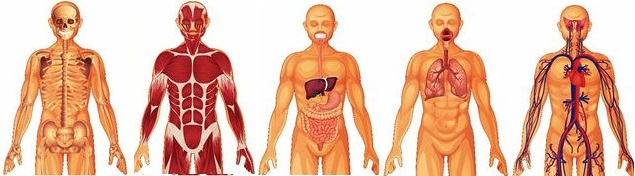
EFA Functions
(5) In pregnancy and child development

Mother's EFA intake during pregnancy and breast-feeding affect her and her child's health
A mother’s inadequate intake of omega-3 fats during pregnancy linked to children’s health.
Researchers found that it was a factor in pPremature births, low birth-weight and hyperactivity in children.
EFAs in breast milk (obtained from mother’s diet) influence structure and function of baby’s retina and central nervous system.
Postpartum depression.
Low omega-3 DHA levels are considered to be a major cause of post partum depression. During pregnancy, the baby will take his or her quota first, leaving the mother with what’s left. The expectant mother should take a dietary supplement of flax oil, ground flaxseed and marine oil.
EFAs are needed for proper growth and development in children
EFAs are particularly involved in neural development and maturation of sensory systems. Male children have greater EFA needs than females.
Behavioral problems in younger children in family.
Studies show that as their mother’s supply of EFAs become more and more depleted, each baby in the womb obtains fewer EFAs from his/her mother than the previous baby.
Research suggests that the reason why younger children in large families often have behavioral and developmental problems is not because they are ‘spoiled’, but because they don’t obtain all the brain fats (EFAs ) they need for normal development. This may also be why the oldest children tend to be the most intelligent – their brain is more optimally developed because of the best supply of EFAs during their development.