Dark Chocolate - "Anti-inflammatory / Anti-depressant"


Cocoa contains antioxidant flavonoids
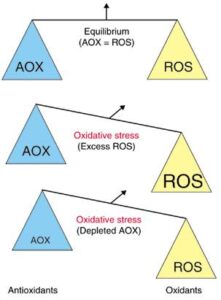
It’s the pure cocoa in dark chocolate that contains phytonutrients called flavonoids. In particular, cocoa contains the flavonoid epicatechin. Most flavonoids have antioxidant properties, and by preventing oxidant damage have an anti-inflammatory effect in the body. Cocoa has a very high ORAC value, reflecting its antioxidant ability. In contrast, “white” chocolate contains no flavonoids. Chronic low-grade inflammation is a main component of many, if not all health problems. Cocoa flavonoids reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines and interleukin-1 beta.
- Cocoa suppresses pro-inflammatory COX-2 enzymes, which suppresses inflammation marker P-Selectin . Selectin is involved in the initial recruitment of white blood cells to the site of injury during inflammation.
- Dark cocoa inhibits pro-inflammatory leukotrienes and increases availability of artery-dilating neurotransmitter NITRIC OXIDE. Epicatechin and other flavanols found in cocoa proved effective at inhibiting the action of pro-inflammatory leukotrienes and potentially inflammatory COX-1 enzymes (e.g. to mucosal cells lining gastric intestinal tract). Also, availability of blood vessel-dilating NITRIC OXIDE was enhanced by consumption of flavanols, possibly explaining its beneficial effects on INSULIN sensitivity and blood pressure. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2005,
Nitric Oxide -“Blood vessel dilator”
- Cocoa lowers inflammation marker C-Reactive Protein. 2009 study at John Hopkins University; Italian study published in the Journal of Nutrition
C-Reactive Protein -“Inflammation Marker”
Eating chocolate stimulates the release of mood-affecting chemicals. E,g. endorphins, phenyl ethylamine and SEROTONIN The cocoa bean is rich in nutrients:- Essential minerals magnesium and iron
- Vitamins B1, B2, and D
- Medium Chain-length Fatty Acids (MUFAs)
- “Dutching”process. Adds alkali-potash (alkalinization) to the cocoa nibs before roasting to neutralize the chocolate’s acidic flavor and alter its color. Unfortunately, this process also removes most of the chocolate’s anti-inflammatory polyphenols;
- Roasting. Temperatures > 100 °F, destroy chocolate’s natural antioxidant compounds
- Has not been alkalized by the Dutching process
- Cold processed – Dried at temps under 100 °F and cool-pressed rather than roasted. The melting point of cocoa butter is just below the human body temperature (98.6 °F)
- Contains at least 70% pure cocoa;
- No added saturated fats – contains cocoa butter, but NO added milk fats or hydrogenated oils;
- Contains natural, low-glycemic sweeteners – E.g.s raw cane rather than refined sugar
- Xocai
- Divine
- Dagoba
- Equal exchange
- Ignafire