increase in vitamin C consumption was able to reduce the relative all-cause mortality rate by 20% – regardless of person’s age, cholesterol count, or blood pressure. Those with the highest levels of C had even greater reductions in the risk of death from all causes. Prof Kay-Tee Khaw et al, 2001
Vitamin C Improves psychological disorders
Vitamin C has also been used for psychological disorders, including schizophrenia, depression, and paranoia. Helps form SEROTONIN – Vitamin C required to convert amino acid tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), the precursor for the mood / brain hormone, SEROTONIN
Vitamin C reduces effects of stress
Vitamin C counters free radical damage caused by stress
Vitamin C fed to rats undergoing stress prevented the expected increase in cortisol levels and other stress-related hormones – CORTISOL is a “fight or flight” hormone released by the adrenal glands in response to stress, and allows us to spring into action when we sense danger. CORTISOLis responsible for relaying the news of stress via the bloodstream to all parts of the body and mind, but frequent exposure to high levels of stress hormones exhausts the body’s physical resources, impairs learning and memory, and makes people susceptible to depression.
Vitamin C is required for the synthesis of stress hormones EPINEPHRINE (ADRENALINE) and NOREPINEPHRINE (NORADRENALINE) – Secreted by the adrenal medulla in a fight or flight response to a stressful situation
- Vitamin C stimulates adrenal medulla gland to release stress hormones – NOREPINEPHRINE, from which EPINEPHRINE is synthesized, and dopamine from adrenal medulla’s chromaffin cells. These are neuroendocrine cells that link the nervous and endocrine systems.
Vitamin C is needed for the DOPAMINE to NOREPINEPHRINE step of the amino acid tyrosine to EPINEPHRINE pathway – the enzyme PNMT (see chart below) is only found in the cytosol of adrenal medullary cells.
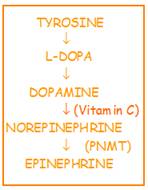
EPINEPHRINE also plays a role in blood pressure regulation – part of an auxiliary electron transport system for the last step of ALDOSTERONE synthesis; ALDOSTERONE is a hormone involved in regulating blood pressure, blood pH and blood volume.
Improves asthma-related breathing disorders
Experts on asthma tell us that some of the reasons for the rise in asthma in our society are – the increased stress on the immune system, earlier weaning and earlier introduction of solid foods to infants, use of food additives, more air pollution, and genetic manipulation of plants resulting in food components with greater allergenic tendencies.
- Psychologically stressed infants more susceptible. When high psychological stress experienced in utero or shortly after birth
- Reduces bronchial spasm. 1g C / day reduces tendency of bronchial passages to go into spasm. Zuskin E et al,1990
- Prevents exercise-induced asthma -double-blind trial – 500 mg C/day for 2 days prevented attacks. Schachter EN et al, 1982
Decrease in respiratory disease
- 31% decrease in respiratory illness per subject receiving 200 mg AA/ day – compared to those receiving a placebo. Cowan et al, 1942
- 63% decrease in illness for subjects receiving 1g AA day. Ritzel G, 1961
- 30% decrease in illness when subjects received 1g AA/day plus an additional 3 g day for first 3 days of a cold. Charleston et al, 1972
- 58% decrease when subjects received 1 g AA / day. Anderson et al; 1972
- 30% decrease in illness for younger children receiving 1 g AA / day, and a 36% decrease for older children receiving 2 g AA / day. Coulehan et al, 1974
- Very little protective effect was observed when a suspension containing large numbers of cold viruses was instilled into the nasal cavities of subjects receiving 3 g AA /day – Presumably the protective effect of AA has its limits. Walker et al, 1967
Back problems / Disk herniation
- Helps prevent back problems by preserving the integrity of intervertebral disks. Our donut-like, spinal column disks have a tough, gristle-like exterior and a soft cushioning interior. Insufficient vitamin C compromises disc integrity. The tough exterior wears down over time resulting in a pinhole through which bending movement can push out some of the soft interior material – called a disc herniation. Squished-out material touching a spinal column nerve can cause severe pain.
- Disk lesion surgery avoided. Greenwood J, Jr., 1964 – 500 patients – “A significant number of patients with disc lesions were able to avoid surgery by the use of large doses (1g / day) of vitamin C“. Effectiveness of ascorbic acid in controlling vertebral disc lesions is likely attributed to its essential role in the synthesis of collagen
Anti-aging / Wrinkle reduction
Skin suffers assault from oxidative damage to proteins from UV-light and pollutants (e.g. cigarette smoke) leading to classic aging skin. Vitamin C can counter damage with its antioxidant functions and in its role in synthesizing collagen (by hydroxylating collagen molecules) as structural support for the epidermis.
Dietary and topically applied vitamin C can improve skin elasticity. Oxidative damage to proteins causes a decline in Vitamin C content in both the dermis and epidermis.
Vitamin C is usually obtained from the diet, but according to the Linus Pauling Institute, topical use of vitamin C may also help prevent and treat UV / pollutant damage by its increased presence in the skin. When used topically, the Linus Pauling Institute recommends a maximum concentration of 20% of vitamin C in solution. Instructions for how to make the solution and apply topically found at: How to boost vitamin C levels
Polio treated early with Vitamin C
Dr. Klenner handled 60 polio cases during an epidemic in Dr. Klenner’s home state. “These patients presented all or almost all of these signs and symptoms: fever of 101 to 104.6 degrees F., headache, pain at the back of the eyes, conjunctivitis, scarlet throat; pain between the shoulders, the back of the neck, one or more extremity, the lumbar back; nausea, vomiting and constipation.”
“The treatment employed was Vitamin C in massive doses. The initial dose was 1000 to 2000 milligrams (1 to 2 grams) depending on age. Children up to four years received the injections intramuscularly . . . the temperature curve was adopted as the guide for additional medication. Temperature response after the second hour was taken to indicate the second one or two gram injection. If there was a drop in fever after two hours, two more hours was allowed before the second dose. This schedule was followed for 24 hours. After this time the fever was consistently down, so the drug was given 1 to 2 grams every six hours for the next 48 hours. All patients were clinically well after 72 hours. After three patients had a relapse the drug was continued for at least 48 hours longer, one to two grams every eight to twelve hours.”
“Where spinal taps were performed, it was the rule to find a reversion of the fluid to normal after the second day of treatment.” ( Note: No paralysis developed in any of the 60 cases. )
Reduces risk of cancer and metastases
Clinical, experimental, and population studies have shown that Vitamin C (especially in aqueous solutions) can reduce cancer rates. A high Vitamin C intake reduces the risk for virtually all forms of cancer, including cancers of the lung, colon, breast, cervix, esophagus, oral cavity, and pancreas.
- C inhibits formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines
- Protects lymphocyte (type of WBC) DNA. A misleading test-tube study published in Nature indicated 500 mgs of C may damage lymphocyte DNA, which could cause cancer. However, other studies reveal that C actually protects against DNA damage to lymphocytes, with its effect greatly enhanced by bioflavonoids, which usually accompany vitamin C in nature. Five subsequent human high-dose C (up to 5g / day) could not find evidence that vitamin C induces gene mutations.
- Reduces metastases. Increased collagen production increases the resistance of tissues to invasion by metastases and infiltration by malignant tumors. Cameron E & Pauling L, 1973 pdf
Liquid preparations seem to be more effective against cancer than dry doses. Dr. Ewan Cameron was a former Scottish surgeon, who later became Medical Director and Senior Research Professor at the Linus Pauling Institute, working with Dr. Linus Pauling until his death in 1991. While working in the Scottish hospital, his patients diagnosed with cancer were often subject to waiting months before a scheduled surgery. Dr. Cameron decided to place diagnosed cancer patients on vitamin C rather than do nothing. He collaborated with Dr. Pauling, who advised a 10g dose, but his patients objected to taking the several large tablets required. Dr. Cameron’s pharmacist suggested that a liquid preparation of AA be more acceptable. Conversion of AA, to a non-sour liquid was accomplished by adding baking soda (Also added were sorbitol as a preservative / sweetener, and cherry syrup for flavor). Cameron’s patients in rural Scotland were sent back home with a several week supply of the concocted AA mixture in two brown one liter bottles, with refrigeration recommended. Dr. Cameron reported dramatic improvements in median cancer survival. In addition to much longer survival, some patients experienced protracted remissions – there were survival plateaus observed in cancers which had been uniformly fatal.
Constance Tsao, a researcher at the Pauling Institute, carried out a substantiating experiment under Pauling’s guidance.
Four groups of identical mice were given human breast cancer. The diet of each group was different:
- Group 1: Given standard food
- Group 2: Given large amounts of vitamin C in food
- Group 3: Given large amounts of vitamin C in drinking water
- Group 4: Received food with vitamin C and copper salts (known to markedly accelerate the oxidation of vitamin C).
The result: Only the aqueous vitamin C was of significant benefit. The mice receiving copper salts vitamin C lived longer than the rats receiving vitamin C in food, which were not benefitted at all.
Dr. Moertel’s Clinical Trial. A physician at the Mayo Clinic, Dr. Charles Moertel, then reported a clinical trial in cancer patients which was purportedly designed to confirm or refute Cameron’s claims of cancer patient benefit from vitamin C. Moertel took advanced cancer patients, many with advanced colon cancer who had failed chemotherapy (a devastating therapy that suppresses the immune system to the point where vitamin C would be of little benefit), and subjected them to a randomized clinical trial. Patients either received 1 gram of vitamin C three times daily in the dry state, or patients received a look-alike placebo to use as a comparison. The results: no improvement in survival. Moertel wrote a prominent paper for the literature which asserted vitamin C was useless in advanced cancer patients.
Dr. Cameron’s Theory was that large amounts of vitamin C may stimulate the immune system by simulating an infection. Vitamin C (ascorbate) is oxidized to dehydroascorbate (DHAA) when it stops an oxidant. For body homeostasis, under normal circumstances DHAA is converted back into ascorbate by the enzyme dehydroascorbate reductase. Therefore, the presence of progressively increasing concentrations of vitamin C breakdown products simulates (1) major infection or (2) some other major deterioration of normal homeostatic reduction of oxidized vitamin C, which is the method by which vitamin C is restored after losing its ability to absorb a free radical. We now know that vitamin C is chemically unstable in aqueous solutions and progressively undergoes oxidative change. Therefore it seems quite possible that a rise in oxidation by-products of vitamin C from the employment of such as Dr. Cameron’s pharmacological AA mixture used to ingest the vitamin C may be the alert signal that a serious attack on the vital integrity of the body was in force, and that an immune activation was the appropriate adaptive response. Pauling, himself, seems to have suspected this hypothesis as representing an integrating theory.
In summary. The reports by Cameron may well have been valid, in spite of Moertel’s claims to the contrary. The key to the discrepancy lies in the methodology – i.e aqueous compared to dry doses of C .
However, Cameron’s patients may well have benefitted more from the immune stimulating properties of ascorbate breakdown products than from the vitamin C itself.
Dr. Cameron’s 1976 clinical trial of vitamin C therapy for terminal cancer – discussed in the Book “Cancer and vitamin C” by Dr. Ewan Cameron, M.D. and Dr. Linus Pauling, Ph.D.
A dosage of 10 grams a day of Vitamin C was given to 100 terminally ill (“untreatable”) cancer patients. A control group of 1,000 terminal cancer patients(matched for sex, age and type of cancer) received no vitamin C.
The results of this study were rather significant. The average survival rate of the vitamin C patients, at the time of the reporting of the study in 1978, was 4.2 times larger than that of the control group. Moreover, the degree of subjective pain was much less and quality of life much greater for the vitamin C treated patients. Perhaps most striking was the fact that 16 of the 100 vitamin C treated patients were still alive in 1980, all of the 1,000 controls had died.
Other health bebefits of Vitamin C
- Enhances healing of wounds, burns and fractures. Vitamin C‘s ability to facilitate the healing of wounds, fractures and burns is no doubt attributed to its role in the synthesis of collagen (Stone, 1972)
- Used as an aid in withdrawal from drug addictions. Narcotics, alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, and sugar
- Protects against pollution and cigarette smoke
- Reduces pain
- Reduces the risk of cataracts
- Decrease in non-respiratory disease. 30% decrease in amount of illness of non-respiratory disease in subjects receiving 1 g AA / day, relative to those receiving placebo. Anderson TW et al, 1972
- Increases IQ in children
- May help fatigue. Due to stimulation of thyroid hormone production;
- Anemia Prevention

Symptoms of vitamin C deficiency
People today are generally consuming enough vitamin C to prevent full-blown scurvy, but intake is not optimal to prevent a multitude of health problems:
Symptoms of low level scurvy (i.e. an ongoing C deficiency)
Connective tissue degenerates, revealed as:
- Prematurely aging skin
- Heart problems from underlying atherosclerosis / CVD
- Capillary walls weaken/hemorrhage
- Poor wound healing
- Bone lesions develop
- Teeth loosen/fall out
- May increase gallstone formation
- Liver function impaired
- Tendency to bruise easily
- Visible broken capillaries
- Weakness / Lethargy / Fatigue
- Irritability / Reduced capability to tolerate stress
- Weight loss
- Digestive disorders
- Bleeding / painful gums
- Gingivitis
- Shortness of breath
- Aching muscles / bones / joints in arms and legs
- Dry / rough skin (maybe pigmented)
People with a tendency for low tissue levels of Vitamin C
- Smokers. Pelletier O, 1970
- Elderly. Burr et al, 1974
- People under stressful conditions
- Those with liver disease – worsened by toxic effects of treatment medications
- High blood copper levels – depletes body’s C; copper water pipes are a source of copper
- Those with high blood pressure, gallbladder disease, stroke, some cancers,atherosclerosis and PAD. Langlois M et al, 2001
Testing for Vitamin C presence in tissues
The usual test is to measure vitamin C in blood plasma – which more accurately informs about C‘s presence in the recent diet, not in the body. A better indicator is the concentration of ascorbic acid (AA) in the white blood cells, which parallels tissue concentration. Scurvy is diagnosed when C concentration is 2 mg/L in the white blood platelet layer. An even better method is a saturation test. Without access to these tests, look for signs and symptoms of C deficiency.

Vitamin C tissue distribution
Blood Plasma vitamin C level is 10-20µg /mL
- Generally, the metabolically active and developing / fast growing tissues have the highest levels of vitamin C.
- Biological tissues accumulating > 100 times the level of blood plasma vitamin C include: adrenal glands (1600-1700 μg /mL), pituitary, thymus, corpus luteum (involved in estrogen / Progesterone production during pregnancy), and retina.
- Those tissues with > 10-50 times the concentration present in blood plasma include: brain (has a double-pump to ensure its vitamin C supply), spleen, lung, testicles, lymph nodes, liver, thyroid, small intestinal mucosa, leukocytes, pancreas, kidney and salivary glands.
- Other tissues levels: skeletal Muscles (3-5 x plasma), RBC (3-4 x plasma), WBC (20-30 x plasma), Healing Wounds (high levels)
- Pregnancy. Vitamin C crosses the placenta; cord blood concentration is ~ 2- 4 times the concentration in maternal blood; Vitamin C is distributed into milk, which contains 40 to 70 µg/mL with mother on normal diet.

Most animals and plants synthesize their own Vitamin C - Man does not
Vitamin C synthesis is achieved through a sequence of four enzyme-facilitated steps – which convert glucose to ascorbic acid (AA).
It is carried out:
- In the KIDNEYS – in reptiles and birds;
- In the LIVER – in most mammals (but not man) and perching birds; AA is converted to various mineral ascorbates.
Humans cannot make vitamin C, since we have a defective gene for synthesizing the last enzyme in the process (called gulonolactone oxidase (GLO)). If we don’t obtain sufficient C from outside sources, we will be dealing with a condition called hypoascorbemia setting the stage for many of the familiar diseases we see today – heart disease, cancer, premature aging, arthritis . . .
After the “Fall of man” the defective gene became significant. We obtain vitamin C (and other essential nutrients) from foods such as leaves, fruit, vegetables and meat. After Adam and Eve were driven from the garden, people had to work hard to cultivate produce, since because of sin, the ground was cursed. And maybe God allowed this same gene to gradually become defunct in order to shorten man’s lifespan. (Adam lived 930 years (Gen. 5:5), Noah 950 years (Gen. 9:29). After Noah the human lifespan decreased – Shem lived 600 years, Arphaxed 438 years, down through to Abraham who lived 175 years, Moses 120 years (Deut. 34:7), and finally man’s lifespan was shortened to our “three score years and ten”, or 80 “by reason of strength”. (Psa. 90:10)
Vitamin C has been shown to increase longevity significantly
The loss of the GLO enzyme needed for ascorbic acid synthesis has affected a number of species. E.g. Some fish (E.g. rainbow trout, coho salmon), many birds (e.g. red-vented bulbul), some bats (E.g. Indian fruit-eating bat), guinea pigs, and most primates, including humans. Fortunately for the survival of these species, ascorbic acid is prevalent in surrounding food sources.

Vitamin C chemistry
Active vitamin C Active vitamin C occurs in either a reduced or oxidized form
(1) REDUCED FORM – Ascorbic acid (AA) a.k.a.HYDROGEN ASCORBATE(C6H8O6);
- AA has a simple chemical structure. AA is technically not an acid. Although referred to as an acid, AA does not contain a free carboxylic group (The CO2H group reacts with an -OH group in the molecule to eliminate a molecule of water and form a ring compound).
- AA decomposes at 190ºC (374ºF)
- AA is a weak sugar acid structurally related to GLUCOSE which naturally occurs either attached to:
- A hydrogen ion – forming hydrogen ascorbate (i.e. Ascorbic acid)
- A metal ion – forming a mineral ascorbate (e.g. sodium ascorbate,potassium ascorbate).
(2) OXIDIZED FORM – Dehydroascorbic acid (DHAA) a.k.a. Dehydroascorbate (C6H6O6);
- Vitamin C enters and leaves most cells as DHAA – except for renal tubular and eye cells.
- The most important property of vitamin C is its reversible oxidation-reduction ability -is readily oxidized to DHAA, thereby protecting other compounds from oxidation (in its antioxidant capacity), and yet DHAA can be easily converted (reduced) back into AA. DHAA, however, may also be further oxidized to an inactive form – Diketogulonic acid. Parviainen and Nyvssonen, 1992. DHAA decomposes at 225°C (437°F).
- The main enzyme responsible for AA’s oxidation to DHAA is ascorbate oxidase – which increases during stress or pathogen / chemical exposure. Loewus and Loewus, 1987
For the Technical “Want to Knows”During respiration O2 is sometimes incompletely reduced to the superoxide ion (O2–) (instead of being reduced completely to its -2 oxidation state as in H2O). Normally the enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) converts: O2– + O2– +2H+ → H2O2 + O2 but in the presence of Fe2+, H2O2 may be converted into the highly-reactive hydroxyl radical (•OH). The hydroxyl radical can initiate unwanted, deleterious reactions within a cell (by removing a hydrogen atom (H+) from an organic compound to form H2O plus a new, potentially more reactive free radical). Ascorbic acid can donate a hydrogen atom (H+) to a free radical – thereby preventing damaging reactions inside the cell and in other “watery” areas. E.g. in the blood. A 2-electron redox process, ascorbic acid, becomes monodehydroascorbic acid, which soon gains another electron to become dehydroascorbic acid (DHAA), both of which oxidized forms are relatively non-reactive, and do not cause cellular damage. |
ONLY the L-isomer (natural) forms of vitamin C have anti-ascorbutic (i.e. anti-scurvy) benefit. The names ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid (DHAA) without a prefix refer to the L-forms. L-ascorbic acid means that if polarized light is passed through ascorbic acid crystals, then the light is twisted to the left. Synthetic (manufactured) ascorbic acid comprises both d- and l- forms, but they can be separated or “purified” to include just l-forms, and although this ascorbic acid is synthesized, it is true vitamin C, as found in nature.
Vitamin C acts as an electron donor for 8 different enzymes
- Form Collagen (3 enzymes) – nearly 1/3 of body’s total protein mass [TBHB]. AA keeps iron in its reduced state, preserving the activity of iron-containing enzymes. Iron-containing enzymes prolyl and lysyl hydroxylases catalyze the hydroxylation of amino acids proline and lysine, to produce hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine. These provide sites for cross-linking of collagen fibrils responsible for TENSILE STRENGTH and ELASTICITY in connective tissue, such as in scar tissue, blood vessels, cartilage and skin.
- Synthesize Carnitine (2 enzymes) – Carnitine is essential for the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria for ATP energy generation. The more vitamin C in blood plasma, the lower the body fat and waist circumference in healthy adults. Journal of Nutrition 2007
- Biosynthesizes Norepinephrine from dopamine (1 enzyme) – tyrosine is converted to catecholamines (neurotransmitters in neurons/hormones in adrenal medulla):dopamine, norephinephrine, and eventually epinephrine (adrenaline), via dopamine beta hydroxlase.
- Stabilizes Peptide Hormones (1 enzyme) – enzyme adds amide groups to peptide hormones, greatly increasing their stability.
- Modulates Tyrosine Metabolism (1 enzyme) – tyrosine is catabolized in the liver. The enzyme system which catalyses this reaction, p-hydroxyphenyl-pyruvic hydroxylase, uses ascorbic acid as a cofactor.
Levine M etal;
References
An excellent article by physicist Gary Wade on Vitamin C studies used against Cancer and AIDS: http://www.rifeenergymedicine.com/vitaminc.html
The work and professional publications of Dr. Fred R. Klenner, M.D., former chief of staff at Memorial Hospital in Reidsville, NC, has provided us with much supporting evidence for the beneficial uses of Vitamin C.
Book “Cancer and Vitamin C“, by Dr. Ewan Cameron, M.D. and Dr. Linus Pauling, Ph.D.
Anderson TW, Reid DB, Beaton GH. (1972) Vitamin C and the common cold: a double-blind trial. Can Med Assoc J. 1972 Sep 23;107(6):503-508. PMC free article PubMed
Burr ML et al, (1974) Plasma and leucocyte ascorbic acid levels in the elderly. Am. J.Clin. Nutr., 27, 144-51
Cameron, Ewan, and Linus Pauling. (1973) “Ascorbic Acid and the Glycosaminoglycans: An Orthomolecular Approach to Cancer and Other Diseases.” Oncology 27, 2: 181-92. pdf
Charleston SS, Clegg KM. (1972) Ascorbic acid and the common cold. Lancet ;1(7765):1401-1402.
Coulehan JL et al, (1974) Vitamin C and upper respiratory illness in Navaho children preliminary observations pdf
Cowan DW,M.D.; Diehl HS, M.D.;Baker AB, M.D. (1942) Vitamins for the prevention of Colds, JAMA. ;120(16):1268-1271 Jama Link
Engstrom JE et al, 1992).Vitamin C intake and mortality among a sample of the United Statespopulation. 1992
Furumoto K, et al,(1998.) Age-dependent telomere shortening is slowed down by enrichment of intracellular vitamin C via suppression of oxidative stress, Life Sciences,
Langlois M et al, Serum vitamin C concentration is low in peripheral arterial disease and is associated with inflammation and severity of atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2001;103(14):1863-1868
Levine M etal; Vitamin C. In Stipanuk MH (ed): “Biochemical and Physiological Aspects of Human Nutrition.”
E. Cameron, Linus Pauling (1973) Ascorbic Acid and the Glycosaminoglycans: An Orthomolecular Approach to Cancer and Other Diseases. PubMed pdf
Linus Pauling (1974 (Nov) Nat. Acad. Science USA Loewus F and Loewus P, (1987) Biology, Environmental Science Semantic ScholarMcEvoy GK, (1993) Drug Information The American Hospital Formulary Service, American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc., MD.,
Murata, A., K. Kitagawa, and R. Saruno (1971) Inactivation of bacteriophages by ascorbic acid. Agr. Biol. Chem. 36:1065-1067.
Pelletier O., (1970) Vitamin C status of smokers and non-smokers. Am. J.Clin. Nutr., 23, 520-4
Prof Kay-Tee Khaw et al. (2001) Relation between plasma ascorbic acid and mortality in men and women in EPIC-Norfolk prospective study: a prospective population study. The Lancet – 3 March 2001 (Vol. 357, Issue 9257, Pages 657-663 ) Abstract
Ritzel G, (1961) Ascorbic Acid and Infections of the Respiratory tract, Helv. med. Acta 28: 63-68.
Schachter EN et al, (1982) The attenuation of exercise-induced bronchospasm by ascorbic acid. Ann. Allergy .
Stone I (1972) “The Healing Factor: Vitamin C against disease”
Walker GH, Bynoe ML, Tyrrell DA. Trial of ascorbic acid in prevention of colds. Br Med J. 1967 Mar 11;1(5540):603-606. PMC free article PubMed Zuskin E et al, Byssinosis and airway responses due to exposure to textile dust. Lung 1976; Bucca C et al, Effect of vitamin C on histamine bronchial responsiveness of patients with allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy, 1990.