Expeller-pressed vs. solvent-extracted oils

What's the difference?
Commercial edible oils are either expeller-pressed or solvent-extracted.
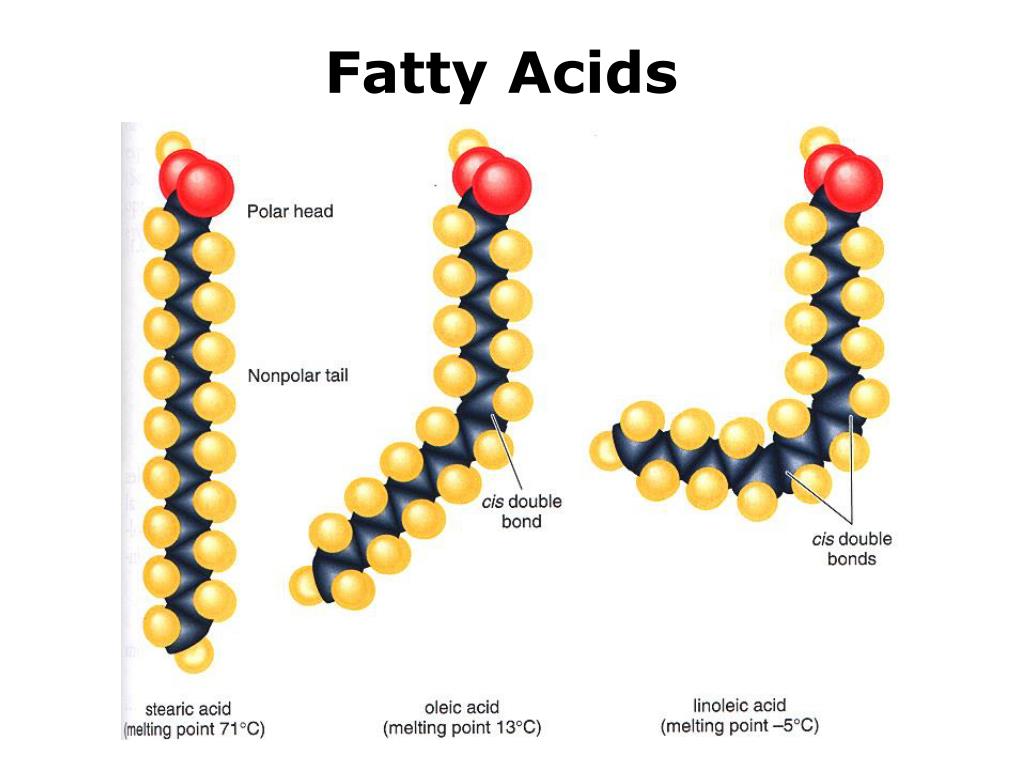
Whichever method is employed, the oil will be damaged if it is exposed to oxygen, and especially in the presence of light or heat. Of these, light is the most damaging, causing rancidity 1000 times more rapidly than oxygen alone. It is important to store undamaged oils in dark bottles or in the dark Applying HIGH heat to UNSATURATED oils produces TRANS FATTY ACIDS (tFAs) and other altered, unnatural fatty acids e.g. Partially hydrogenated fats. Unsaturated fatty acids become mutagenic (i.e. can damage our genes) when heated above 320 °F:
> 320 °F tFAs begin to form
> 392 °F tFAs form substantially
> 428 °F tFAs form exponentially, also forms other altered, unnatural unsaturated fatty acids
Seed / Nut / Bean oil production methods
LOW HEAT, expeller-pressed oils
Sometimes referred to as COLD-PRESSED, processing temperatures should not exceed 120°F (49 °C) during the extraction process.
Typically produced using a low-resistance expeller-pressing that retains their fragrance and nutritious components, including enzymes, EFAs, minerals, vitamins, amino acids, lecithin, chlorophyll, and phytosterols. Britain has an even lower temperature requirement of 104 °F (40 °C)
EXPELLER-PRESSED
vs.
SOLVENT EXTRACTED oils
EXPELLER-PRESSED OIL | TYPICAL SOLVENT-EXTRACTED OIL |
CLEAN / HULL | |
▼ | ▼ |
COOK (~248 °F, ~2 hours) Cracks seed | GRIND FINELY |
▼ | ▼ |
PRESS (185-203 °F) (Oil mechanically squeezed out) Removes protein, fiber, some
| ADD then EVAPORATE SOLVENT (dissolves oil) Usually using hexane or Can leave up to 100 parts per million of solvent
|
▼ | ▼ |
Expeller-Pressed, Unrefined Oil: Still contains lecithin, phytosterols, These unrefined oils are not rancid if they have been protected from air during the extraction process and will remain fresh for a long time if stored in the refrigerator in dark bottles. | DEGUM Using water and phosphoric acid. Removes phospholipids (incl. |
▼ | |
REFINE (167 °F) Oil mixed with caustic soda (aka. Drano®), Removes free fatty acids, | |
| ▼ |
BLEACH (230 °F) Filters (such as Fuller’s earth) remove pigments Removes beta-carotene, Degrades some PEROXIDES | |
▼ | |
DEODORIZE (468-482°F, 30-60 mins.) Steam distillation removes vitamin E, High heat forms TRANS | |
▼ | |
Fully Refined Oil: Tasteless, Vitamin/Mineral/Antioxidant
| |