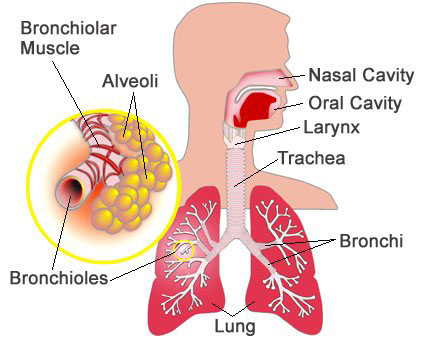
Iodine at work in the body

Distribution of body’s iodine
A typical body can retain ~1500mg of iodine. Contrary to popular belief, Dr. Abraham’s studies indicate that given a sufficient amount of iodine the body will retain 1,500 mg (that’s 30 times more than the presumed 50 mg), with only 3% of that 1500 mg residing in the thyroid gland, and the rest of the body’s iodine concentrated in extra-thyroidal tissues (70% in muscle/fat cells, 7% in skin) where its roles are only now being understood.
Iodine functions
Iodine is used by almost every cell in the body, but some cells have higher needs than others to enable their normal healthy function
Thyroid Hormone production
The thyroid combines iodine with the amino acid tyrosine to make thyroid hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). This well-known need for iodine is critical for cellular metabolism rate, and protein synthesis and growth,
Iodine against thyroid disorders
However, iodine has many other functions in the body . . .
Hormone Balancing
Iodine increases the sensitivity of the receptors for almost every major hormone and neurotransmitter – in order for them to function efficiently.
- Thyroid hormones. For cellular metabolism, protein synthesis and growth
- INSULIN. Helps with diabetes;
- CORTISOL. Manages stress
- Neurotransmitters (e.g., SEROTONIN, DOPAMINE, GABA) in the brain. Helps reverse depression;
- Testosterone, estrogen, FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone), LH (Luteinizing Hormone). In the reproductive organs.
Iodine balances estrogen levels. Iodine/iodide is especially necessary for optimal function of the breasts, ovaries, endometrium, and prostate;
Antimicrobial
Elemental iodine taken into body organs and tissues has an oxidant effect against microbes. In an aqueous environment, iodine converts to hypoiodous acid, with double the oxidizing potential of iodine. Blood passing through the thyroid is mildly “disinfected”. Iodine is also used to disinfect drinking water and swimming pools!
Anti-Cancer
Iodine prevents cancer by a process that induces apoptosis (programmed cell death).
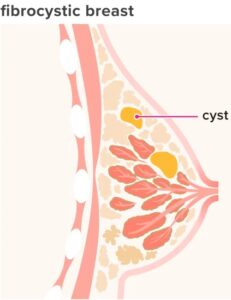
Anti-Cysts
Iodine deals with breast, thyroid, ovarian and skin cysts.
Cells which require a higher iodine concentration express (produce) more iodine “pumps” in their cell membranes.
Iodine pumps concentrate iodine into body’s cells. Enables more iodine to be transported into the cell.
Iodine concentration is highest in the thyroid, ovaries and breast tissues. However, this is only when iodine is ingested in milligram amounts (as opposed to the RDA micrograms);
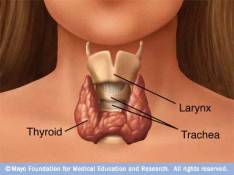
- The thyroid gland. Accomplishes the major feat of concentrating iodide to 20-40 times higher than blood levels (determined by Baumann back in 1896). The mechanism used for concentrating iodine in cells is the iodine pump, which is highly expressed in thyroid epithelial cells. The thyroid’s iodine concentration is influenced by Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) under negative feedback control.
- Ovaries. Only the thyoid gland contains a larger concentration of iodine than the ovaries. (Slebodzinski AB, 2005)
- Mammary glands. These glands contain iodine pumps, which during lactation, enable iodide transfer to breast milk for the nursing newborn’s thyroid function; Evidence is presented that iodine is essential for breast normality and protection against fibrocystic breasts and breast cancer. Interestingly, Eskins et al found that the mammary glands prefer iodine and the thyroid prefers iodide. (Eskin et al, 1995)
Salivary glands, stomach cells (gastric mucosa) and colon have the ability to concentrate almost as much iodine / iodide as the thyroid
Iodide uptake in non-thyroidal tissues does not appear to be influenced by TSH. However, a number of other hormones are known to maintain a dynamic iodide balance in tissues. (Cann et al, 1999)
| Tissues that use iodine pumps to concentrate iodine include: | ||
|---|---|---|
| • Thyroid gland | • Mammary gland | • Stomach cells (gastric mucosa) |
| • Fat | • Muscles | • Mucosa of small and large intestine |
| • Ovaries | • Uterus | • Placenta |
| • Prostate | • White blood cells | • Liver |
| • Lung | • Heart | • Adrenal cortex |
| • Renal cortex | • Thymus (master of adaptive immune system) | • Pituitary gland |
| • Pineal gland | • Skin | • Joints |
| • Arteries | • Bones | • Nasopharynx |
| • Ciliary body of eye deals w/aqueous fluid and intraocular pressure | • Choroid plexus in brain, makes cerebrospinal fluid | • Specific brain cells (related to Parkinson’s) |
References
Abraham GE. “The concept of orthoiodosupplementation and its clinical implications.” The Original Internist, 2004;Abraham GE (2005) “The historical background of the Iodine Project.” The Original Internist;
Abraham GE (2004) The safe and effective implementation of orthoiodosupplementation in medical practice. The Original Internist:11:17-36.
Brown-Grant K (1961) Extrathyroidal iodide concentrating mechanisms. Physiol Rev;
Cann SA (1999) Johannes P. van Netten, David W. Glover, Iodide Accumulation in Extrathyroidal Tissues, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume 84, Issue 2, Page 821; Link
Carrasco N (1993) Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta;
Eskin B et al (1995) Different Tissue Responses for Iodine and Iodide in Rat Thyroid and Mammary Glands. Biological Trace Element Research;
Siebodzinski AB (2005) Ovarian iodide uptake and triiodothyronine generation in follicular fluid. The enigma of the thyroid ovary interaction. Domest Anim Endocrinol;
Spitzweg C et al (1999) Analysis of human sodium iodide symporter immunoreactivity in human exocrine glands. J Clin Endocrinol & Metab;
Spitzweg et al (1998) Analysis of human sodium iodide symporter gene expression in extrathyroidal tissues, J Clin Endocrinol & Metab;