Phytonutrients - Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative

What are phytonutrients?
Phytonutrients are chemicals / compounds produced by plants to protect them against damage from trauma, insects, and pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi.
- Typically found in high amounts in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, tea, nuts, beans, and spices.
- Phytonutrients have one or more of the following health-related properties: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, neuroprotective.
- There are two main types of phytonutrients: carotenoids and polyphenols
Carotenoids - Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer

Carotenoids provide orange and red pigments of vegetables and fruits
- High amounts found in pumpkins, carrots, spinach, kale, tomatoes, oranges, yams
- Support immune system and eyes
- There are > 600 carotenoids
Better-known carotenoids
Beta-carotene
- Can be converted to vitamin A.
- Beta-carotene is converted in the duodenum to retinal, the body’s usable form of vitamin A
Lutein, Lycopene, Zeaxanthin
- Lutein, lycopene and zeaxanthin support eye health. Allow rods and cones in the eyes to absorb blue light, which can potentially induce oxidative damage
| Carotenoids | Beta-carotene | Carrots | ||
| Lutein | Carrots | |||
| Lycopene | Tomatoes | |||
| Zeaxanthin | ||||
| FLAVONOIDS | Anthocyanidins | Cyanidin | Red fruits and berries |
| Petudinin | ||||
| Malvidin | ||||
| Delphinidin | ||||
| Pelargonidin | Sweet cherries, raspberries, blueberries | |||
| Flavones | Apigenin | |||
| Luteolin | ||||
| Christin | ||||
| Tangeretin | ||||
Methoxy flavones | Di-, tri- and penta-methoxyflavone | Black / Thai ginger (Kaempferia parviflora) | ||
| Xanthohumol | Hops | |||
| Synephrine | Bitter orange | |||
| Vitexin | Passion flower | |||
| Flavanones | Naringenin | Grapefruit | ||
| Pinocembrin | Honey, propolis, damiana | |||
| Hesperetin | Citrus fruits | |||
| Neohesperetin | Citrus fruits | |||
| Eriodictyol | Yerba Santa extract | |||
| Isoflavonols | Genistein | |||
| Daidzein | ||||
Flavan-3-ols (also referred to as Flavanols) | Catechin | Fruit peel – especially dragon fruit, mango | ||
| Gallocatechins, Epigallocatechins | EGCG in green tea, matcha tea) | |||
| Epicatechins | green tea | |||
| Chalcones | Arbutin | |||
| Phloretinl | Apple tree leaves, Manchurian aprocot | |||
| Phloridzin | ||||
| Flavanols | Kaempferol | Cloces, cumin, caraway, capers, fruit peel – | ||
| Quercetin | Onions (esp.red onion), fruit peel (especially | |||
| Rutin | buckwheat, elderflowers, apple peel | |||
| Myricetin | ||||
| NON-FLAVONOIDS | Lignans | Enterodiol, enterolactone | Flaxseed | |
| Stilbenes / Stilbenoids | Resveratrol | Red grape skins and red wine); | ||
| Pinoxylvin | ||||
| Piceid. | ||||
| Tannins | Hydrolyzable: Gallotannins. Elagitannins. Punicalin. Punicalagin. | |||
| Condensed: Proanthocyanadins | Apple and grape seeds, cocoa | |||
Complex: Acutissimin. | ||||
SIMPLE PHENOLS | PHENOLIC ACIDS | Hydroxycinnamic acids (all fruits, highest in outer parts of ripe fruits) | ||
| Caffeic acid | Barley grain | |||
| Ferulic acid | Cereal brans: e.g. maize, wheat, rice, oat | |||
| Sinapic acid | ||||
| Coumaric acid | ||||
| Diarylheptanoids | Curcumin | Turmeric rhyzome (Curcuma longa) | ||
| Hydroxybenzoic acids | Gallic acid. | Red fruits, especially peel (especially mango), onions, tea | ||
| Ellagic acid | Fruits/berries such as raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, pomegranites | |||
| Vanillic acid | ||||
| Protocatechic acid | ||||
| Syringic acid | ||||
| Gentisic acid | ||||
| Gingerols | Gingerol | Ginger root (Zingiber officinale) | ||
| COUMARINS | Coumarin | |||
| Psoralene | ||||
| Scopaletin | ||||
| Esculetin | ||||
| OTHER |
Polyphenols - Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer effects
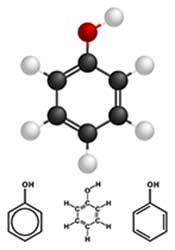
Polyphenols provide most of our dietary antioxidants
Polyphenols recognized for their value in restoring health
Polyphenols have the potential for having antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antineoplastic (anti-tumor), antiaging, cardioprotective / anti-hypertensive, and antimicrobial properties/effects. There are over 4,000 polyphenol compounds, some having a potent effect on disease and health issues with sufficient dosages.
Polyphenols contain multiple phenols. A phenol (C6O5OH) has 6 carbon atoms bonded into a hexagonal ring, 5 of which are bonded to hydrogen atoms and 1 is bonded to a hydroxyl group (OH);
The original hypothesis that polyphenols are direct antioxidants has been disproven. i.e. they don’t directly fight against inflammation and free radicals. Instead, they act by stimulating and upregulating the body’s natural antioxidant / anti-inflammatory defense systems, involving such as:
- Cell signaling and inflammation. Shimizu, 2017
- Oxidative stress Hussain et al, 2016
- INSULIN signaling and INSULIN resistance (www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2016/7432797/)
- Adipose tissue modeling DomÃnguez Avila et al, 2017
Polyphenols have preventive and restorative roles in neurodegenerative diseases
Polyphenols (aka phenolics) add astringency to the taste of food or drinks
In plants, polyphenols defend against attack by insects and provide color to plants
Examples: Resveratrol in red wine, and polyphenols in the culinary spices – capsaicin in chili and paprika, thymol in thyme, cinnamic acid in cinnamon, rosmarinic acid in rosemary, thyme, oregano, sage and peppermint.

Types of foods rich in polyphenols
Top foods having >1 mg polyphenols in a serving size
- Spices: Ginger, Cloves, star anise, capers, curry powder, ginger, cumin, cinnamon, nutmeg, chili peppers (red and orange habeneros, cayenne);
- Dried herbs: Peppermint, oregano, sage, rosemary, thyme, basil, lemon verbena, parsley, marjoram;
- Beverages: red wine, cocoa, green tea, black tea;
- Dark berries: Black chokeberry, black elderberry, low bush blueberry, plum, cherry, blackcurrant, blackberry, strawberry, raspberry, prune, black grapes.
- Other fruit: Apples, apple juice, pomegranate juice, peach, blood orange juice, lemon juice, apricot, quince.
- Seeds: Flaxseed, celery seeds, fennel, chili pepper seeds (red and orange habenero seeds, cayenne)
- Nuts: Chestnuts, hazelnuts, pecans, almonds, walnuts;
- Olives: black and green olives;
- Vegetables: globe artichokes, red chicory, green chicory, red onion, spinach, broccoli, curly endive;
- Oils: Extra-virgin olive oil, rapeseed (canola) oil;

Of special mention
Ginger (Zingiber officale)
- All of its bioactivities and properties attributed to its phenolic compounds. Mainly gingerols, shogaols and paradols
- Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-microbial, anti-cancer
- Inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes as well as other pro-inflammatory chemicals
Manuka Honey
- Polyphenols found in plant nectar. Bees convert nectar into honey.
- Polyphenol antioxidant content of honey counters oxidant activity. The polyphenols account for its anti-inflammatory activity and are able to prevent the feedback amplification of inflammation via hydrogen peroxide.
Boswellia Serrata (Frankincense)
Red wine
Some of the better-known polyphenols
Anthocyanin
High content in cherries
- Tart cherries (e.g. Montmorency) contain roughly twice as many phenolic compounds than sweet cherries (E.g. Bing), but sweet cherries contain roughly twice as many anthocyanins. Cherries are also rich in carotenoids, quercetin, melatonin, and vitamins E and C.
- High anthocyanin content in cherries thought to provide an anti-inflammatory effect. A Review of the Health Benefits of Cherries
- Consuming cherries, or juice or extract effective against GOUT (a form of arthritis marked by sudden attacks of joint pain /inflammation) – eating at least 10 cherries (type not specified)/day is associated with a 50% reduction of recurrent gout flares over a 48hr period – study by Boston univ Med. Center, published 2012 in J. Arthritis & Rheumatism.
- 2010 study at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School in New Brunswick, N.J., involving 24 gout patients, achieved similar results when taking 1 Tbsp. cherry extract (equiv. ~45-60 cherries) twice daily for 4 months. Study reference?
- Drinking an 8oz bottle of tart cherry juice ( juice of ~45 cherries) twice daily for 6 weeks relieved OSTEOARTHRITIS. So found a 2013 study by Philadelphia VA medical center. Participants showed significant decrease in the standard inflammation marker, C-reactive protein (CRP).
- Selective COX-2 inhibitor better than both COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors. NSAID (or coxib) drugs such as ibuprofen® and naproxen®, reduce pain and inflammation by suppressing the COX-2 enzyme. Unfortunately, they also suppress the COX-1 enzyme, which is a primary protector of the stomach lining, and extended use of these coxibs can cause GI discomfort and stomach ulcers leading to internal bleeding, with the risk of dying after only 2 months of NSAID use increasing to 1 in 1200. (To put this in perspective: this is 1000 times more perilous than taking a single flight) Number Needed To Kill Individual Drug Risk with NSAIDs
- Comparing data published from pre-1997 to that from 1997-2008, mortality in patients suffering from an upper gastrointestinal bleed or perforation has fallen from 1 in 9 to 1 in 13 overall, but has actually increased from about 1 in 7 to 1 in 5 in those exposed to NSAID or aspirin! S.Straube et al, Mortality with upper gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation: effects of time and NSAID use. 2009 Jun 5;BMC Gastroenterol. 9:41.
- Obscenely expensive Vioxx® was an attempt at suppressing COX-2, whilst preserving COX-1 – it failed. Causing tens of thousands of deaths due to heart attack or stroke. HOWEVER 🙂 it turns out that cherries are a natural selective COX-2 inhibitor.
Proanthocyanidins
High content in grape skins and juice, but highly concentrated in grape seed extract (up to 70-90% proanthocyandins). Also contain many other polyphenols. Main active ingredient is the polyphenol flavonoid oligomeric proanthocyanidin (OPC) – OPCs are major free-radical scavengers / antioxidants
Catechins (flavonols)
High content in:
- Green tea, green tea extract (Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)); Lipton Green teabag contains 71mg EGCG;
- Unprocessed cocoa component of dark chocolate (epicatechin)
Dark chocolate -“Anti-inflammatory / Antidepressant”
Both their caffeine and polyphenol content increase energy levels – promote activity of the neurotransmitter NOREPINEPHRINE to increase metabolic rate, which burns/oxidizes fat.
Curcuminoids
- High content in turmeric – Curcumin is the main curcuminoid found in the rhyzome of turmeric (Curcuma longa) – a popular Indian spice and a member of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae); curcuminoids are natural phenols responsible for turmeric’s yellow color; turmeric root extract is ~4% curcumin.
- Curcumin shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect – but its mechanism is as yet unknown; has shown beneficial in IBS, Crohn’s disease and osteoarthritis; 4-month, 160 patient, double-blind study demonstrating anti- inflammatory effect in osteoarthritis of the knee; In vitro study shows curcumin’s effect on certain inflammatory makers in IBD
- Supports cognitive function / memory – breaks down build-up of plaque (protein-clumps) on brain tissue which interrupts cell signaling. Also aids brain cell growth.
- Curcuminoids inhibit enzymes which participate in the synthesis of inflammatory prostaglandins and leukotrienes (locally operating communication messengers derived from polyunsaturated fats) – the anti-inflammatory effect of curcumnoids has been found comparable to steroidal drugs, and such nonsteroidal drugs as indomethacin and phenylbutazone, but without the negative side-effects;
- Heating curcumin destroys many of its beneficial properties
- Curcumin must be in bioavailable form. Typically used as 95% standardized extract, but when refined curcumin extract is combined with a water-soluble substance called PVP and fat-soluble forms of vitamins A and C, it is made 136 times more bioavailable than standardized form. Preferable to use 100% organic form. (Jager et al, 2014)
- Turmeric seen to kill H. Pylori. Suspected of being the microbe responsible for hijacking cells and turning them cancerous.
Cinnamic acid
- High content in cinnamon.
- Active ingredient methylhydroxychalcone polymer (MHCP) – identified as the substance lowering the probability of getting type 2 diabetes in those eating apple pies. (Dr. Richard Anderson)
- Having similar effects as INSULIN, MHCP stimulates glucose uptake and aids glycogen (storage form of glucose) synthesis – both helpful in blood sugar metabolism:
Ellagic Acid
High content in:
- Raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, grapes, pomegranates, walnuts, pecans;
Lignans
Lignan precursors high in a wide variety of plant-based foods – including seeds (superlatively high amounts are found in flaxseeds, but not their oil), whole grains, legumes, fruit, and vegetables.
- Lignans enterodiol and enterolactone have weak estrogenic activity – may have a role in hormone-related cancers (breast, uterine, ovarian, and prostate), heart disease and osteoporosis (estrogen improves bone density); Oregon state article
Resveratrol

High amounts in: grapes (in skins and seeds – especially high in red wine, which is fermented with skins), peanuts, pistachios, strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, dark chocolate.
| Beverage | Resveratrol (μg/100 mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| mean | range | |
| Muscadine grape (red wine) | 270 | 1410 — 4410 |
| Red wine | 270 | 0 — 2780 |
| Rosé wine | 120 | 5 — 290 |
| White wine | 40 | 0 — 170 |
| Sparkling wine | 9 | 8 — 10 |
| Green grape juice | 5.08 | 0 — 10 |
A stilbene:
- Supports cardiovascular and cognitive health – also associated with increased blood flow to the brain;
- Pairs with body’s major in-house-produced antioxidant glutathione – to prevent oxidative damage to cell
Quercetin
High amounts of this flavonol in: fruits, vegetables (especially red onions), leaves and grains.
Methoxylated flavones
- Potent antioxidants in the brain. Especially helpful in reducing neuroinflammation involved in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease)
- Modulate neurotransmitters, including Dopamine and Serotonin, to enhance mood issues (e.g. depresseion, anxiety, stress)
Available in capsules, tablets and liquid extracts. Dosage depends on type of flavone being used. Clinical studies used xanthohumol as a nootropic at100-200 mg /day with promising results

References
Dr. Richard A. Anderson, at the HumanNutritionResearchCenter (USDA)
DomÃnguez Avila JA, Rodrigo GarcÃa J, González Aguilar GA, de la Rosa LA (2017 May 30) The Antidiabetic Mechanisms of Polyphenols Related to Increased Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP1) and Insulin Signaling. Molecules; 22(6) Link
Hussain, Tarique et al (2016) Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us? Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. Volume 2016, Article ID 7432797, 9 pages Link
Jager R. et al (2014) Comparative absorption of curcumin formulations, Nutr.J; 13:11 PubMed
Oregon State Article https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/phytochemicals/lignans#food-sources
Shimizu, Makoto (Jan 2017), Multifunctions of dietary polyphenols in the regulation of intestinal inflammation. J. of Food and Drug Analysis Volume 25, Issue 1:93-99. LInk
Taussig SJ, Batkin S. (1988) Bromelain, the enzymecomplex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update. J Ethnopharmacol. 22:191-203.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228035536_Phenols_Polyphenols_and_Tannins_An_Overview